16.8 : Indicators
Certain organic substances change color in dilute solution when the hydronium ion concentration reaches a particular value. For example, phenolphthalein is a colorless substance in any aqueous solution with a hydronium ion concentration greater than 5.0 × 10−9 M (pH < 8.3). In more basic solutions where the hydronium ion concentration is less than 5.0 × 10−9 M (pH > 8.3), it is red or pink. Substances such as phenolphthalein, which can be used to determine the pH of a solution, are called acid-base indicators. Acid-base indicators are either weak organic acids or weak organic bases.
The equilibrium in a solution of the acid-base indicator methyl orange, a weak acid, can be represented by an equation in which we use HIn as a simple representation for the complex methyl orange molecule:
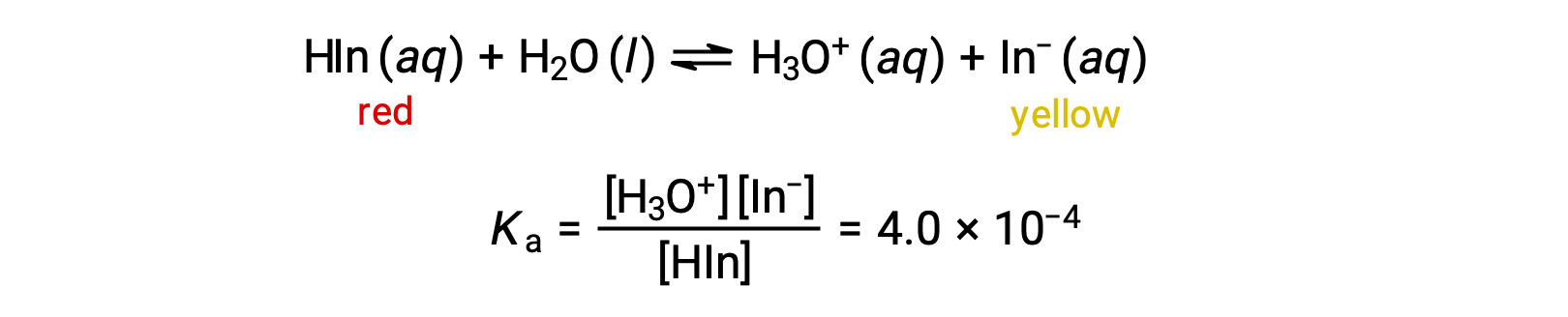
The anion of methyl orange, In−, is yellow, and the nonionized form, HIn, is red. When we add acid to a solution of methyl orange, the increased hydronium ion concentration shifts the equilibrium toward the nonionized red form, in accordance with Le Châtelier’s principle. If we add base, we shift the equilibrium towards the yellow form. This behavior is completely analogous to the action of buffers.
The perceived color of an indicator solution is determined by the ratio of the concentrations of the two species In− and HIn. If most of the indicator (typically about 60−90% or more) is present as In−, the perceived color of the solution is yellow. If most is present as HIn, then the solution color appears red. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is useful for understanding the relationship between the pH of an indicator solution and its composition (thus, perceived color):
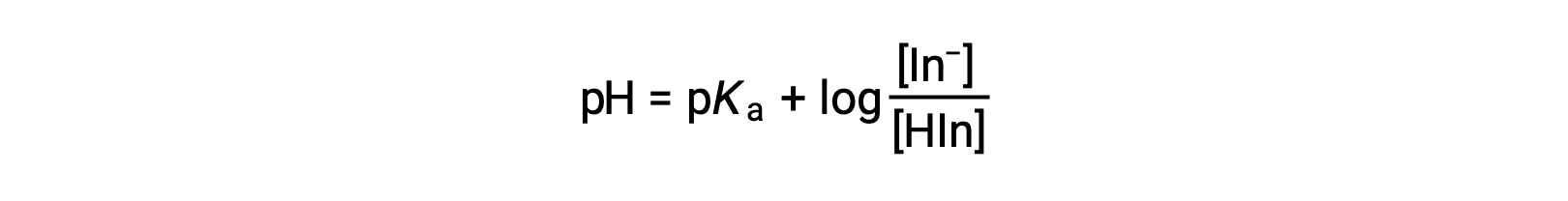
In solutions where pH > pKa, the logarithmic term must be positive, indicating an excess of the conjugate base form of the indicator (yellow solution). When pH > pKa, the log term must be negative, indicating an excess of the conjugate acid (red solution). When the solution pH is close to the indicator pKa, appreciable amounts of both conjugate partners are present, and the solution color is that of an additive combination of each (yellow and red, yielding orange). The color change interval (or pH interval) for an acid-base indicator is defined as the range of pH values over which a change in color is observed, and for most indicators this range is approximately pKa ± 1.
There are many different acid-base indicators that cover a wide range of pH values and can be used to determine the approximate pH of an unknown solution by process of elimination. Universal indicators and pH paper contain a mixture of indicators and exhibit different colors at different pHs.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.7: Acid-Base Titrations.
Z rozdziału 16:

Now Playing
16.8 : Indicators
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
47.8K Wyświetleń

16.1 : Wspólny efekt jonowy
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
40.9K Wyświetleń

16.2 : Buffers
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
163.4K Wyświetleń

16.3 : Równanie Hendersona-Hasselbalcha
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
68.1K Wyświetleń

16.4 : Obliczanie zmian pH w roztworze buforowym
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
52.6K Wyświetleń

16.5 : Skuteczność bufora
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
48.4K Wyświetleń

16.6 : Obliczenia miareczkowania: mocny kwas - mocna zasada
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
29.0K Wyświetleń

16.7 : Obliczenia miareczkowania: słaby kwas - mocna zasada
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
43.8K Wyświetleń

16.9 : Miareczkowanie kwasu poliprotonowego
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
95.7K Wyświetleń

16.10 : Równowaga rozpuszczalności
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
52.0K Wyświetleń

16.11 : Czynniki wpływające na rozpuszczalność
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
33.0K Wyświetleń

16.12 : Powstawanie jonów złożonych
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
23.2K Wyświetleń

16.13 : Wytrącanie jonów
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
27.5K Wyświetleń

16.14 : Analiza jakościowa
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
21.5K Wyświetleń

16.15 : Krzywe miareczkowania kwasowo-zasadowego
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
126.4K Wyświetleń
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone