A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Zebrafish Optogenetics: Activating Genetically Modified Somatosensory Neuron to Study Larval Behavioral Responses
Overview
This video describes optogenetic techniques by activating genetically modified somatosensory neurons and recording elicited behavioral response with a high-speed video camera.
Protocol
1. Mount Larvae for Behavior Experiments
- Make 1.5% low melt agarose in ddH2O and store in a 42 °C heat block to prevent it from solidifying.
- Using a glass Pasteur pipette, transfer one of the pre-screened larvae into a tube of 1.5% low melt agarose with as little blue/embryo water as possible.
- Transfer larvae in a drop of agarose onto a small Petri dish.
- Under a dissecting microscope, position larva dorsal up.
- When agarose has solidified, cut away the agarose with a thin razor blade (#11 scalpel), leaving a wedge of agar around the entire larva.
- Make two diagonal cuts at either side of the yolk; take care not to nick the larva.
- Fill the area surrounding the agarose with embryo/blue water.
- Pull agarose away from the trunk and tail of the larva (Figure 1).
2 . Prepare High-speed Camera and Imaging Software
- Mount high-speed camera onto dissecting scope.
- Connect camera to computer.
- Turn on computer.
- Turn on high-speed camera.
- Open video/imaging software (We use AOS imaging software and will describe procedures for using it here, but other imaging software is equally acceptable).
- Adjust camera settings accordingly (i.e. 1,000 frames per sec (fps), 50% trigger buffer or other preferred settings).
- Start recording.
3. Activate Single Neurons Using a 473 nm Laser
- Attach stimulator, laser and optic cable.
- Turn on stimulator.
- Set stimulator to a maximum of 5 Volts and a pulse duration of 5 msec.
- Turn on laser according to manufacturer's instructions.
- Use a dissecting microscope to position the tip of the optic cable near cell body of a neuron with ChEF-tdTomato expression (Figure 1).
- Deliver pulse of blue light to activate sensory neuron.
- Record behavior using a high-speed camera set at 500 or 1,000 frames per sec.
- Repeat experiment as desired, waiting 1 min between each activation to avoid habituation. (We record a minimum of three responses for each neuron).
- To release larvae, pry apart agarose with forceps, taking care not to injure the animal. This animal can be allowed to develop further and the procedure can be repeated at an older stage to characterize development of the behavior. The embryo can also be remounted for high-resolution confocal imaging of the activated cell to correlate behavior with cellular structure, as described below.
- Transfer larva to culture plate with fresh blue/embryo water. We use a 24-well plate to keep track of individual larvae.
Results
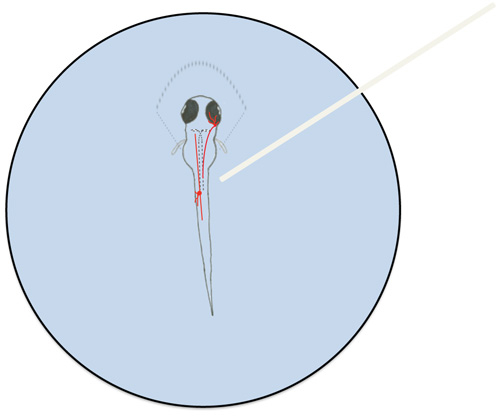
Figure 1. Diagram of a mounted zebrafish larva and representative neurons involved in the larval touch response. Zebrafish larvae were partially mounted in 1.5% low melt agarose (represented by dashed lines surrounding the rostral portion of the larva). A trigeminal neuron (in the head) and a Rohon-Beard neuron (in the trunk) are depicted in red. Mauthner cells are outlined by dashed lines in the larva. The optic cab...
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Low Melt agarose | Sigma | A9045 | or equivalent |
| Petri dish (100x15 mm) | Any | Any | |
| Non-Sterile scalpel blades | Fine Scientific Tools, Inc. | 10011-00 | or equivalent |
| blue/embryo water | 10 L ddH2O 0.6 g Instant Ocean 6 drops methylene blue | ||
| High speed camera | AOS Technologies, Inc. | X-PRI (130025-10) | or equivalent |
| Glass Pasteur pipette | Fisher | 1367820B | or equivalent (10-15 mm diameter) |
| 473 nm portable laser | Crystal lasers | CL-473-050 | or higher power, with TTL option |
| S48 Stimulator | Astro-Med, Inc. Grass Instrument division | S48K | or equivalent |
| Tricaine | Sigma | A5040 | |
| 200 μm optic fiber | ThorLabs | AFS200/220Y-CUSTOM | Patch Cord, Length: 3 m, End A: FC/PC, End B: FC/PC, Jacket: FT030 |
| 50 μm optic fiber | ThorLabs | AFS50/125Y-CUSTOM | Patch Cord, Length: 3 m, End A: FC/PC, End B: FC/PC, Jacket: FT030 |
| 24 culture plates | Genesee | 25-102 | or equivalent |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Palanca A. M. S., et al. Optogenetic Activation of Zebrafish Somatosensory Neurons using ChEF-tdTomato. J. Vis. Exp. (2013).
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved