14.16 : Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
In the early 17th century, German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler postulated three laws for the motion of planets in the solar system. His first law states that all planets orbit the Sun in an elliptical orbit, with the Sun at one of the ellipse's foci. Therefore, the distance of a planet from the Sun varies throughout its revolution around the Sun.
While in an elliptical orbit, the total energy of the planet is conserved. Therefore, the planet slows down when it is at apogee and speeds up when it is at perigee. These conclusions led Kepler to state his second law, that the radius vector of the planet sweeps out in equal areas in equal time. This means that if a planet takes the same time to travel from A to A1, and then from B to B1, then the areas AF1A1 and BF1B1 are equal, as shown in Figure 1.
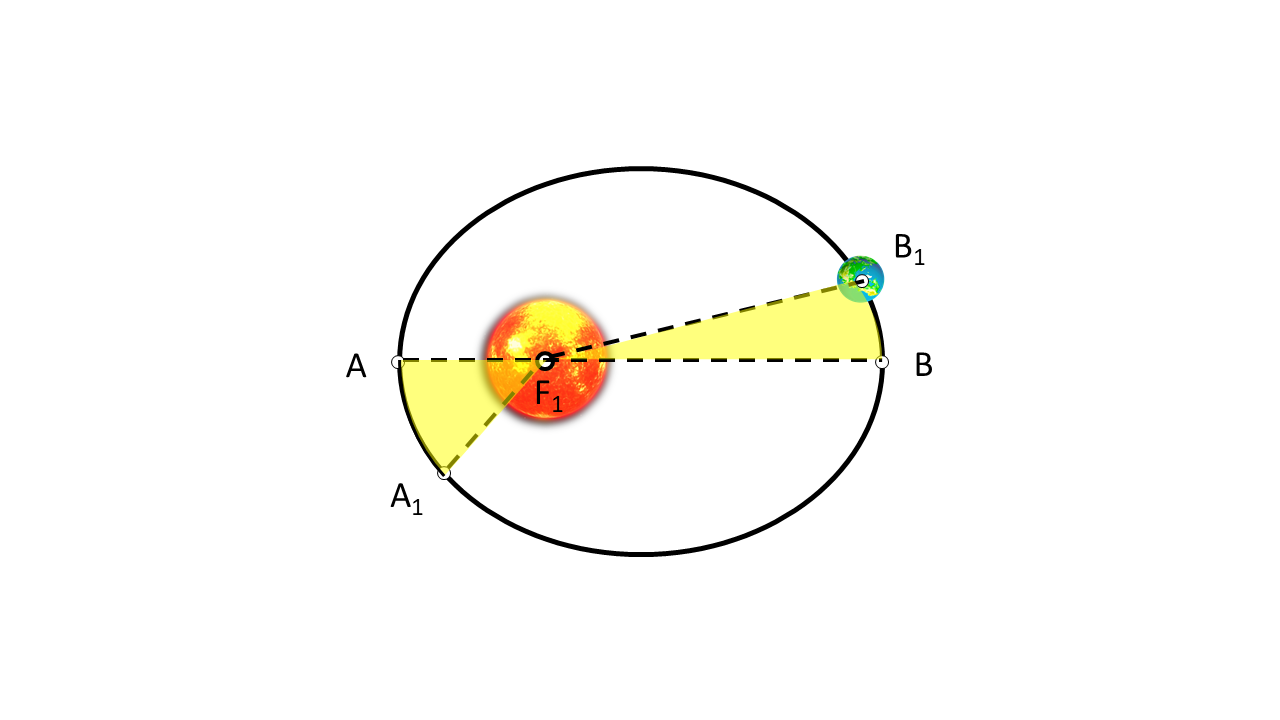
Since the area is constant in a given time interval, the planet's sector velocity remains constant. Since the sector velocity is proportional to the planet's angular momentum, Kepler’s second law implies that the angular momentum of a planet in an elliptical orbit is conserved.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 13.5 Kepler’s Laws of Motion.
Z rozdziału 14:

Now Playing
14.16 : Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
Gravitation
4.1K Wyświetleń

14.1 : Grawitacja
Gravitation
6.3K Wyświetleń

14.2 : Prawo grawitacji Newtona
Gravitation
12.5K Wyświetleń

14.3 : Grawitacja pomiędzy sferycznie symetrycznymi masami
Gravitation
854 Wyświetleń

14.4 : Grawitacja między ciałami sferycznymi
Gravitation
8.3K Wyświetleń

14.5 : Zmniejszone współrzędne masy: izolowany problem dwóch ciał
Gravitation
1.2K Wyświetleń

14.6 : Przyspieszenie grawitacyjne na Ziemi
Gravitation
10.6K Wyświetleń

14.7 : Przyspieszenie grawitacyjne na innych planetach
Gravitation
4.2K Wyświetleń

14.8 : Ciężar pozorny i ruch obrotowy Ziemi
Gravitation
3.5K Wyświetleń

14.9 : Zmiany przyspieszenia spowodowane grawitacją w pobliżu powierzchni Ziemi
Gravitation
2.4K Wyświetleń

14.10 : Energia potencjalna spowodowana grawitacją
Gravitation
5.5K Wyświetleń

14.11 : Zasada superpozycji i pola grawitacyjnego
Gravitation
1.3K Wyświetleń

14.12 : Prędkość ucieczki
Gravitation
5.6K Wyświetleń

14.13 : Orbity kołowe i prędkość krytyczna dla satelitów
Gravitation
2.9K Wyświetleń

14.14 : Energia satelity na orbicie kołowej
Gravitation
2.2K Wyświetleń
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone