A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
An In Vitro Technique to Study Antimicrobial Treatments on Bacterial Aggregates
Overview
This video demonstrates an in vitro technique to study the impact of antimicrobial treatment on Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pa) aggregates. Fluorescently-labeled Pa cells are grown as aggregates, mimicking the growth pattern during infection. Upon challenging the aggregates with a sublethal concentration of the antibiotic colistin, the real-time assessment of the bacteria-antibiotic interaction is performed via fluorescence microscopy.
Protocol
1. Prepare synthetic cystic fibrosis medium (SCFM2)
NOTE: Preparation of SCFM2 comprises three main stages outlined below (Figure 1).
- Sterilization of porcine mucin
- Prepare sterile mucin at a final concentration of 5 mg/mL in SCFM2. For example, for a 5 mL volume of SCFM2, weigh 25 mg of Type II mucin in a sterile Petri dish, and place it into an ultraviolet (UV) sterilizer for 4 h, gently agitating every hour. <.......
Representative Results
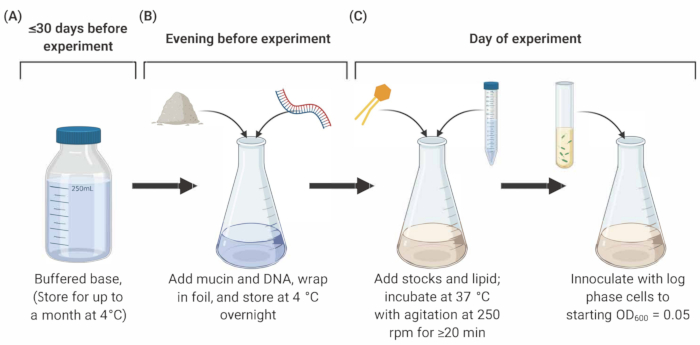
Figure 1: Preparation and inoculation of SCFM2 medium. (A) Buffered base is prepared using salts and amino acids listed in Table 1 and Table 2. Buffered base can be stored at 4 °C for up to 30 days, but must be protected from light exposure. (B) Mucin and DNA are added to an aliquot of buffered base and dissolved into solution overnight at 4 °C. (C) Lipid and additional stocks are added.......
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Gannon, A. D., et al. Tools for the Real-Time Assessment of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection Model. J. Vis. Exp. (2021).
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved