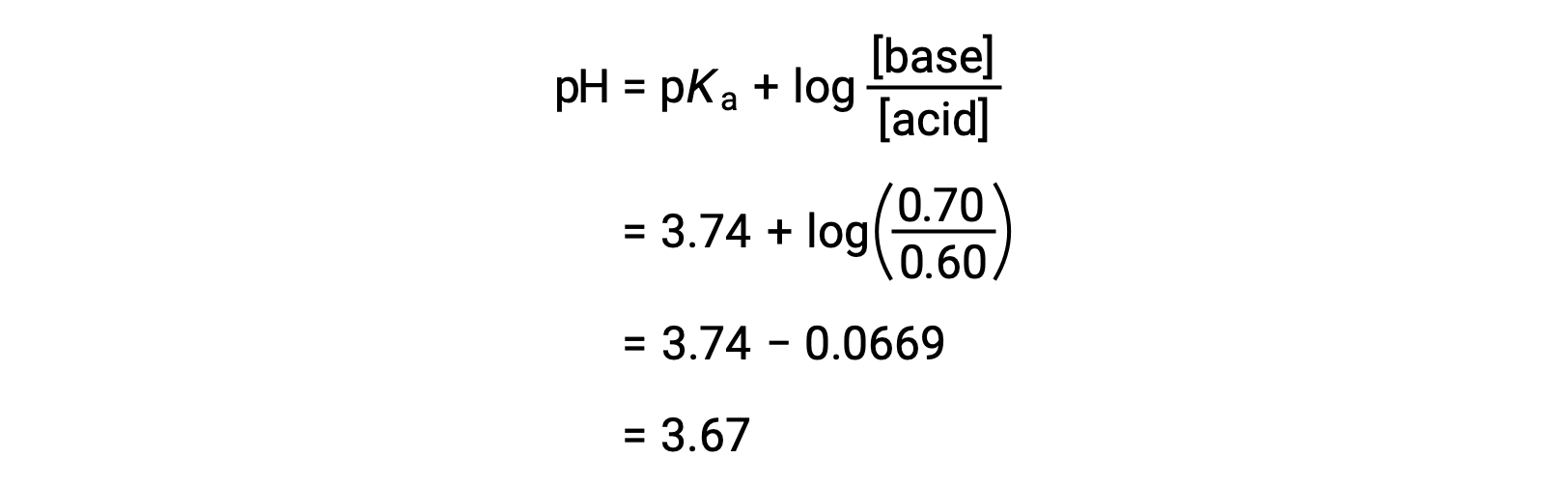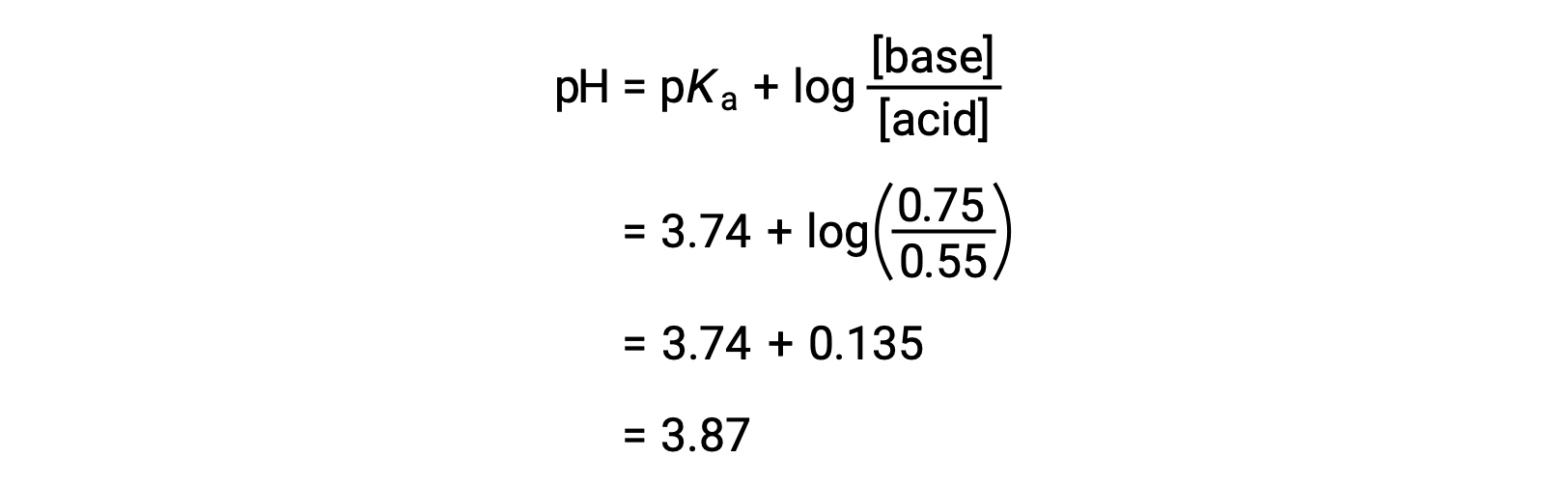A slight pH change occurs in a buffer solution upon the addition of a small amount of strong acid or the addition of a small amount of strong base.
This pH change is calculated in two distinct steps.
First, a stoichiometric calculation is used to determine the change in the concentrations.
Then, an equilibrium calculation is used to determine the new pH of the solution, either using an ICE table or the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
The pH of a buffer containing 2.0 M of both hydrofluoric acid and sodium fluoride can be calculated before and after adding a strong acid or base.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the initial pH of this buffer because the concentrations are high relative to the Ka of the weak acid, and the change in the concentrations is less than 5%.
The pKa for hydrofluoric acid can be calculated to be 3.46. When the concentration of weak acid and conjugate base in a solution are equal, the pH is equal to the pKa. Therefore, the initial pH is 3.46.
If 0.2 moles of hydrochloric acid is added to one liter of this buffer, with the assumption that it causes a negligible change in volume, the added acid is neutralized by the fluoride ions, producing hydrofluoric acid. This leads to a stoichiometric decrease in the concentration of fluoride ions by 0.2 moles and an equal increase in hydrofluoric acid concentration.
The new concentrations can be inserted into the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. When solved, the new pH is 3.37, less than the initial pH value of 3.46.
As strong acid was added, there is a decrease in the pH, but the reduction is small because the solution is buffered.
In contrast, if 0.1 moles of sodium hydroxide is added to one liter of the buffer, with the assumption that it causes a negligible change in volume, the added base is neutralized by reacting with hydrofluoric acid. This causes a stoichiometric decrease in hydrofluoric acid concentration by 0.1 moles and an equal increase in fluoride ion.
Using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, the pH of the solution is 3.50, which is slightly higher than the initial pH value of 3.46 due to the addition of sodium hydroxide.