A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Maule Staining for Lignin: A Technique to Characterize Lignin Distribution in Arabidopsis Thaliana Stem Sections
Overview
In this video, we describe the Maule staining technique for staining syringyl lignin present in the specialized plant cells. This staining technique helps to characterize the lignin distribution in the xylem and interfascicular fibers.
Protocol
1. Mäule Staining
- Dissolve 0.2 g of potassium permanganate in 40 ml distilled water to prepare a 0.5% potassium permanganate solution. Store in a dark bottle at room temperature for a maximum of 7 days.
- Prepare a 3.7% HCl solution by adding 1 ml concentrated HCl (37 N) to 9 ml distilled water (1:10). Prepare a fresh 3.7% HCl solution on the day of the experiment. Make sure that the 37 N HCl stock solution being used is not too old. Concentrated ammonium hydroxide solution (14.8 M) should be stored at 4 °C to prevent the molarity of the saturated solution from decreasing.
- Transfer stem sections to a 2.....
Representative Results
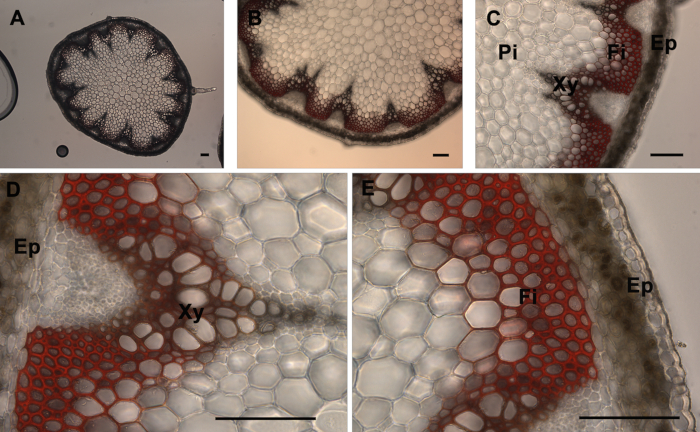
Figure 1. Mäule staining of A. thaliana stem cross-sections. Mäule staining (red color) of a wild type A. thaliana stem section showing the normal lignin deposition in the walls of interfascicular fibers and xylem cells (A-E). The positions of the epidermis and cortex (Ep), interfascicular fibers (Fi), pith (Pi), and xylem (Xy) are indicated. Magnifications: Panel A: 5X; Panel B: 10X; Panel C: 20X; Panels D and E: 40X........
References
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Pradhan Mitra, P. et al., Histochemical Staining of Arabidopsis thaliana Secondary Cell Wall Elements. J. Vis. Exp. (2014).
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved