19.2 : Stream Function
In two-dimensional incompressible fluid flow, the continuity equation is essential for ensuring mass conservation, meaning that any change in fluid entering or exiting a region is balanced by a corresponding change elsewhere. For incompressible flow, where density remains constant, this requirement simplifies to the condition that the divergence of the velocity field must be zero. Mathematically, this is expressed as,
where u and v represent the horizontal and vertical velocity components, respectively.
To inherently satisfy this equation, we introduce the stream function ψ, which allows the velocity components to be defined in terms of ψ as:
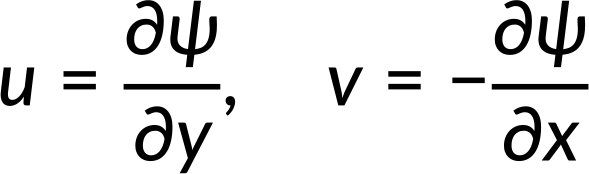
These definitions automatically satisfy the continuity equation, as the mixed partial derivatives of ψ cancel out.
The stream function ψ is constant along streamlines, which are the paths that fluid particles follow within the flow. Streamlines can therefore be visualized as contour lines of ψ, providing a clear representation of fluid motion. Each streamline is tangent to the velocity vector at any point along its path, illustrating the direction of flow without the need for calculating velocities at each point individually.
Moreover, the difference in ψ\psiψ values between two streamlines represents the volumetric flow rate per unit depth between them, enabling direct calculation of flow rates. This property significantly simplifies the analysis of two-dimensional incompressible flows by removing the need to solve separate equations for u and v. As a result, the stream function ψ is a powerful tool for modeling and interpreting fluid behavior in applications involving incompressible, steady flow.
Z rozdziału 19:

Now Playing
19.2 : Stream Function
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
1.1K Wyświetleń

19.1 : Euler's Equations of Motion
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
426 Wyświetleń

19.3 : Irrotational Flow
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
411 Wyświetleń

19.4 : Velocity Potential
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
351 Wyświetleń

19.5 : Plane Potential Flows
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
369 Wyświetleń

19.6 : Navier–Stokes Equations
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
428 Wyświetleń

19.7 : Steady, Laminar Flow Between Parallel Plates
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
141 Wyświetleń

19.8 : Couette Flow
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
209 Wyświetleń

19.9 : Steady, Laminar Flow in Circular Tubes
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
157 Wyświetleń

19.10 : Design Example: Flow of Oil Through Circular Pipes
Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow
103 Wyświetleń
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone