A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Dissection of 6.5 dpc Mouse Embryos
Summary
Isolation of postimplantation-stage embryos allows one to study gene patterning and analyze cell-lineage decision making processes during embryonic development, but proper dissection of the early embryo can be challenging. This protocol describes a method for isolating early primitive-streak-stage embryos (~6.5 days post coitum [dpc]).
Abstract
Analysis of gene expression patterns during early stages of mammalian embryonic development can provide important clues about gene function, cell-cell interaction and signaling mechanisms that guide embryonic patterning. However, dissection of the mouse embryo from the decidua shortly after implantation can be a challenging procedure, and detailed step-by-step documentation of this process is lacking.
Here we demonstrate how post-implantation (6.5 dpc) embryos are isolated by first dissecting the uterus of a pregnant mouse (detection of the vaginal plug was designated day 0.5 poist coitum) and subsequently dissecting the embryo from maternal decidua. The dissection of Reichert's membrane is described as well as the removal of the ectoplacental cone.
Protocol
Dissection of reproductive organs from a female mouse
- Pregnant animals are euthanized by CO2 asphyxiation using compressed gas.
- Lay the animal supine on absorbent pad and soak it in 70% ethanol to reduce the risk of contaminating the dissection with mouse hair.
- Pinch the skin and make a small lateral incision at the midline with regular surgical scissors. Hold the skin firmly above and below the incision and pull the skin apart toward the head and tail to expose the abdomen.
- Grasp the peritoneum with forceps and cut to expose the abdominal cavity.
- Locate the reproductive organs in the dorsal region of the body cavity: two uterine horns, the oviduct and the ovaries.
Primitive Streak-stage (6.5 dpc) Dissection
- Remove the uterine horn by grasping the uterus below the oviduct and cut it free along the mesometrium. Place dissected uterus in ice cold PBS.
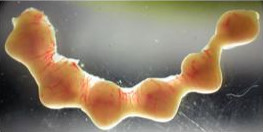
Figure 1 - Separate each embryo by cutting between implantation sites along uterine horn.
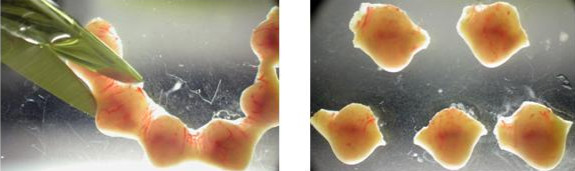
Figure 2 - Grasp the muscular uterine lining by sliding watchmaker's forceps between the surrounding muscle layer and enveloped decidua tissue. Peel back the muscle layer, exposing the decidua.
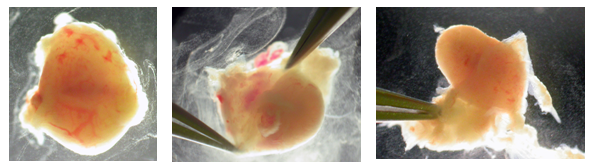
Figure 3 - Clip off a portion of the exposed decidua at the apex (approximately 1/5 of the decidua tissue) which will expose the midventral or distal tip of the enclosed embryo.
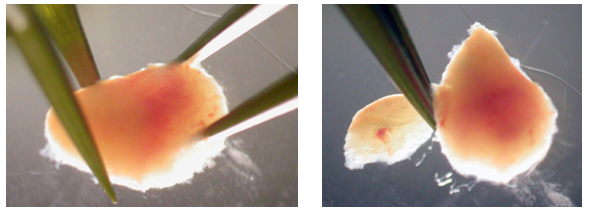
Figure 4 - The embryo can be shelled out using the tips of forceps. Pierce the decidua with forceps surrounding the embryo and open forceps to tear decidua apart.
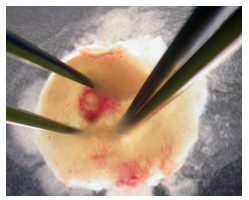
Figure 5 - Once embryo is removed, Reichart's membrane may still be attached as well as the ectoplacental cone (trophoblast). The embryo can be dissected further by careful dissection.
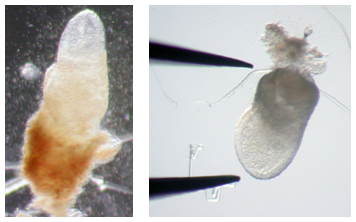
Figure 6
Discussion
Postimplantation in the mouse occurs between 4.5 dpc and birth. This dissection method can be applied, essentially as described, to isolate earlier or later stage embryos at 5.5-8.5 dpc.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| Micro Dissecting Forceps serrated, straight | Tool | Roboz Surgical Instruments Co. | RS-5130 | 2 pairs |
| Micro Dissecting Tweezers Pattern #55 INOX | Tool | Roboz Surgical Instruments Co. | RS-5010 | 2 pairs |
| Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (1x) | Reagent | Invitrogen | 14190 | |
| Fisherbrand Sterile Polysytrene Petri Dish | Tool | Fisher Scientific | 08-757-12 | |
| 4% Paraformaldehyde in PBS | Reagent | |||
| Straight Sharp-Pointed Dissecting Scissors | Tool | Fisher Scientific | 08-940 | |
| Pregnant female mice | Animal | |||
| Dissecting Microscope | Microscope |
References
- Nagy, A., et al. . Manipulating the mouse embryo: A laboratory manual third edition. , (2003).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved