A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Isolation and Culture of Avian Embryonic Valvular Progenitor Cells
In This Article
Summary
This article will provide a method for isolating and culturing quail or chicken HH14- valve endocardial cells and HH25 valve cushion mesenchymal cells.
Abstract
Proper formation and function of embryonic heart valves is critical for developmental progression. The early embryonic heart is a U-shaped tube of endocardium surrounded by myocardium. The myocardium secretes cardiac jelly, a hyaluronan-rich gelatinous matrix, into the atrioventricular (AV) junction and outflow tract (OFT) lumen. At stage HH14 valvulogenesis begins when a subset of endocardial cells receive signals from the myocardium, undergo endocardial to mesenchymal transformation (EMT), and invade the cardiac jelly. At stage HH25 the valvular cushions are fully mesenchymalized, and it is this mesenchyme that eventually forms the valvular and septal apparatus of the heart. Understanding the mechanisms that initiate and modulate the process of EMT and cell differentiation are important because of their connection to serious congenital heart defects. In this study we present methods to isolate pre-EMT endocardial and post-EMT mesenchymal cells, which are the two different cell phenotypes of the prevalvular cushion. Pre-EMT endocardial cells can be cultured with or without the myocardium. Post-EMT AV cushion mesenchymal cells can be cultured inside mechanically constrained or stress-free collagen gels. These 3D in vitro models mimic key valvular morphogenic events and are useful for deconstructing the mechanisms of early and late stage valvulogenesis.
Protocol
1. Preparation
- Incubate fertile quail or chicken eggs to stage 14- (about 2 days) or 25 (about 4.5 days) at 60% humidity and 37°C.
- Prepare sterile Earl's Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS)
- Add 100 mL 10X EBSS to 600 mL 18 MΩ water
- Add 2.2 g sodium bicarbonate
- Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.2
- Bring the solution up to 1000 mL
- Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 μm filter
- Prepare sterile M199 culture medium.
- Add 1 package of M199 powder to 700 mL 18 MΩ water.
- Add 2.2 g sodium bicarbonate
- Adjust the pH of the solution to 7.2.
- Add 10 mL (1%) Penicillin-Streptomycin
- Bring the solution up to 1000 mL
- Sterilize the solution by passing through a 0.2 μm filter
- Add 1 mL sterile 100X Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium-G supplement
- Add 10 mL (1%) sterile chicken serum
- Prepare three dimensional collagen gels at a collagen concentration of 1.5 mg/mL. Previous work in our lab has shown that a collagen concentration of more than 1.5 mg/mL provides a matrix that is too biomechanically stiff for the cells to move through. Collagen gel concentrations lower than 1.5 mg/mL have so few collagen fibers that the cell clump can shred the fibers locally, producing an island of cells.
- Add the following ice-cold reagents to a sterile 15 mL centrifuge tube in order:
- 3X M199: Volume = total volume necessary / 3
- Sterile 18 MΩ water: Volume = total volume necessary (M199 volume + chicken serum volume + 0.1 M NaOH volume + collagen volume)
- Sterile chicken serum: Volume = total volume necessary * 0.01
- Rat tail collagen I: Volume = (collagen gel concentration * total volume necessary) / collagen stock concentration
- Sterile 0.1 M NaOH: Volume = collagen volume * 0.2
Note: The amount of water, 0.1 M NaOH, and collagen added will vary depending on the concentration of the collagen stock solution.
- Mix the collagen solution well with a sterile pipette.
- Immediately transfer 0.3 mL of the collagen solution into 1.9 cm2 growth area wells. This is enough collagen solution to completely cover the well and to provide a gel that is approximately 3 mm thick. A gel thickness of at least 250 μm is necessary for cell invasion studies.
- Allow the collagen solution to gel for at least 1 hour at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 100% humidity.
- Add the following ice-cold reagents to a sterile 15 mL centrifuge tube in order:
2. Pre-EMT Endocardial Cell Isolation and Culture
- Embryo isolation
- Place one inch long piece of laboratory tape over the larger end of the egg. This is where the air cell is located. The tape stabilizes the fragile quail egg shell.
- Gently puncture the taped area of the egg in the air cell with the tip of sterilized curved scissors.
- Cut a hole in the taped portion of the egg that is large enough to allow the yolk to pass through. Start the hole at the puncture and cut outward in a spiral shape. Make sure to cut through the outer membrane, but avoid piercing the yolk.
- When the hole in the shell is complete, visualize the quail embryo. The embryo is normally located on the top side of the yolk.
- Begin to pour the yolk through the hole cut in the egg with one hand. Hold a #55 tweezer in the other hand. As the embryo exits the egg on the top side of the yolk, gently slide the #55 tweezers under the embryo and remove it from the yolk. Note: For chicken eggs, the embryo isolation involves cracking the chicken egg on a sharp, clean surface and breaking the egg into a 100 mm Petri dish. The embryo should be located on the top side of the yolk. Gently slide #55 tweezers under the embryo and remove it from the yolk.
- Place the embryo into a 100 mm Petri dish containing ice-cold, sterile EBSS.
- Stage the embryos according to the criteria of Hamburger and Hamilton1. Embryos at stage 14- are past stage 13, but not yet at stage 15, with 20-21 somites and a tail bud. A key characteristic of stage 14- embryos is the head angle, which is slightly greater than 90° to the body.
- Remove the hearts from quail embryos at stage 14- with #55 tweezers by cutting transversely where the AV canal and OFT make contact with the thoracic wall. Place the hearts together on one side of the Petri dish.
- Collect the isolated hearts with a sterile transfer pipette and place them into a new 100 mm Petri dish filled with sterile, ice-cold EBSS.
- Cut the OFTs and AV canals transversely from the ventricles with #55 tweezers.
- Section the remaining AV canals and/or outflow tracts (OFTs) longitudinally.
- Set a pipette to a volume of 20 uL. Use this pipette to aspirate six longitudinally-cut AV canals and OFTs.
- Expel the AV canals and OFTs onto the collagen gel. Aspirate any excess EBSS from the surface of the gel.
- Use #55 tweezers to orient the explants so they are flat and so the lumen side faces the collagen gel. Try not to puncture the collagen gel with the tweezers.
- After 2 hours at 37°C and 5% CO2, remove the myocardium from the explants with #55 tweezers. The endocardial cells should be left behind on the surface of the collagen gel. Alternatively, the myocardium can be left on the explant. With the myocardium removed, the endocardial cells with not undergo EMT without intervention. With the myocardium present a subset of endocardial cells will transform into mesenchyme, but the degree of transformation can be modulated with external factors. Note: Even if the myocardium will be left on, the explant must be allowed at least 2 hours to attach to the gel before medium is added.
- Add 0.4 mL M199 medium to each well containing explants.
- Culture the cells at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 100% humidity.
3. Post-EMT AV Cushion Mesenchymal Cell Isolation and Culture
- Crack the chicken egg on a sharp, clean surface and break the egg into a 100 mm Petri dish. The embryo should be located on the top side of the yolk. Pick up the embryo with #5 tweezers by grabbing the membranes surrounding the embryo and then place the embryo into a 100 mm Petri dish filled with ice-cold, sterile EBSS.
- Stage the embryos according to the criteria of Hamburger and Hamilton1. Features of a stage 25 embryo include distinct elbow and knee joints and slight eye pigmentation.
- Isolate the hearts from all HH25 embryos and place the hearts together on one side of the Petri dish.
- Collect the isolated hearts with a sterile transfer pipette and place them into a new 100 mm Petri dish filled with sterile, ice-cold EBSS.
- Isolate the AV region from all hearts at once. Place the AVs together on one side of the Petri dish. Gently agitate the AV region to remove all blood, which can affect cell viability.
- Collect the isolated AVs with a sterile transfer pipette and place them into a new 100 mm Petri dish filled with sterile, ice-cold EBSS.
- Sequentially isolate the cushions from the AV. Make sure there is no myocardium present on the AV cushions.
- Collect the isolated cushions with a sterile transfer pipette and place them into a sterile 15 mL centrifuge tube.
- Spin the cushions to the bottom of the centrifuge tube at 15 xg for 3 minutes.
- Use a sterile 1000 mL tip to remove as much of the EBSS supernatant as possible without disturbing the cushions.
- Add 1 mL of 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA that has been pre-warmed to 37°C. Allow the cushions to incubate in trypsin until they are completely dissolved, which is normally about 3-5 minutes.
- Add 100 μL of chicken serum to the centrifuge tube to quench the trypsin.
- Pellet the cells at 160 xg for 5 minutes. Remove the supernatant with a sterile, 1000 μL tip.
- Resuspend the cells in 2 mL of M199 medium and mix by pipetting. Take 10 μL of the cell suspension to count on hemocytometer and determine the total number of cells that have been isolated
- Determine how many collagen gels will be made based on the number of cells isolated. Cells need to be plated at a density of 2 x 105 cells/mL with a 250 μL gel volume.
- Pellet the cells at 160 xg for 5 minutes. Remove the supernatant with a sterile, 1000 μL tip.
- Using the protocol listed above, add 3X M199, water, chicken serum, collagen, and 0.1 M NaOH, in that order, to the cell pellet. Mix by gentle pipetting.
- Add 250 μL to each 1.9 cm2 growth area well.
- Allow the collagen solution to gel for at least 1 hour at 37°C, 5% CO2, and 100% humidity.
- Add 0.4 mL of culture media and incubate overnight.
- To continue culturing the gels in stress-free conditions, liberate the gels from the sides of the culture well using a sterile 200 μL pipette tip. Mechanically constrained cultures are gels that remain attached to the sides of the culture well.
4. Representative Results
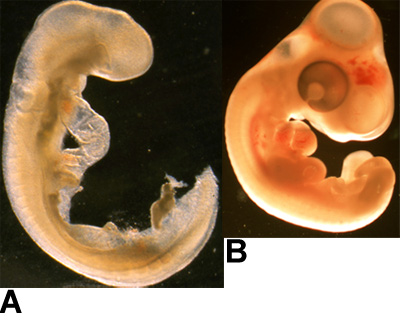
Figure 1: Examples of embryos. (A) HH14- quail embryo, and (B) HH25 chicken embryo are shown here.

Figure 2: HH14- valve endocardial explants after 2 hours of culture. (A) with the myocardium present, or (B) with the myocardium removed.
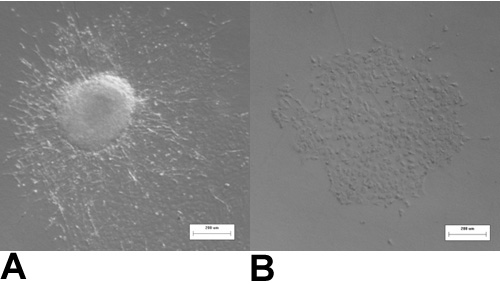
Figure 3: HH14- valve endocardial explants. (A) With the myocardium present, many of the cells undergo endocardial to mesenchymal transformation and have a spindle-shaped, mesenchymal phenotype after 48 hours of culture. (B) When the myocardium is removed all of the cells maintain a cobblestone-shaped, endocardial phenotype after 48 hours in culture.

Figure 4: HH25 valve mesenchymal cells in a collagen gel. Cells are rounded immediately after seeding.

Figure 5: HH25 mesenchymal cells in culture. (A) After 48 hours of culture in a constrained collagen gel the HH25 mesenchymal cells are beginning to spread. (B) HH25 cells in a stress-free collagen gel 7 days after seeding and 6 days after liberation have compacted the gel to approximately 50% of the original area.
Discussion
The method for isolating endocardial cells from stage HH14- hearts originally developed by Runyan and Markwald provides a controlled, in vitro environment to study the factors that initiate and modulate embryonic EMT2. HH14- endocardial explants cultured without myocardium will not undergo EMT without biomechanical or biochemical intervention. If the myocardium is left on the explant it will signal a subset of endocardial cells to undergo mesenchymal transformation, but external ...
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest declared.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by The Hartwell Foundation, the American Heart Association (Scientist Development Grant #0830384N) and the Foundation Leducq: Mitral 07CVD04.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Extra fine Bonn scissors, curved | Fine Science Tools | 14085-08 | |
| Dumont tweezers #55 | World Precision Instruments, Inc. | 14099 | |
| Dumont tweezers #5 | World Precision Instruments, Inc. | 14098 | |
| Sterile transfer pipettes | Samco Scientific, Thermo Fisher Scientific | 2041S | |
| 4-well culture plates | Nalge Nunc international | 176740 | |
| Sterile disposable filter units, PES, 0.2 μm pore size membrane | Nalge Nunc international | 566-0020 | |
| Sterile 15 mL centrifuge tubes | Corning | 430828 | |
| Sterile petri dishes, 100 mm x 15 mm | VWR international | 25384-342 | |
| Laboratory tape | VWR international | 89097-920 | |
| Rat-tail collagen I | BD Biosciences | 354236 | |
| 10X Earl’s Balanced Salt Solution | Quality Biological, Inc. | 119-064-131 | |
| M199 powder | Invitrogen | 31100-035 | |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Invitrogen | 15140-122 | |
| Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium-G supplement (100X) | Invitrogen | 41400-045 | |
| Chicken serum | Invitrogen | 16110-082 | |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | Invitrogen | 25200-056 | |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Sigma-Aldrich | S5761 | |
| Sodium hydroxide solution, 1.0 N | Sigma-Aldrich | S2770 | |
| Fertile quail eggs (Coturnix coturnix) | Lake Cumberland Game Bird Farm | ||
| Fertile chicken eggs (Gallus gallus) | Cornell University Poultry Farm |
References
- Hamburger, V., Hamilton, H. L. A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J Morphol. 88, 49-92 (1951).
- Runyan, R. B., Markwald, R. R. Invasion of mesenchyme into three-dimensional collagen gels: A regional and temporal analysis of interaction in embryonic heart tissue. Developmental Biology. 95, 108-108 (1983).
- Butcher, J. T., Norris, R. A., Hoffman, S., Mjaatvedt, C. H., Markwald, R. R. Periostin promotes atrioventricular mesenchyme matrix invasion and remodeling mediated by integrin signaling through Rho/PI 3-kinase. Developmental Biology. 302, 256-256 (2007).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved