Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Mistletoe Eradicator - A Novel Tool for Simultaneous Mechanical and Chemical Control of Mistletoe
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
The protocol describes an easy-to-handle tool called Mistletoe Eradicator which combines mechanical and chemical approaches and is efficient in the control of mistletoe infestation on the host trees. The manuscript uses the European mistletoe (Viscum album subsp. album L.) as an example.
Streszczenie
Some species of mistletoes, an aerial plant hemiparasites, play a Janus-like role in ecosystems by being rich biodiversity hotspots due to their trophic and topic associations with various organisms and at the same time acting as biological pirates, exhausting the host trees by stealing water and nutrients via the haustorium. Many crop and timber trees are attacked by mistletoes, for example, dwarf mistletoes parasitize conifers, representatives of genus Tapinanthus target guava, and Phoradendron mistletoe target pecans. Recently, an increasing infestation of the European mistletoe (Viscum album subsp. album L.) in monoculture stands of common walnuts (Juglans regia L.) was recorded for the first time during 2018 in different regions of Kashmir Valley, India. The common chemical approach based on the spraying of mistletoe exophytes with the growth regulators, ethephon and glyphosate, was not efficient since V. album resprouted in the next vegetation season. Hand pruning of mistletoe was time-consuming, and a polyethylene covering resulted in the localized rotting of host tissues. The most efficient approach to eradicate mistletoe was the use of a novel tool called Mistletoe Eradicator, which allows to use mechanical and chemical means of mistletoe control simultaneously. It consists of a manipulating pole with the terminal pruning saw having a container filled with the growth regulator, from which the liquid slowly drops onto the saw blade through the nozzle. It allows working both from the ground and in the tree canopy. After the targeted application of 5%-10% ethephon or glyphosate to the base of the just pruned V. album stems (stubs), exophyte resprouting was significantly reduced 9 months after the pruning as compared to the only pruned or sprayed exophytes. An alternative variant of Mistletoe Eradicator was constructed in Ukraine filled just with a food color additive to track the liquid dropping and was successfully tested.
Wprowadzenie
Mistletoes are a taxonomically diverse group of aerial stem hemiparasites belonging to the Loranthaceae, Viscaceae, Santalaceae, Amphorogynaceae, and Misodendraceae families (order Santalales). They attach to the susceptible host trees by a specific anatomical bridge called a haustorium (endophyte) and are largely dependent on the host for water and nutrient supply, but are still able to photosynthesize via the green aerial portion called exophyte1,2. Although mistletoes may be considered hotspots of diversity providing food and shelter for various organisms, some mistletoe species are indeed biological pirates, affecting host health, fitness, and lifespan by the reducing their annual apical and lateral growth, flowering and fruiting as well as facilitating attacks of biological invaders such as fungi and bacteria3,4,5. At the same time, mistletoes are intensely used in both traditional and folk medicine, are components of compost, mulch, forage, and act as seasonal ecotourism attractions6,7,8.
Some of the notorious parasitic mistletoes are the dwarf mistletoes (Arceuthobium spp.; Santalaceae) reducing the growth of coniferous trees in North America9 and Mexico10; Tapinanthus (Blume) Rchb. mistletoes (Loranthaceae) attacking cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) and Citrus L. plantations in Africa11,12; hairy mistletoes (Taxillus tomentosus (Heyne ex Roth) van Tiegh.; Loranthaceae) affecting the Indian Euphorbiaceae trees, Phyllanthus emblica L. and Phyllanthus indofischeri Bennet, both known locally as Amla13; and the European mistletoe (Viscum album subsp. album L.; Viscaceae) having a broad host spectrum (more than 450 tree species)14,15 and rapidly spreading in Europe with its range shifted northwards16.
Walnut (Juglans regia L.) is an important horticultural cash crop in Kashmir valley constituting approximately 85% of India's annual walnut production17. Besides other biotic stresses such as leaf blotch, anthracnose, crown galls, stem cankers, walnut blight, or lace bug (Paracopium cingalense (Walker, 1873); Heteroptera: Tingidae) that attack the walnuts in Kashmir Valley, the V. album, locally called banada, kaw-khoor or nalkachul, also heavily infests these trees and can also rarely parasitize poplars (Populus L.; poplars in Kashmir valley are secondary hosts)18. Such a localized infestation might be explained by the possible concomitant introduction of V. album at the early developmental stages of 2-3 years, when its exophytes are almost invisible, with the planting material of walnuts from some plant nurseries. In turn, local poplar trees, the widespread susceptible primary host of this mistletoe in Europe, might be attended by birds vectoring sticky viscin-covered mistletoe fruits to the neighboring J. regia orchards.
Besides walnuts, leafy mistletoes parasitize other nut-producing trees, for example, almonds (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A. Webb) are attacked by V. album in the Mediterranean Europe and in Crimea (Ukraine) as well as by the representatives of Phoradendron Nutt. genus in North America14,15,19; common hazel (Corylus avellane L.) by V. album in Europe14,15; pecan (Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K.Koch) by oak mistletoe (Phoradendron flavescens (Pursh) Nutt.) in the southeastern United States20,21, and V. album in Europe14; macadamia (Macadamia F. Muell.) by shiny-leaved mistletoe (Benthamina alyxifolia (F.Muell. ex Benth.) Tiegh.), concomitant coast mistletoe (Mullerina celastroides (Sieb. ex. Schult & Schult. f.) Tiegh.), erect mistletoe (Amyema congener (Sieber ex Schult. & Schult. f.) Tiegh.), smooth mistletoe (Dendrophthoe glabrescens (Blakeley) Barlow), and long-flowered mistletoe (Dendrophthoe vitelline (Sieb. ex. Schult & Schult.f.) Tiegh.) in Australia22 (Watson, 2018); kolanut (Cola nitida (Vent.) Schott & Endl.) by Phragmanthera incana (Schumach.) Balle and Tapinanthus bangwensis (Engl. & K.Krause) Danser in Nigeria23; and cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) by Psittacanthus plagiophyllus Eichler in Amazonian savanna24.
Currently, the strategy of mistletoe control develops in frames of the integrated pest management paradigm combining mechanical, chemical, and biological means to reduce infestations4,7,25,26,27,28. An environmentally friendly mistletoe biocontrol method involves the use of the natural enemies of mistletoe such as bacteria, necrotrophic fungi, herbivores, or even epiparasitic mistletoes3,4,7,29,30 but have limited applications due to the non-specificity and small-scale of action of the biotic agents. Although cutting and pruning are recognized as the most traditional and efficient means of mistletoe control26,30,31,32, exophytes frequently resprout. For spraying of mistletoe exophytes with chemicals, mistletoe stubs or host stems are injected with systemic herbicides such as glyphosate, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy) butyric acid (2,4-DB), or 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T)3,33 or ethylene-releasing defoliants and ripening enhancers such as ethephon or (2-chloroethyl)-phosphonic acid)34,35. The combination of exophyte pruning to 2-3 cm stubs along with ethephon application to cut end of mistletoe stubs with a fine brush resulted in reduced V. album resprouting. This inspired the development of Mistletoe Eradicator, which can perform mechanical and chemical control of mistletoe growth simultaneously.
Here, we introduce an easy-to-handle and broadly available tool called Mistletoe Eradicator, which combines the benefits of mechanical and chemical means of mistletoe control and prevents its resprouting. The tool allows the certified arborists, plant pathologists, foresters, horticulturists, silviculturists, plant ecologists, experienced gardeners and other instructed users to deal with mistletoe challenge from the ground, from aerial platforms or from the trees. The tool performs a targeted pruning of mistletoe exophyte with the simultaneous dropping of a small amount of growth regulator directly on the pruned mistletoe stem. Mistletoe Eradicator was patented in India36 and used for the successful control of an increasing V. album subsp. album infestation on walnuts in Kashmir Valley. An updated version of this tool was designed in Ukraine and introduced to local arborists to practice in field tests with just a food color additive to track the herbicide dropping. It is noteworthy that Mistletoe Eradicator can be easily assembled and used for the control of other host-aggressive mistletoe species at the sites of their infestation in accordance with the national environmental law and after the approval of the local human communities.
Protokół
The growth regulators used in the work are available in the market after approval by the Central Insecticide Board (http://ppqs.gov.in/central-insecticides-board). Moreover, personal invitations and permissions of the farmers and owners of walnut plantations, who offered their infected trees for experiments, were obtained. Experiments presented here were done by a certified arborist in the closed research and monitoring zone of M.M. Gryshko National Botanical Garden of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (Kyiv, Ukraine). Before starting to work with Mistletoe Eradicator in your country, please check the environmental regulation, get permissions for the use of herbicides from the relevant authorities of the country, where Mistletoe Eradicator will be operated, and obtain agreement on its use with the local human communities (farmers, landowners, etc.).
1. Long-term preparations
- Briefly introduce yourself or/and other users of Mistletoe Eradicator into the basics of mistletoe biology and ecology, and approaches to its control.
- Optional: Assess the mistletoe incidence, the degree of infestation, host tree mortality rates, and the degree of mistletoe biotic damage of the host trees (e.g., crone defoliation and water stress in host branches acropetal to mistletoe exophyte) to select the priority of mistletoe control on the most infested host trees based on the approaches described in20,30,32,37,38.
- Check weather forecast including wind direction and strength, temperature, probability of rain, snowing, fog, or frost with a reliable meteorological service. Operate Mistletoe Eradicator under dry weather and under adequate light conditions to see the working area clearly.
2. Assembly of Mistletoe Eradicator
NOTE: All components of Mistletoe Eradicator are publicly available in supermarkets and gardener stores and are better to be custom-tailored and connected with the help of the professional welding engineer. Details and equipment used for the assembly of Mistletoe Eradicator must be modified and adjusted based on the country of use and availability of the components in an open market.
- Prepare all components according to the list and (Figure 1)36 assemble them as follows: acquire a wooden/plastic/metal telescopic or non-telescopic pole with a light telescopic handle, up to 3 m in length, and connect a pruning saw safely and firmly to the pole (Figure 1A; Figure 3A); prepare a container (10-150 mL) with a metal screw plug cap having a custom-drilled 2 mm aperture (inner diameter) for the growth regulator (Figure 1B) and a nozzle with a 2 mm aperture (e.g., stainless steel hollow-through lamp with hole screw).
NOTE: The commercial off-the-shelf manual pole saw with further installation of the container for the growth regulator might also be used to construct the Mistletoe Eradicator. Light weight facilitates the work at high peripheral branches of the host tree both from the ground and from the tree. The apertures of both screw plug cap and nozzle might vary in between 2-5 mm and define the herbicide dropping speed. The optimal aperture is 2 mm. - Firmly connect all metal details with the welding gun in a way that one side of the nozzle (Figure 1B-4) is connected by welding to the metal screw plug cap (Figure 1B-3) tightly fitting the container (Figure 1B-2), while its opposite side is welded to the upper outer corner of the saw blade (Figure 1B-1). Keep a pore (Figure 1B-5) at the point of the attachment of the nozzle and the cutter blade open (Figure 1D).
- Fill the container with water for the dropping test, close the screw plug cap firmly and twist the pole in working position - the sharp surface of the saw blade downwards, the container upwards and upside down. Ensure that the liquid slowly drops down on the saw blade (Figure 2A (inset), Figure 3C).
- In case of clogging, clean the 2 mm-wide nozzle using fine needle (e.g., with a syringe needle or a fine sewing needle) until the clog is removed and the herbicide dropping is restored.
- For transportation or storage, empty the container and secure Mistletoe Eradicator with a saw cover or scabbard.
CAUTION: Misuse of Mistletoe Eradicator may result in serious or fatal injuries, so the sharp surface of the blade must be covered.
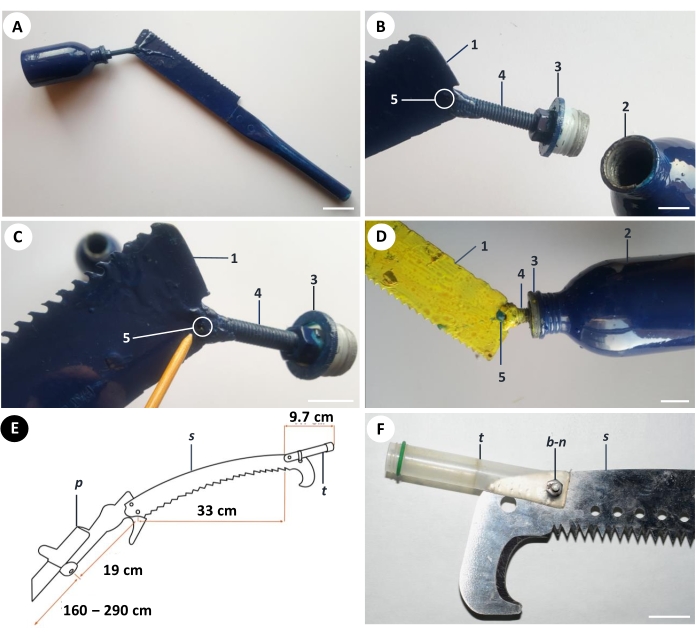
Figure 1: Variants of Mistletoe Eradicator tool. (A-D) An original Indian prototype constructed, tested on walnuts in Kashmir Valley, and patented in India36: (A) the terminal unit of the tool, which needs to be adjusted on the wooden/plastic/metal telescopic or non-telescopic pole with a length up to 3 m; (B) the junction between the pruning saw blade (1) and the container (2) with the drilled metal screw plug cap with 2 mm aperture (3) welded to the nozzle with 2 mm aperture (4) ending with a pore (5); (C) a pore (5) at the point of the joint of the nozzle with the pruning saw blade; (D) the slow dropping of herbicide through the screw plug cap from the container to the nozzle, and from the nozzle to the pruning saw blade through a pore (5); general scheme. (E) and (F) provide details of an alternative version of Mistletoe Eradicator constructed in Ukraine from a commercial tree manual pole saw (s); perforated garden saw with pole handle (p); (b-n) adjustable bolt-nut connection between the screw cap tube (t) with rounded false bottom and the saw blade. Scale bars for (A) is 5 cm and for (B-D, F) is 2 cm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
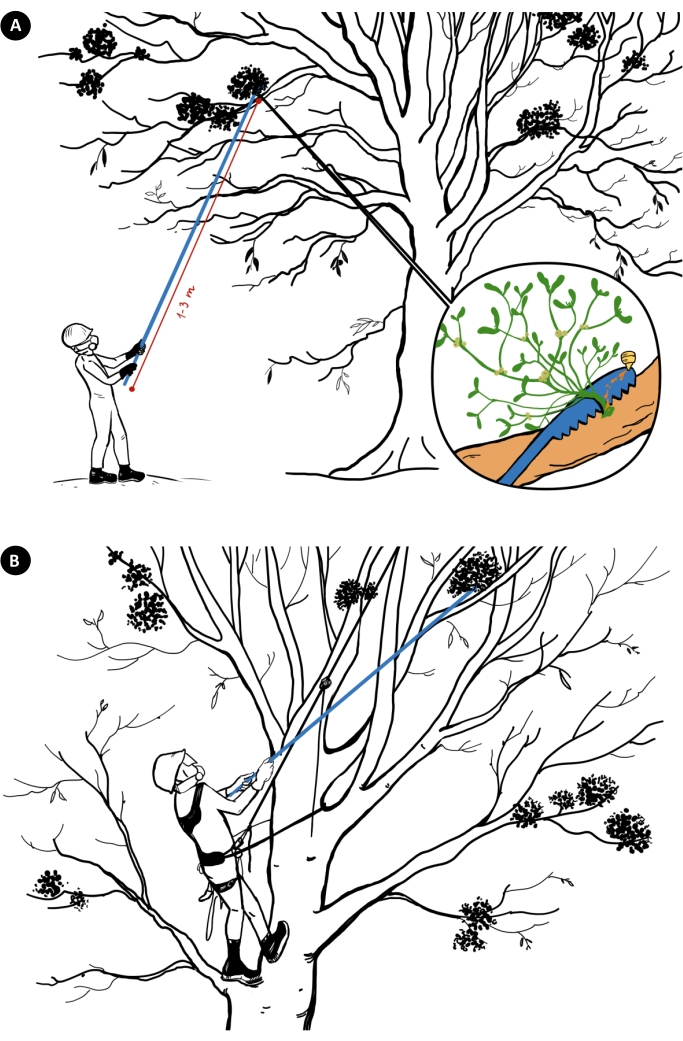
Figure 2: Mistletoe Eradicator operation mode. (A) from the ground; (B) from the tree by a certified arborist. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
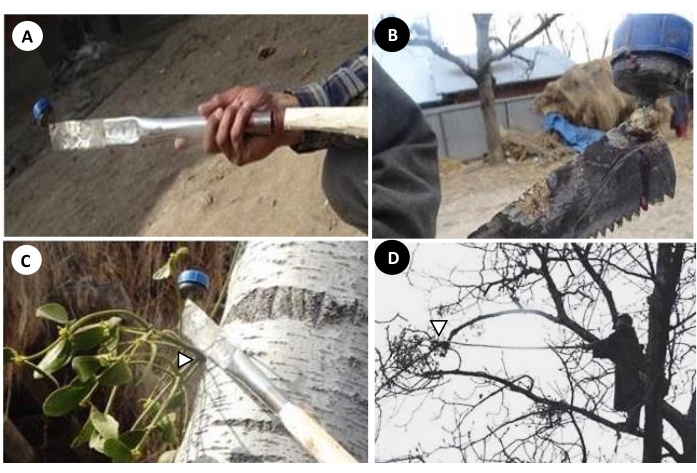

Figure 3: A working prototype of Mistletoe Eradicator tested on walnut trees in Kashmir valley in action. (A, B) A demonstrative tool set up without the growth regulators in hands of the operator. (C) The pruning position of Mistletoe Eradicator in relation to V. album exophyte. At the hidden side of the tool the slow release of the growth regulator from the container through the pore at the distal end of the nozzle occurs at the site of pruning. (D) Alternative on-the-tree operation mode and eradication of V. album parasitizing the peripheral host branch. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Herbicide preparation
- Choose local, commercially available analogue of mistletoe growth regulator(s), ethephon (2-Chloroethylphosphonic acid) or glyphosate (N-(Phosphonomethyl)glycine. Check the correspondence of the chosen herbicides to local legislation since ecological permissions and licenses might be necessary.
- Dilute plant growth regulators according to their specification sheets and manufacturer instructions to prepare stock solutions for short-term storage (not longer than 1-2 days) at 4 °C. On the day of work, prepare 4% -10% working solutions from stock solutions ex tempore.
NOTE: Treatments with the growth regulators must be performed by certified workers and arborists according to the current legislation in the country of operation.
4. On-site safety rules
- For all operator(s) and assistant(s) allowed to operate Mistletoe Eradicator from the ground, provide sufficient personal protection (Figure 2A; Figure 4B): nonslip steel toe work boots; liquid-proof, chemical-resistant coverall or a suit with a hood; a helmet; a chemical respirator due to the risk of inhaling herbicide fumes; an eye/face shield/protecting goggles that conforms to ANSI Z87.1 or CE safety standard; chemical-resistant gloves to protect hands from mechanical damage and/or chemical injuries or heavy nonslip gloves for improved grip. In the neighborhood of the operation area, ensure water access is available in case of emergency.
- Ensure that only licensed arborists with at least one assistant is allowed to operate Mistletoe Eradicator from the tree, using safe gear, bright ropes, arborist lanyards and other professional equipment (Figure 2B). Do not use Mistletoe Eradicator in recreational places. Mark the operation zone and trees with bright stripe tape to prevent the presence of outsiders.
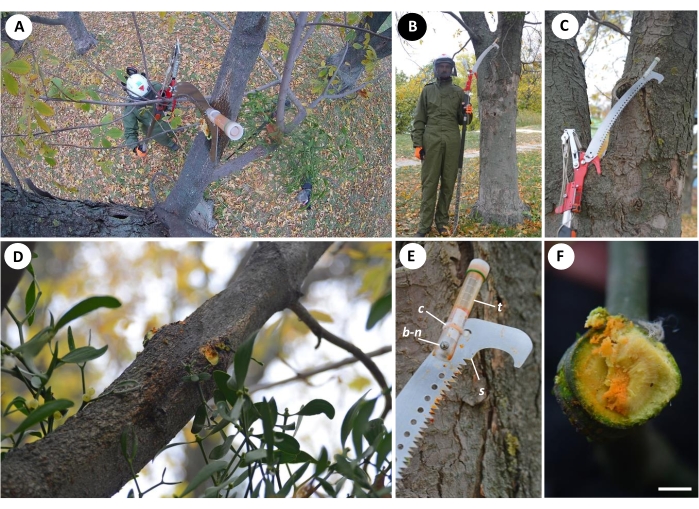

Figure 4: An alternative version of Mistletoe Eradicator tested in Ukraine. (A) Free-hand ground-based pruning of the European mistletoe (Viscum album subsp. album L.) exophyte parasitizing the red buckeye (Aesculus pavia L.) branch in M.M. Gryshko National Botanical Garden, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine. (B) An arborist with the tool. (C) Close-up of the tool on the tree bifurcation. (D) Pruned exophyte, (E) cable tie (c) and adjustable bolt-nut connection (b-n) between the screw cap tube (t) with rounded false bottom and the perforated garden saw blade (s) saw blade with traces of the demonstrative liquid (prepared using a dry E-160с food color additive) mimicking the growth regulator. (F) V. album exophyte stub treated with the demonstrative liquid. Scale bar is 2 cm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Mistletoe Eradicator operation mode
- Prune the mistletoe foliage before their fruiting with sticky viscin-covered berries, and after the harvesting of the host trees. Remove the saw cover or scabbard from the tool and check the reliability of the connection between all parts of Mistletoe Eradicator. Do not operate a damaged, improperly adjusted, or not completely or insecurely assembled tool.
CAUTION: Do not hit rocks, stones, or other foreign objects with the blade of Mistletoe Eradicator. Do not cut solid metal, sheet metal, plastics or any non-wood materials with it. - Evaluate the distance from the operator to the targeted mistletoe on the peripheral host branches and adjust the appropriate length of the telescopic stick to get free access to the attachment point of mistletoe with the host tree (Figure 2A). Ensure that there are no obstructions in the way of Mistletoe Eradicator toward the mistletoe on the tree.
- Find an appropriate saw position (~45° of inclination) in relation to the mistletoe exophyte present in the closest proximity to the host branch/stem (Figure 2A (inset), Figure 3C, Figure 4A).
- Fill the container up to ¾ of its volume with only one growth regulator in working concentration, close the screw plug cap firmly and place Mistletoe Eradicator in a non-working position - the sharp surface of the saw blade upwards, the container downwards, no liquid dropping (Figure 1A).
- Stand closer to the tree and place the tool in the working position by twisting the pole (Figure 2A, inset). Operate Mistletoe Eradicator with both hands while maintaining a safe distance from the assistant(s) and any bystanders (Figure 2A).
- Ensure a good firm grip on the tool and prune an exophyte with short sawing movements of the cutting blade (Figure 4A). Ensure that the distal end of the saw blade does not touch the neighboring host branches and/or stem which might damage them and the container.
- Add more growth regulator as it gets exhausted. The amount of herbicide for one V. album stub varies between 1-5 mL depending on the nozzle diameter.
- After the pruning of one mistletoe exophyte, place the Mistletoe Eradicator in non-working position and let the air come inside the container through the pore. Relocate to another mistletoe exophyte, place Mistletoe Eradicator in working position and repeat the procedure.
NOTE: If the Mistletoe Eradicator is operated from the tree by a trained arborist (Figure 2B), the rules for high-altitude work in the country of operation must be followed.
6. Mistletoe foliage piling and finishing
- Pile the pruned exophytes between the host trees. Mistletoe pruned using Mistletoe Eradicator cannot be collected for pharmacological, ritual, or forage purposes because of the potential danger posed by the growth regulators to human and animal health.
- Dispose the growth regulators following manufacturer instructions and local environmental regulations.
- Clean the tool mechanically after work, empty and thoroughly wash the container with tap water and dry it. Discard the disposable protective gloves and respirators in special containers. Thoroughly rinse the reusable cloth, boots, helmets, and eye protection with tap water, dry, and store separately.
- Protect the sharp part of the Mistletoe Eradicator with a saw cover or scabbard.
Wyniki
Different V. album management approaches were tested in Kashmir (India) in walnut plantations during 2012-2016 before the use of the Mistletoe Eradicator, such as targeted foliar spraying with glyphosate and ethephon in different concentrations, pruning/clipping of mistletoe exophytes, secure covering of the wound with polyethylene wrap and application of the same herbicides to the cut ends of 2-3 cm-long mistletoe stubs.
Each approach was tested on five V. album exophytes on...
Dyskusje
Mistletoes cannot be treated exclusively as pests, since many of them play a crucial role in the ecosystem as biodiversity hotspots and connecting tropical and topical hubs for multiple organisms, behaving more like epiphytes than parasites with negligible negative consequences for their hosts6,8. Therefore, the measures aimed to control their spread have to be highly selective and based on the understanding of both biology and biotic associations of definite mis...
Ujawnienia
SKUAST-Kashmir reserves copyright of the Mistletoe Eradicator tool under patent number 340843 of Indian Patents. The authors declare no other conflict of interests.
Podziękowania
The authors thank plant taxonomist Dr. Norbert Holstein (Nees-Institute for the Biodiversity of Plants, Bonn University, Germany) for his kind help in the primary identification of mistletoe species. Permissions from the following farmers and owners of walnut plantations in Kashmir, who offered their infected trees for our experiments, were obtained, namely from Abdul Rashid Reshi (R/O Village Reshii Mohalla, Khag, Budgam), Habib-Ullah Sheikh (R/O village Trapii, Khag, Budgam), Showket Ahmad Rasray (R/O Village Hamchii Pora, Budgam), Ghulam Hassan Shah (R/O Nagbal, Khag, Budgam), and Javeed Ahmad Qureshi (R/O village Lowahi Pora, Khag, Budgam).The drawings of Mistletoe Eradicator operation mode was made by the fine artist Natalia Pendiur (Kyiv, Ukraine) and are highly appreciated. Maksym Lashchenko (Olomouc, Czech Republic) kindly helped with the image processing and technical descriptions.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Components of Indian Mistletoe Eradicator* | |||
| Bosch 2607010538 HSS-G Drill Bit Set, Silver | Bosch | 2607010538 | https://www.amazon.co.uk/Bosch-Professional-2607010538-HSS-G-Silver/dp/B001IBMPL2 |
| Container- Aluminium Bottle- with screw plug Cap | Suparna Exports, Pvt. LTD | n/a | http://www.aluminumbottlecans.com/aluminum-bottles-with-screw-plugs.php |
| Drill GSR12V-300HXB22 | Bosch | GSR12V-300HXB22 | https://www.boschtools.com/us/en/boschtools-ocs/cordless-screwdrivers-gsr12v-300hxb22-207019-p/ |
| Genuine C04AL-1487425 engine valve guide for engine spare parts | Shangchai | C04AL-1487425 | https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/Genuine-C04AL-1487425-engine-valve-guide_60704258097.html?spm=a2700.details.0.0.2cfb6b8b2k JBOB |
| HBCHEN Handheld Welder Gun Portable Welding Machine, 220V Small Welding Machine and 110V Arc Welder | HBCHEN | YB320 | https://www.amazon.com/HBCHEN-Handheld-Portable-Eliminate-Experience/dp/B097BWBCMB |
| The nozzle: stainless steel outer bolt hollow-through lamp with hole screw | n/a | M6M8M10M12 | https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32950601820.html?spm=a2g0o.seo_rank.0.0.62642d1 fLzjNFL |
| The pruning saw blade | Lee Valley | 09A0356 | https://www.leevalley.com/en-us/shop/garden/garden-care/saws/76626-pruning-saw-blade?item=09A0356 |
| Components of an alternative Ukrainian Mistletoe Eradicator* | |||
| Aluminium Telescopic Hand Gardena Combisystem 160-290 cm | ROZETKA | Code 03720-20 | https://rozetka.com.ua/202484293/p202484293/characteristics/ |
| Amazon Basics Multi-Purpose Cable Ties - 4-Inch/100mm | Amazon Basics | n/a | https://www.amazon.com/AmazonBasics-Multi-Purpose-Cable-Ties-200-Piece/dp/B087MKMSDY/ref=sr_1_1_sspa?crid=3FEZFXGOR4VPC&keywords =cable%2Bties&qid=1642924567&sprefix =Cable%2Btie%2Caps%2C162&sr=8-1-spons&spLa=ZW5jcnlwdGVkUXVh bGlmaWVyPUEyTU9QMEo2WUp YMjBLJmVuY3J5cHRlZElkPUEwM jYzMDkxQUtWODVWU00xU0ZYJ mVuY3J5cHRlZEFkSWQ9QTA1O Tc2NjUyVzdHV0E4UUZOWkU1Jn dpZGdldE5hbWU9c3BfYXRmJmF jdGlvbj1jbGlja1JlZGlyZWN0JmRv Tm90TG9nQ2xpY2s9dHJ1ZQ&th= 1 |
| Garden saw GARTNER 540/360 mm with bar handle | Gärtner | Code 80001003 | https://gartner-tools.com/ru/product/pila-sadovaja-540-360-mm-s-rukojatkoj-pod-shtangu-gartner/ |
| Loppers INTERTOOL HT-3111 | ROZETKA | Code 263723496 | https://rozetka.com.ua/intertool_ht_3111/p263723496/characteristics/ |
| M4 / 4mm DOOR HANDLE SCREWS BOLTS 20-22 mm | Boltworld | n/a | https://boltworld.co.uk/collections/m4-bolts/products/m4-4mm-door-handle-screws-bolts-9mm-50mm-lengths-cupboard-door-drawer-knob?variant=15820185469021 |
| M4 Hexagon Weld Nut A4 Stainless Nut DIN 929 | Boltworld | n/a | https://boltworld.co.uk/products/m4-hexagon-weld-nut-a4-stainless-nut-din-929?_pos=1&_sid=a8a2c15c9&_ss=r& variant=32145946706013 |
| Sarstedt 5ml Screw Cap Tube with Rounded False Bottom and Cap Assembled, with Print, 92x15.3, PP | Sarstedt | n/a | https://www.amazon.com/Sarstedt-Rounded-Bottom-Assembled-92x15-3/dp/B07GXZ51BN |
| Chemicals | |||
| Ammonium salt of Glyphosate 71% SG EXCEL MERA 71 | Excel Crop Care | n/a | http://www.excelcropcare.com/product/domestic/crop-protection/herbicides/excel-mera-71.php |
| E-160c* | EUROIMPEX | n/a | https://euroimpex.net.ua/ru/krasiteli/ |
| Ethephon (“Promoter”) | Fil, India Ltd | n/a | https://www.filindustries.com/our-businesses.php |
| Protection* | |||
| Gloves Tegera Cut Control | EJENDALS | TEGERA 9121 | https://www.ejendals.com/globalassets/inriver/resources/9121_productsheet_en. |
| Helmet CAMP Rockstar | CAMP | ID: 0202 | https://www.camp-usa.com/outdoor/product/helmets/rock-star-helmet/ |
| Mesh visor Stihl | STIHL | n/a | https://www.stihl.co.uk/STIHL-Products/Personal-protective-equipment/Face-and-ear-protection/22184-1545/Face-hearing-protection-nylon-mesh.aspx |
| SAS/STAT | SAS Institute Inc. 2013, USA | statistical analysis software | |
| *materials and equipment marked with asterisks are changeable and can be modified and adjusted basing on the country of the use and avaliability of the components in the market. Moreover, Mistletoe Eradicator can be custom-tailored by the professional welding engineer. |
Odniesienia
- Kuijt, J., Hansen, B. . Flowering plants. Eudicots: Santalales, Balanophorales. , (2015).
- Nickrent, D. L., Malécot, V., Vidal-Russell, R., Der, J. P. A revised classification of Santalales. Taxon. 59 (2), 538-558 (2010).
- Kahle-Zuber, D. . Biology and evolution of the European mistletoe (Viscum album). , (2008).
- Varga, I., Taller, J., Baltazár, T., Hyvönen, J., Poczai, P. Leaf-spot disease on European mistletoe (Viscum album) caused by Phaeobotryosphaeria visci: a potential candidate for biological control. Biotechnology Letters. 34, 1059-1065 (2012).
- Watson, D. M., Herring, M. Mistletoe as a keystone resource: an experimental test. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 279, 3853-3860 (2012).
- Kuijt, J. . The Biology of Parasitic Flowering Plants. , (1969).
- Watson, D. M., Cook, M., Fadini, R. F. Towards best-practice management of mistletoes in horticulture. Botany. 98 (9), 489-498 (2020).
- Těšitel, J., et al. The bright side of parasitic plants: what are they good for. Plant Physiology. 185 (4), 1309-1324 (2021).
- Geils, B. W., Cibrián Tovar, J., Moody, B. Mistletoes of North American Conifers. General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-98. US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service. , (2002).
- González-Elizondo, M., et al. Effects of Mexican dwarf mistletoe (Arceuthobium vaginatum subsp. vaginatum) on the growth of Pinus cooperi in Durango, Mexico - A case study. Forest Pathology. 49, 12473 (2019).
- Room, P. M. Ecology of the mistletoe Tapinanthus bangwensis growing on cocoa in Ghana. Journal of Ecology. 61 (3), 729-742 (1973).
- Terna, T. P., Okogbaa, J. I., Waya, J. I., Markus, M. Incidence and severity of Amyemas pp. and Tapinanthus globiferus on citrus trees in Federal University Lafia campus, Lafia. Journal of Phytopathology and Plant Health. 4, 21-28 (2017).
- Rist, L., Shaanker, U. R., Ghazoul, J. The spatial distribution of mistletoe in a southern Indian tropical forest at multiple scales. Biotropica. 43 (1), 50-57 (2011).
- Barney, C. W., Hawksworth, F. G., Geils, B. W. Hosts of Viscum album. European Journal of Forest Pathology. 28, 187-208 (1998).
- Krasylenko, Y., et al. The European mistletoe (Viscum album L.): distribution, host range, biotic interactions, and management worldwide with special emphasis on Ukraine. Botany. 98 (9), 499-516 (2020).
- Tikkanen, O. P., et al. Freezing tolerance of seeds can explain differences in the distribution of two widespread mistletoe subspecies in Europe. Forest Ecology and Management. 482, 118806 (2021).
- Mir, S. A., Modi, S. Walnut (Juglans regia L.) production and its disease management in Jammu and Kashmir. International Journal of Recent Advances in Multidisciplinary Topics. 2 (9), 76-78 (2021).
- Ahmad, S., Mir, N., Sultan, S. White-berry mistletoe (Viscum album L.): a hemiparasitic plant: occurrence and ethnobotanical use in Kashmir. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 7 (1), 1831-1833 (2018).
- Paine, L. K., Harrison, H. C. Mistletoe: its role in horticulture and human life. HortTechnology. 2, 324-330 (1992).
- Hawksworth, F. G. The 6-class dwarf mistletoe rating system. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service. , (1977).
- Wood, B. W., Reilly, C. C. Control of mistletoe in pecan trees. HortScience. 39 (1), 110-114 (2004).
- Watson, D. M. Reconnaissance and recommendations for mistletoe management in macadamia orchards. Hort Innovation. , (2018).
- Asogwa, E. U., et al. Kola nut production, processing and marketing in the South Eastern states of Nigeria. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural & Environmental Science. 4, 463-468 (2012).
- Fadini, R. F., Lima, A. P. Fire and host abundance as determinants of the distribution of three congener and sympatric mistletoes in an Amazonian savanna. Biotropica. 44, 27-34 (2012).
- Ančić, M., Pernar, R., Bajić, M., Sletković, A., Kolić, J. The application of hyperspectral images for detection of mistletoe infected silver fir trees on large areas. First Croatian Computer Vision Workshop (CCVW 2012). , (2012).
- Shaw, D. C., Mathiasen, R. L. Forest diseases caused by higher parasitic plants: Mistletoes. Infectious Forest Diseases. , 97-114 (2013).
- Maes, W. H., et al. Can UAV-based infrared thermography be used to study plant-parasite interactions between mistletoe and eucalypt trees. Remote Sensing. 10 (12), 2062 (2018).
- León-Bañuelos, L. A., Endara-Agramont, A. R., Gómez-Demetrio, W., Martínez-García, C. G., Nava-Bernal, E. G. Identification of Arceuthobium globosum using unmanned aerial vehicle images in a high mountain forest of central Mexico. Journal of Forest Research. 31, 1759-1771 (2020).
- Kotan, R., et al. Parasitic bacteria and fungi on common mistletoe (Viscum album L.) and their potential application in biocontrol. Journal of Phytopathology. 161, 165-171 (2013).
- Szmidla, H., Tkaczyk, M., Plewa, R., Tarwacki, G., Sierota, Z. Impact of common mistletoe (Viscum album L.) on Scots pine forests − a call for action. Forests. 10 (847), 1-15 (2019).
- Mathiasen, R. L., Nickrent, D. L., Shaw, D. C., Watson, D. M. Mistletoes: pathology, systematics, ecology, and management. Plant Disease. 92, 988-1006 (2008).
- Mistletoe Management. SAFE TREES Available from: https://www.safetrees.cz/specialni-ochrana-zelene/index.html (2020)
- Lichter, J. M., Reid, M. S., Berry, A. M. New methods for control of leafy mistletoe (Phoradendron spp.) on landscape trees. Journal of Arboriculture. 17 (5), 127-130 (1991).
- Adams, D. H., Frankel, S. J., Lichter, J. M. Considerations when using ethephon for suppressing dwarf and leafy mistletoe infestations in ornamental landscape. Journal of Arboriculture. 19 (6), 351-357 (1993).
- Hoyt, H. M., Hornsby, W., Huang, C. H., Jacobs, J. J., Mathiasen, R. L. Dwarf mistletoe control on the Mescalero Apache Indian Reservation, New Mexico. Journal of Forestry. 115 (5), 379-384 (2017).
- . Mistletoe Eradicator. Indian Patent. , (2017).
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/ACCESS 9.4 Interface to ADABAS. SAS Institute Inc. , (2019).
- Sananse, S. L., Maidapwad, S. L. On analysis of two-way ANOVA using data transformation techniques. International Journal of Scientific Research. 3 (11), 480-483 (2014).
- Kartoolinejad, D., Hosseini, S. M., Akbarinia, M., Shayanmehr, F., Mirnia, S. The relationship among infection intensity of Viscum album with some ecological parameters of host trees. International Journal of Environmental Research. 1 (2), 143-149 (2007).
- Queijeiro-Bolaños, M., González, E. J., Martorell, C., Cano-Santana, Z. Competition and facilitation determine dwarf mistletoe infection dynamics. Journal of Ecology. 5 (3), 775-785 (2016).
- deBruyn, R. A., Paetkau, M., Ross, M. A., Godfrey, D. V., Friedman, C. R. Thermogenesis-triggered seed dispersal in dwarf mistletoe. Nature communications. 6, 6262 (2015).
- Watson, D. M., Rawsthorne, J. Mistletoe specialist frugivores: latter-day "Johnny Appleseeds" or self-serving market gardeners. Oecologia. 172 (4), 925-932 (2013).
- Michael, J. L., Talley, K. L., Fishburn, H. C. Forest herbicide washoff from foliar applications. Proceedings on the 45th Annual Meeting Southern Weed Science Society. , 236-243 (1992).
- Han, S., Berry, A. M., Reid, M. S. New ways to control mistletoe. Proceedings: Fortieth Annual California Weed Conference. , (1988).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone