Method Article
多発性硬化症での遠隔監視付き頭蓋直流刺激(TDCは)を使用するためのプロトコル(MS)
要約
The goal of this pilot study is to describe a protocol for the remotely-supervised delivery of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) so that the procedure maintains standards of in-clinic practice, including safety, reproducibility, and tolerability. The feasibility of this protocol was tested in participants with multiple sclerosis (MS).
要約
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a noninvasive brain stimulation technique that uses low amplitude direct currents to alter cortical excitability. With well-established safety and tolerability, tDCS has been found to have the potential to ameliorate symptoms such as depression and pain in a range of conditions as well as to enhance outcomes of cognitive and physical training. However, effects are cumulative, requiring treatments that can span weeks or months and frequent, repeated visits to the clinic. The cost in terms of time and travel is often prohibitive for many participants, and ultimately limits real-world access.
Following guidelines for remote tDCS application, we propose a protocol that would allow remote (in-home) participation that uses specially-designed devices for supervised use with materials modified for patient use, and real-time monitoring through a telemedicine video conferencing platform. We have developed structured training procedures and clear, detailed instructional materials to allow for self- or proxy-administration while supervised remotely in real-time. The protocol is designed to have a series of checkpoints, addressing attendance and tolerability of the session, to be met in order to continue to the next step. The feasibility of this protocol was then piloted for clinical use in an open label study of remotely-supervised tDCS in multiple sclerosis (MS). This protocol can be widely used for clinical study of tDCS.
概要
tDCS is a relatively recent therapy that operates through the use of low amplitude (2.0 mA or less) direct current to modulate cortical excitability 1. Hundreds of clinical trials have demonstrated tDCS to be safe and well-tolerated2-4. tDCS is easier to use, lower in cost, and better tolerated when compared to other methods such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (e.g., tDCS has not been associated with the development of seizures 5,6). Multiple tDCS sessions are required for benefit, especially when administered with the goal of enhancing rehabilitation outcomes.7-10
It is not yet known how many tDCS sessions are necessary or optimal, but the effects are cumulative with little evidence that tDCS over a single session produces behaviorally meaningful changes.2,11 For example, studies of depression have found 30 or more sessions needed for full benefit in some participants. 12,13 Multiple sessions are especially important when pairing tDCS with a behavioral therapy, which only occurs with rigorous repetition across many sessions. 14
For many patients and caregivers, traveling to the outpatient facility to receive repeated tDCS treatment sessions is a major obstacle in terms of time, cost and travel arrangements. This real-world limitation has resulted in studies with small sample sizes and without adequate power or design to draw conclusions that can lead to clinical use.15 Remote tDCS delivery would allow for participation in study protocols from home or other locations, and reach those patients who otherwise would not have access to these trials. Further, it allows the possibility for testing "on-demand" application for indications such as epilepsy and migraines.
We have worked with a diverse group of clinical investigators interested in remotely-supervised tDCS to develop guidelines and standards for remotely-supervised tDCS delivery including specialized equipment and specific training requirements both for staff and study participants16. Here, we developed a protocol to follow these guidelines and test for feasibility in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), a disorder where tDCS may be a useful tool for the management of its symptoms. 11,17-23
プロトコル
倫理声明:ストーニーブルック大学施設内倫理委員会(IRB)は2015年2月10日にこのプロトコルを承認しました。
リモート教師付きTDCのための参加者の募集1。
- デバイスと10日の試験プロトコルに関する情報を募集し、研究参加者を提供します。
2.包含/除外基準
- 健康
- 臨床医は、ベースライン訪問時にすべて登録し、参加者のための医療クリアランスを提供していることを確認してください。
- TDCの忍容性およびラップトップの適性
- 参加者は、基本的なラップトップコンピュータの機能とどのようにのWi-Fiインターネットにコンピュータを接続するために精通していることを確認してください。ノートパソコンを使用すると、TDCのデバイスのセットアップの両方のために、参加者(またはプロキシ)が、手続きを完了するための器用さを持っていることを確認してください。
- セットアップを超えて、ベースラインの訪問で、参加者に1.5の1分のトライアル線量を与えます忍容性を決定するためのTDCのミリアンペア。参加者がこのセッションに耐えることができない場合は、1.0ミリアンペアの低用量を適用することができます。どちらが許容されている場合は、参加者を除外します。
- 環境
- 参加者は装置およびキットを格納するための安全なエリアと気晴らしのない、明るいだけでなく、クリーンな環境へのアクセス権を持っていることを確認します。
- コンプライアンス
- 参加者はタイムリーにスケジュールされたビデオ会議セッションに従わない場合は、その参加者を除外します。
- 条件を停止
- 各参加者との対話では、参加者がセッションを許容していることを確認し、試験スケジュールを遵守し、安全に悪影響せずにデバイスを動作させるために所定の「停止基準」のシリーズを確認します。これらのいずれかが研究(図1)からの参加者を除外し、満たされるべきです。
3.材料
注意:リモート・監修使用16公開されたガイドラインで推奨されているように、正確な電極の準備と配置を制御し、継続的な監視を用量に関してクリニックプロトコルをミラー化する必要があります。
- デバイスキット
- すべてのリモートTDCの参加者のために同じ材料を準備します。これは、セキュアなビデオ会議ソフトウェア、デバイス、およびデバイスキットで試験提供ラップトップコンピュータを含みます。
- 使いやすさのためのデバイスキットを設計した(図2)日によってそれを整理します。
- 各スポンジのポケットのための生理食塩水の6 mLを予め充填された上部に穿孔とサイズ5x5cmの20包んだスポンジポケット付きキットを準備する(10日間の試験のために必要な1日あたり2)、20シリンジは、洗浄瓶を満たしました余分な生理食塩水、デバイス用の予備の電池、およびヘッドセットアプリケーション用ハンドヘルドミラー付き。
- また、研究のユーザーがそれぞれのために自分のワークスペースで、携帯用の自宅の電話や携帯電話を持っている必要がありセッション。
- デバイス
- 1回だけ使用のロック解除コードを介してセッションを解放TDCのデバイスを選択します。研究装置は、参加者が唯一の研究技術者のコードを提供された後にセッションを管理することができる機能があることを確認してください。また、研究機器の選択において、接触品質が継続的に安全かつ適正な使用を確保するために監視されていることを確認してください。
- ビデオ監視
- デバイス、最適な接触品質の適切なセットアップの遠隔監視を可能にするために、セキュアなビデオ会議ソフトウェアを選択し、目的のユーザーがセッションを適用していること。
- トレーニングの別の方法として、ビデオ会議ソフトウェアを使用してください。 、上のデバイスの電源を入れ、その接触の質を読み、接触不良の品質のトラブルシューティングを行う、一回使用のロック解除コードを入力して、安全にシャットダウンした後、デバイスを削除する方法をユーザーに指示します。
- ヘッドギア
- シム用ヘッドギアをデザインPLEと堅牢な電極の位置。ユーザー・エラーの余地を排除するために、とモンタージュの配置を節約するのに役立ち、単一の位置ヘッドギアを使用してください。左側に配置された陽極電極とシングルポジションヘッドギアへの配置の信頼性を向上することが明らかにラベルされたスポンジマーカーと、キャップなどのデザインを設定します。
4.トレーニング
注:リモート研究の最初のベースラインのセッション中に、参加者の研修の大半を完了します。ベースライン訪問の約1〜2時間はトレーニングに費やされるべきです。参加者は彼らの最初の命令として教育TDCの映像を表示することができます。
- 教育ビデオ
- ベースライン訪問以下の参加者のためにプレーするための教育ビデオを設定します。視聴中に、参加者は装置およびキットへのアクセス権を持つようにし、各ステップで一緒に従うことができます。
- 最初participを紹介するビデオを準備します材料にアリと、実際の勉強会の流れを模倣ステップバイステップガイドに移行します。
- ゆっくり、はっきりとTDCのヘッドセットのセットアップを提示(および再生のためにそれを利用できるようにする)は、ユーザが明確にする必要がありますする必要があります。研究参加者は、デバイスの画面を期待すると、特定の測定値を提供する際にどのようにデバイスの画面が表示されますどのような感を得ることができるように、また参加者のビューを提供します。
- ビデオセクション
注意:適切な接触品質が達成されていない限り、リモート技術者は、デバイスのためのロック解除コードを提供することはありません。- 詳細に圧力を加えると、スポンジポケットを潤しなど、接触不良の品質のトラブルシューティングを行うための手段を教育ビデオを設計します。ビデオはまた、研究材料の安全な使用と同様に、セッションを終了するために従うべきプロトコルについての情報を提供していることを確認してください。
- セッションを終了し、パーを要求する手続きに参加者を指示イン・クリニック安全性のレベルは、緊急の場合に維持されることを確実に、セッションの期間を通じて電話回線を維持するticipants、
- ビデオに続いて、参加者が研究技術者の助けを借りて、独自のセットを構成しようとすることができます。
- 取扱説明書
- マニュアルの形で、ビデオで提示された情報だけでなく、写真や資料の図は、デバイスのスクリーンショット、およびラップトップの情報のトランスクリプトを準備します。
- 対面トレーニング
- 彼らはセットアップを開始すると、参加者を監視します。
- (スポンジポケットを湿らせたスポンジに電極を挿入し、ヘッドセットの上にスポンジを固定、頭の上に置いて、ヘッドセット、センターヘッドセットを、研究技術者に確認して、上のデバイスをオン)各工程を経て参加者をコーチ。
- 必要に応じて手順や機器を明確にします。
- 参加者その経験セットのトラブルシューティング難易度アップ
- 参加者は、セットアップに苦労する場合は、この方法のデモンストレーションを繰り返します。
- 参加者が設定した後、繰り返し試行を完了できない場合は、セッションを終了します。これは、研究、「停止」の基準として定義されます。
5.参加者勉強会の準備
- きれいな、よく明るい場所で彼らの研究のノートパソコン、携帯電話、デバイスキット、デバイスとヘッドセットを設定するには、参加者に指示します。バックの髪を引っ張ると気晴らしを最小限に抑えるために、参加者に通知します。
- 参加者は、プロトコルのステップバイステップガイドのための教育ビデオやマニュアルを参照してくださいすることができます。
- まず、コンプライアンス16継続的な監視が存在するようにセットアップを開始する前に、研究参加者とのWeb会議を開始します。
勉強会中に6デバイスのセットアップ
- ビデオ会議が開始された後、集合Uを開始するために、参加者に指示しますP。
- スポンジポケットを開き、6 mLのシリンジ(スポンジポケットあたり1シリンジ)を使用して湿らせます。約3mLのスポンジポケットの各側面を湿らせるために使用することができます。
- TDCの刺激からの電流を運ぶために、炭素 - ゴム電極を適用します。スポンジポケットに電極を包みます。完全にスポンジポケットに各炭素ゴム電極を挿入します。注意:ゴム電極との直接皮膚接触が苦痛であるため、電極は、スポンジポケットに包まれています。
- 赤のケーブルは、デバイス上で「陽極」ラベルの赤いレシーバプラグに接続されていることを確認。黒のケーブルは、デバイスの「カソード」ラベル黒レシーバプラグに接続されていることを確認。これらのケーブルは、デバイスから削除されることはありません。
- 左側に配置された陽極電極(赤い線に接続された1つ)で、一般的な二国間の背外側前頭前皮質(DLPC)を使用してヘッドセットにスポンジポケットと電極を接続します。注:適切な確保するために赤と黒でヘッドセットにラベルを付けます電極配置。
- ヘッドセットの溝に収まるスポンジポケットのボタンを使ってヘッドセットを固定します。スポンジポケットの滑らかな面が常に額に向かって直面しています。
注意:これは、信頼性の高い電極配置と広い治療用途を簡単に行うことができます。 - スポンジポケットが締結された後、頭にヘッドセットを配置します。タック頭の後ろの溝の下にバックストラップとナジオンと中央のボタンを合わせます。これは、ビデオ会議ソフトウェアを介してデバイスキットおよび試験技術者によって供給されたハンドヘルドミラーを用いて確認することができます。
- この時点では、デバイスのディスプレイ上の接触品質を読み上げるために、参加者に指示します。注:中程度または最適な読み取りがセッションコードの管理のために必要とされます。
- 接触の質を改善する必要がある場合は、予め設定されたトラブルシューティング手順に従うように、参加者に指示します。まず、スポンジポケットに圧力を加えることをお勧めします。このDの場合OESは、成功した証明する参加者(ペーパータオルは、任意の流出のために提供されている)洗浄ボトルを使用したスポンジポケットに生理食塩水を少量を適用するためのオプションを与えていません。
- 適切な接触品質が達成されると、セッションのために一回使用のロック解除コードを管理します。注:これらのコードは、時間と振幅の設定量のための研究スタッフによって事前にプログラムされています。
7.セッションの終了
注意:参加者がロック解除コードを入力した後、デバイスの画面は、セッションが終了するまで数分をカウントダウンタイマーが表示されます。デバイスは、セッションを通じて、電極の接触の質を示します。 1分タイマーに残っている場合、秒単位でカウントダウンが発生します。
- 接触品質は「中程度」を下回った場合は6.9のトラブルシューティングの手順を使用してそれを改善する方法について説明します。
- までヘッドセットを削除しないようにするために参加者を思い出させます秒は完全にゼロまでカウントダウンしているデバイスは(ビープ音で確認)シャットオフします。
- デバイスがビープ音ときにヘッドセットを削除するには、参加者に指示します。
- デバイスからスポンジポケットを削除し、それらを破棄するように参加者に指示します。注射器は、同様に1回の使用であり、また、廃棄されるべきです。
- 参加者は、キット内のデバイスとヘッドセットを格納していることを確認してください。
- 安全にラップトップ、デバイス、および次のセッションのためにすべての材料を格納するための参加者を思い出させます。
研究分析8.終了
- 参加者のトラッカーを使用して、各研究参加者を評価します。これは、研究のコンプライアンス、有害事象、及びセッション終了を記録する方法として役立ちます。研究の最後に、研究の成功を決定するために、各参加者のデータを確認します。このプロトコルの目的のために、研究の成功は、試験セッション24の80%を完了した参加者の80%によって定義されます。
- SESの検証毎日のセッションの出席の記録、毎日の痛みのスケールの見直しによる有害事象のための刺激アンケート前後のシオンの成功は、サンプル調査票のために補足コードファイルを参照してください。
注意:刺激の20分が完全に配信されたことを検証では、研究の終了時に確認することができます。研究技術者が確認として完了コードのためのデバイスにアクセスすることができます。
結果
我々は、MSで使用するためにこのプロトコルを適応しています。我々は二週間にわたって送達10 TDCの刺激セッションの配信をターゲットに。10の9,10最初の2つのセッションがで人研修であり、以下の8つがリモートで監視された(図3)。第二 セッションは、環境適合性で構成されてい研究の技術者は、適切なセットアップを確認するために、参加者の自宅を訪問した評価。
次のリモート・監修のセッションを完了するために、参加者がリモートで使用するために特別に設計されたTDCデバイスと正確な電極配置を導くために使いやすさのために変更されたヘッドセットを提供しました。デバイスキットが提供され、個別に昼と臓器によって標識のすべての項目で、それぞれのスポンジに必要な生理食塩水の測定量充填電極および注射器のためのデバイスとヘッドセット、一回使用のスポンジポケットが含まれていました使いやすさのために化さ。電極が左側に配置された陽極電極との二国間背外側前頭前皮質(DLPC)の位置に配置した。10これは信頼性の高い電極配置の容易性、幅広い治療用途を提供しています。9,10私たちは20分間1.5ミリアンペアを対象と以前の研究に基づいて、セッション。これは全体的な主題の忍容性を向上させた場合のプロトコル9,10は、ベースラインで1.0ミリアンペアの電流の低減を可能にしました。
参加者は、研究技術者との安全なビデオ会議接続のための簡単にアクセスできる教育ビデオやリンクを含め、研究のために構成された研究が提供するラップトップコンピュータを与えられました。ラップトップは、すべてのコンピュータの活動をリモート監視するためのプログラム、および遠隔技術サポートのためのコンピュータにアクセスするためのプログラムが含まれています。操作の詳細なマニュアルは、参加者と研究技術者、および自己-R用のバインダーの両方で使用されました EPORT策が提供されていました。
合計N = 20のMSの参加者が試験を完了しました。選択基準は、デバイスを動作させるための最小限の運動要件を確実にするために、25 * 6.0以下6.5またはプロキシと上記拡大障害状態尺度(EDSS)を指定しました。登録はMS内の障害(運動障害、認知障害、またはその両方)の範囲の代表となっています。すべての参加者20、n = 4のプロキシで、首尾に訓練されたTDCのセッションを自己適用し、192総セッションが完了しました。 図4に示すように、the192セッションの40は、トレーニングを含め、残りの152は、排他的に遠隔監督のセッションでした。遠隔監督セッションのうち、100%が正常に電極の配置、デバイスの動作や刺激の良好な忍容性の配信を正常に実行されました。
ロード/ 53542 / 53542fig1.jpg "/>
図1.停止基準フローチャート 。チャートはもはや進行しないか、またはリモート・監督TDCの研究に参加できる参加者を示すさまざまな基準を詳しく説明しています。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
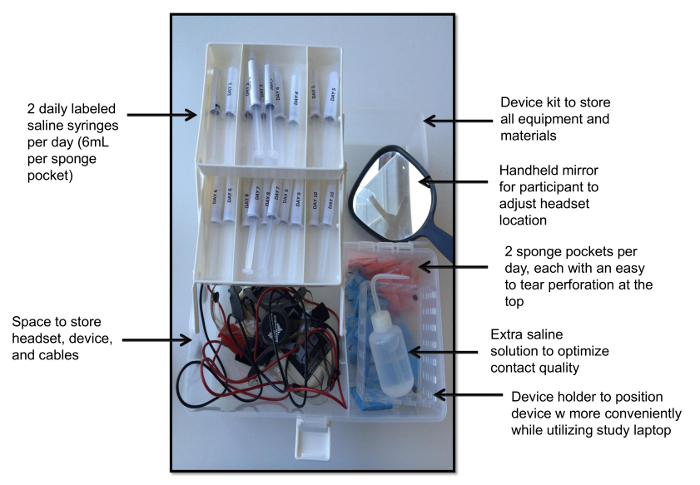
図2.デバイスキット。このビューには、デバイスの個別包装スポンジポケット付きキット、一日あたりのスポンジあたり1生理食塩水で満たされた注射器、携帯型ミラーデバイスホルダ、予備の生理食塩水、およびヘッドギアを持つデバイスを示しています。 ご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてくださいこの図の拡大版。

図3.参加者の研究のタイムライン 。このタイムラインは、研究の各10日の参加者の登録を循環研究キットおよびデバイスへの道を示している。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
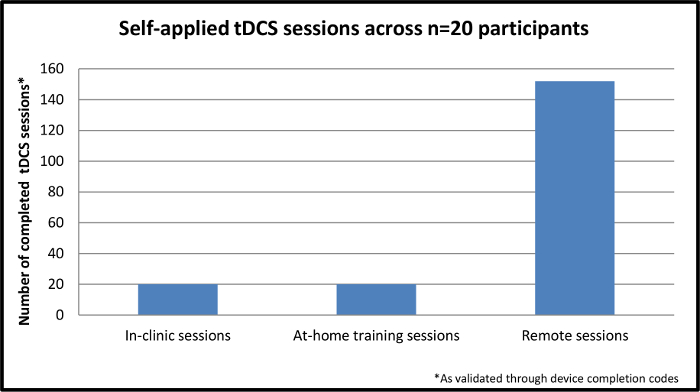
N = 20の参加者全体の図4.自己適用されたTDCのセッション。この図は、全体の完成、自己適用のセッションを示しているのn = 20の参加者が研究に登録。残りの9セッションは参加者の家庭における遠隔監視を経て完成されている間、最初のセッションは、インクリニック完了します。 より大きなVを表示するには、こちらをクリックしてくださいこの図のERSION。
ディスカッション
プロトコル内の重要なステップ
リモート・教師のTDCは離れて臨床医の直接の監督から投与され、および除外基準は、参加者が何の禁忌健康状態や環境の気晴らしを持っていないことを保証するために設計されており、適応を有するものを含むラップトップコンピュータを(使用して完全に可能となっています研究チームとの通信のための技術)。また、参加者は、研究の期間に予定セッション時間にTDCのセッションを許容し、コミットすることができなければなりません。
リモートたTDCは治療の研究と管理の利便性を提供していますが、自己主導の参加者使用は、安全性の問題と配信される刺激を監視し、標準化することができないことの両方にお勧めできません。代わりに、私たちのプロトコルはCL拡張するリモート・教師TDCの16のための基準やガイドラインに従っ遠隔地での配信を通じてINIC規格。ガイドラインは、ユーザーがリモートのTDCに参加するための適切な能力を持っていることを、研究スタッフが適切参加者の相互作用のために訓練されていることを確認し、研究の各段階での参加で作られた継続的なトレーニング資料と同様に評価があること。刺激は、セッションまたは個人全体の中断または変化なしに、すべてのセッションで配信1.5ミリアンペアの正確に20分で均一で再現性がありました。
プロトコルおよびトラブルシューティングのヒントへの変更
プロトコルは、いくつかの小さな修正を含みます。まず、私たちはそれぞれの用量を投与するアクセスプロキシがある場合の6.5以上のEDSSスコアを有するMSの参加者にこのプロトコルの使用を拡大しました。また、我々はリモートのWeb confeを開始するために、参加者の研究に提供ノートPCにアクセスすることにより手順を実装しています忍容性の余分なサポートやレビューの措置を必要とする人のためにrenceと共有ドキュメントを通じて経験を研究しています。現在のプロトコルへの将来の変更は技術に最も有能な証明参加者は唯一のデバイスで設定を確認するために早期の監督を必要とし、ロック解除コードを受信するように、遠隔監視の様々な度合いを可能に含まれています。
技術の限界
我々の予備的な結果は、このプロトコルの実現可能性をサポートしながら、サンプルサイズが制限されます。登録が膨張すると、訓練のギャップのために、セッションを合理化教育ビデオを高め、運動障害を持つものに技術よりアクセシブルにするための方法を説明する分析( すなわち 、さらに、コンピュータの使用状況、スポンジポケット/ヘッドセットの変更のための適応マウスアプリケーションを容易に)。 EDSSの一部の参加者は、まだいくつかのDIFが発生する可能性があり、(プロキシを必要としない)6.5未満の範囲ヘッドセットの準備とトラブルシューティングコンピュータ関連の問題でficulty。この研究は、すべてのセッションを通して参加者の完全なリモート監視をお勧めしながら、さらに、今後の研究が十分にセッション全体のための監督なしでデバイスを動作させるために訓練を受けた一部の参加をとみなすことができます。
既存の方法に関する方法の意義
これらの初期の結果は、安全に使用されなければならないガイドラインや基準のセットに続いて、臨床試験のための遠隔教師TDCの配信のための我々のプロトコルの実現可能性を実証し、効果的に遠隔監視の下でのTDCを管理します。プロトコルは、各ステップで進行するためにクリアする必要があり、「停止」基準(上記のセクション2.5.1)とチェックポイントの決定木のシリーズを持つように設計されていた( 図1を参照)。これらのチェックポイントは、痛みや悪影響の忍容性(経験に対処治療への)およびコンプライアンス(タイムリーなセッションへの参加と適切な技術)。 10を介して各セッション1では、参加者は、(以前の試験で最も一般的なのTDCの副作用のリストから派生アイテムで)そのセッションの前と後の簡単な有害事象報告を完了しました。また、参加者は(セッションの前と後)忍容性に対処するための自己報告対策を完了し、同様の症状の在庫を完了することができます。また、TDCの治療に広範なアクセスを提供しながら、十分な電力をMSでの治療を検討するための技術を確立し、その中で本研究は重要です。
技術の将来のアプリケーション
遠隔監督TDCの方法は完全にMS集団において操縦された後、より大きな、ランダム化試験は、症状管理を標的化するために開始することができます。毎日参加intera周りの教育研修教材や構造を使用することによりctions、遠隔監督TDCのは、患者集団の広い範囲によってアクセスされ、技術の臨床研究を展開することができます。
開示事項
CUNY has patents with Marom Bikson as inventor. Marom Bikson has equity in Soterix Medical Inc. CUNY has patents with Abhishek Datta as inventor. Abhishek Datta has equity in Soterix Medical Inc.
謝辞
Supported by The Lourie Foundation, Inc.
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Mini-CT transcranial direct current stimulation device | Soterix | Device to deliver direct current stimultion in a remote manner | |
| Study Kit | Provided to participant with all required setup items - device, headset, sponge pockets, pre-filled syringes, Kleenex, handheld mirro, spare batteries | ||
| Laptop | Provided to allow secure video conferecing during device setup and headset placement | ||
| Instruction Manual | Transcription of instructional video and detailed instructions for protocol |
参考文献
- Filmer, H. L., Dux, P. E., Mattingley, J. B. Applications of transcranial direct current stimulation for understanding brain function. Trends in neurosciences. 37, 742-753 (2014).
- Brunoni, A. R., et al. Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): challenges and future directions. Brain stimulation. 5, 175-195 (2012).
- Nitsche, M. A., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation: State of the art 2008. Brain stimulation. 1, 206-223 (2008).
- Iyer, M. B., et al. Safety and cognitive effect of frontal DC brain polarization in healthy individuals. Neurology. 64, 872-875 (2005).
- Vanneste, S., et al. Bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulation for tinnitus by transcranial direct current stimulation: a preliminary clinical study. Experimental brain research. 202, 779-785 (2010).
- Priori, A., Hallett, M., Rothwell, J. C. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial direct current stimulation?. Brain stimulation. 2, 241-245 (2009).
- Demirtas-Tatlidede, A., Vahabzadeh-Hagh, A. M., Pascual-Leone, A. Can noninvasive brain stimulation enhance cognition in neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuropharmacology. 64, 566-578 (2013).
- Martin, D. M., et al. Can transcranial direct current stimulation enhance outcomes from cognitive training? A randomized controlled trial in healthy participants. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology / official scientific journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum. 16, 1927-1936 (2013).
- Elmasry, J., Loo, C., Martin, D. A systematic review of transcranial electrical stimulation combined with cognitive training. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 18 (6), 065018 (2015).
- Brunoni, A. R., Vanderhasselt, M. A. Working memory improvement with non-invasive brain stimulation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain and cognition. 86, 1-9 (2014).
- Meesen, R. L., Thijs, H., Leenus, D. J., Cuypers, K. A single session of 1 mA anodal tDCS-supported motor training does not improve motor performance in patients with multiple sclerosis. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 32, 293-300 (2014).
- Shiozawa, P., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for major depression: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology / official scientific journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum. 17, 1443-1452 (2014).
- Loo, C. K., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for depression: 3-week, randomised, sham-controlled trial. The British journal of psychiatry : the journal of mental science. 200, 52-59 (2012).
- Lampit, A., Hallock, H., Valenzuela, M. Computerized cognitive training in cognitively healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of effect modifiers. PLoS medicine. 11, e1001756 (2014).
- Magalhaes, R., et al. Are cognitive interventions for multiple sclerosis effective and feasible. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 32, 623-638 (2014).
- Charvet, L. E., et al. Remotely-supervised transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for clinical trials: guidelines for technology and protocols. Frontiers in systems neuroscience. 9, 26 (2015).
- Palm, U., Ayache, S. S., Padberg, F., Lefaucheur, J. P. Non-invasive Brain Stimulation Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis: A Review of tDCS, rTMS and ECT Results. Brain stimulation. 7, 849-854 (2014).
- Mori, F., et al. Effects of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on chronic neuropathic pain in patients with multiple sclerosis. The journal of pain : official journal of the American Pain Society. 11, 436-442 (2010).
- Mori, F., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation ameliorates tactile sensory deficit in multiple sclerosis. Brain stimulation. 6, 654-659 (2013).
- Tecchio, F., et al. Multiple sclerosis fatigue relief by bilateral somatosensory cortex neuromodulation. Journal of neurology. 261, 1552-1558 (2014).
- Saiote, C., et al. Impact of transcranial direct current stimulation on fatigue in multiple sclerosis. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 32, 423-436 (2014).
- Ferrucci, R., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for fatigue in multiple sclerosis. NeuroRehabilitation. 34, 121-127 (2014).
- Cuypers, K., et al. Anodal tDCS increases corticospinal output and projection strength in multiple sclerosis. Neuroscience letters. 554, 151-155 (2013).
- Zanao, T. A., et al. Impact of two or less missing treatment sessions on tDCS clinical efficacy: results from a factorial, randomized, controlled trial in major depression. Neuromodulation : journal of the International Neuromodulation Society. 17, 737-742 (2014).
- Kurtzke, J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 33, 1444-1452 (1983).
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved