n-Butyllithium Titration
Source: Vy M. Dong and Diane Le, Department of Chemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA
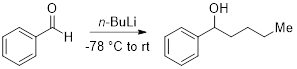
This experiment will demonstrate a simple technique to titrate and obtain an accurate concentration of the organolithium reagent, n-butyllithium (n-BuLi). Organolithium reagents are extremely air- and moisture-sensitive and proper care must be taken to maintain the quality of the reagent so that it may be used successfully in a reaction. The n-BuLi titration experiments should be performed regularly to obtain accurate concentrations prior to use in a chemical reaction. Subsequently, we will demonstrate the addition of the titrated n-BuLi to benzaldehyde.
1. Preparation of Titrant
- To a flame-dried round bottom flask equipped with a stir bar under N2, add diphenylacetic acid (250 mg, 1.18 mmol) and anhydrous THF (5 mL).
2. Titration of n-BuLi
- Calculate the approximate amount of n-BuLi solution (in hexanes) needed to consume the diphenylacetic acid. Using a syringe, slowly adda solution of n-BuLi dropwise. The reaction mixture will turn temporarily yellow and back to a colorless
Representative results for the titration of n-BuLi for Procedures 1-3