A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Extraction of Ramie Fiber in Alkali Hydrogen Peroxide System Supported by Controlled-release Alkali Source
In This Article
Summary
Presented here is a protocol for extraction of ramie fiber in alkali hydrogen peroxide system supported by controlled-release alkali source.
Abstract
This protocol demonstrates a method for ramie fiber extraction by scouring raw ramie in an alkali hydrogen peroxide system supported by a controlled-release alkali source. The fiber extracted from ramie is a type of textile material of great importance. In previous studies, ramie fiber was extracted in an alkali hydrogen peroxide system supported only by sodium hydroxide.However, due to the strong alkalinity of sodium hydroxide, the oxidation reaction speed of hydrogen peroxide was difficult to control and thus resulted in great damage to the treated fiber. In this protocol, a controlled-release alkali source, which is composed of sodium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, is used to provide an alkali condition and buffer the pH value of the alkali hydrogen peroxidesystem. The substitution rate of magnesium hydroxide can adjust the pH value of the hydrogen peroxide system and has great influence on the fiber properties. The pH value and oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) value, which represents the oxidation ability of alkali hydrogen peroxide system, were monitored using a pH meter and ORP meter, respectively. The residual hydrogen peroxide content in the alkali hydrogen peroxide system during the extraction process and the chemical oxygen demand (COD) value of wastewater after fiber extraction are tested by KMnO4 titration method. The yield of fiber is measured using a precision electronic balance, and residual gums of fiber are tested by a chemical analysis method. The polymerization degree (PD value) of fiber is tested by an intrinsic viscosity method using the Ubbelohde viscometer. The tensile property of fiber, including tenacity, elongation, and rupture, is measured using a fiber strength instrument. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction are used to characterize the functional groups and crystal property of fiber. This protocol proves that the controlled-release alkali source can improve the properties of the fiber extracted in an alkali hydrogen peroxide system.
Introduction
Ramie, commonly known as 'China grass' is a perennial herb whose fiber can be used as an excellent material for the textile industry1,2. It is one of the main economic crops native to China; the production of ramie in China has accounted for more than 90% of the total yield in the world1,2. Ramie fiber is one of the strongest and longest plant fibers, lustrous with an almost silky appearance3,4. The long length of ramie fiber make it suitable for single fiber spinning, which is seldom seen in bast fiber. The textile made from ramie fiber possesses many excellent properties, such as coolness, antibacterial, excellent thermal conductivity, ventilation, etc.3,4
Cellulose is the main component of ramie fibers, and the other components in ramie, such as pectin, lignin, water soluble materials, are defined as gums5,6. Ramie fiber can be extracted by dissolving the gums in solution containing chemical reagents, in a process defined as degumming5,6. Mainly two approaches of ramie fiber extraction exist: chemical degumming and bio-degumming. The energy consumption, time consumption, and COD value of degumming wastewater in traditional chemical degumming is rather high, as cellulose fiber is extracted by scouring raw ramie in concentrated NaOH under high pressure for 6 to 8 h7,8. Alternatively, bio-degumming is an eco-friendly option for ramie fiber extraction. Nevertheless, the harsh reaction condition and sophisticated equipment inhibit its further industrial application9,10. Therefore, oxidation degumming with alkali hydrogen peroxide presents a valuable and alternative application to focus on, for it requires shorter degumming time and lower degumming temperature11,12. However, due to the strong oxidation ability of the peroxides, substantial cellulose degradation may occur during the degumming process, which can cause great damage to fiber properties13,14. This is the biggest drawback of alkali peroxide oxidation degumming of ramie.
In previous studies, ramie fiber was extracted in an alkali hydrogen peroxide system supported only by sodium hydroxide15. However, due to the strong alkalinity of sodium hydroxide, the oxidation reaction speed of hydrogen peroxide was difficult to control and thus resulted in great damage to the treated fiber7. To improve the properties of ramie fiber, a controlled-release alkali source, which is composed of sodium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, is used in this study to offer an alkali condition and buffer the pH value of alkali hydrogen peroxide system16,17.
The rationale behind this technology can be described as follows. Magnesium hydroxide is slightly soluble in distilled water, and it can dissolve gradually into the degumming solution with the consumption of OH- and keep the pH value and thus oxidation ability of degumming solution in an appropriate range18. The substitution rate (SR) of magnesium hydroxide is defined as the mole proportion of NaOH replaced by magnesium hydroxide under the total alkali dosage of 10%, and the substitution rate can be calculated by the following equation. Moreover, Mg2+ can prevent cellulose degradation caused by over oxidation19,20.
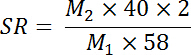
Here, M2 (g) is the weight of Mg(OH)2, M1 (g) is the weight of NaOH, 40 is the molecular weight of NaOH, 58 is the molecular weight of Mg(OH)2, 2 is the number of OHs in Mg(OH)2, and SR is the substitution rate.
The technology of this protocol can be extended to the extracting, bleaching, and modifying of plant materials in an alkali hydrogen peroxide system. However, it must be noted that the selection of pH value and reaction temperature of the alkali hydrogen peroxide system is key for this technology21. The pH value of the alkali hydrogen peroxide system can be adjusted by changing the substitution rate17. The pH value and thus oxidation ability of the alkali hydrogen peroxide system decrease with the increasing of substitution rate. When the reaction temperature is set at 85 °C, the free radical reaction plays the main role in the system and the strong oxidation of the system is suitable for dissolving materials; when the reaction temperature is set at 125 °C, the free radical reaction is inhibited and a large amount of HOO exists in the system, which makes the system suitable for bleaching19.
Protocol
1. Oxidation Degumming of Ramie
- Preparing the oxidation degumming solution
- Dissolve 2 g H2O2, 1 g alkali (a mixture of Mg(OH)2 and NaOH), 0.4 g Na5P3O10, 0.1 g anthraquinone, and 0.2 g HEDP in 100 mL distilled water to make the degumming solution.
- Oxidation degumming of ramie
- Immerse 10 g raw ramie in the degumming solution and scour it under 85 °C for 60 min.
- Raise the temperature to 125 °C (with pressure of 0.6 kg) and scour for another 60 min.
NOTE: See the Discussion for explanation on raising the temperature.
- Reducing the ramie fiber
- Dissolve 0.4 g NaHSO3 in 100 mL distilled water to prepare the reducing solution. Then, treat the degummed fiber in the reducing solution at 90 °C for 60 min.
NOTE: The carboxyl groups and aldehyde groups in cellulose generated in the oxidation reaction cause the reduction of hydrogen bonds and thus damage to the fiber property. Reducing can improve the property of the fiber by converting the carboxyl groups and aldehyde groups back to hydroxyl groups.
- Dissolve 0.4 g NaHSO3 in 100 mL distilled water to prepare the reducing solution. Then, treat the degummed fiber in the reducing solution at 90 °C for 60 min.
- Follow-up treatment
- Wash the degummed ramie fiber thoroughly with deionized water.
- Immerse the fiber in degumming oil at 90 °C for 15 min and then dry the fiber in an oven (125 °C) for 4 h.
2. Testing of the Degumming Solution Property
- Solubility test of Mg(OH)2
- Dissolve 2 g Mg(OH)2 in 100 mL distilled water.
- Separately, dissolve 2 g Mg(OH)2 in 100 mL solution with completely soluble degumming additives, including 0.4 g Na5P3O10 and 0.2 g HEDP.
- Raise the temperature of the solutions described in steps 2.2.1 and 2.2.2 to 85 °C.
- Extract the undissolved Mg(OH)2 with sintered discs.
- Calculate the solubility of Mg(OH)2 by the following formula:
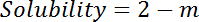
NOTE: Here m (g) is the weight of the undissolved Mg(OH)2.
- Effect of the Mg(OH)2 substitution rate on pH value, ORP value, and residual H2O2 content of the degumming solution
NOTE: ORP12,19 is an important water chemistry parameter and it provides a measurement tool for the oxidizing or reducing capacity of the ambient water. Solutions with stronger oxidation property have a higher ORP value. The Mg(OH)2 substitution rate refers to the mole proportion of NaOH replaced by Mg(OH)2 under the total alkali dosage of 10% (on weight of fabric).- Prepare the degumming solutions with Mg(OH)2 substitution rate of 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% according to step 1.1, respectively.
- Immerse the raw ramie in the degumming solutions described in step 2.2.1.
- Start the degumming process according to step 1.2.
- Wash the combined ORP electrode with distilled water and dry it in the air. Then immerse the combined ORP electrode meter in the degumming solutions to read the ORP value every 10 min. Immerse the pH electrode meter in the degumming solutions to read the pH value every 10 min.
- Test the H2O2 content of the degumming solutions every 10 min by the KMnO4 titration method according to Chinese standard GB 22216-20087.
3. Testing the Ramie Fiber Property
- Yield of degumming
- Calculate the yield of degumming using the following equation:
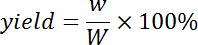
NOTE: Here w (g) is dry weight of fiber after degumming; W (g) is dry weight of ramie before degumming.
- Calculate the yield of degumming using the following equation:
- Residual gums of the fiber
NOTE: Residual gums of fiber were tested according to Chinese standard 5889 - 86.- Measure the dry weight of the fiber (about 5 g) in a weighing bottle and immerse it in a flask (with reflux condensing tube) containing 150 mL NaOH solution (20 g/L).
- Raise the temperature to 100 °C and keep at this temperature for 1 h.
- Refresh the NaOH solution.
- Raise the temperature to 100 °C and maintain for 2 h.
- Wash the fiber in a sample sieve.
- Measure the dry weight of the fiber in weighing bottle.
- Calculate the residual gums of fiber using the following equation:
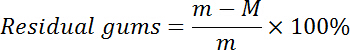
NOTE: Here m (g) is the dry weight of fiber; M (g) is the dry weight of ramie after NaOH scouring.
- PD test
NOTE: Test the PD value of ramie fiber according to Chinese standard GB 5888-8615.- Degrease the ramie fiber by submerging in 2:1 (v/v) benzene and ethyl alcohol mixture.
- Evaporate the solvent in air at room temperature.
- Cut the samples into short pieces (1-2 mm, about ~20-23 mg for each sample) using scissors.
- Keep the samples in a controlled-humidity atmosphere (20 ± 2 °C, relative humidity = 65 ± 2%) in a weighing container until it reaches equilibrium water content before removing the materials required for test purposes.
- Immerse a copper wire (0.5 mm diameter) in concentrated nitric acid, followed by 98% anhydrous ethylenediamine. Then, wash the copper granule thoroughly with distilled water.
- Put the fiber sample and copper granule in a plastic bottle (with top).
- Add 10 mL distilled water and 10 mL 1 mol/L cupriethylenediamine solution into the plastic bottle, and stir using a magnetic stir bar to prepare 0.2 g/100 mL (approximately) ramie fiber cupriethylenediamine solution.
- Transfer 6.5 mL ramie fiber cupriethylenediamine solution to a Ubbelohde viscometer to measure its intrinsic viscosity. Calculate the relative viscosity by the following equation:
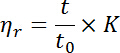
NOTE: Here ηr is the relative viscosity, t (s) is the average time of the ramie fiber cupriethylenediamine solution flowing through the Ubbelohde viscometer, and t0 (s) is the average time of the 0.5 mol/L cupriethylenediamine solution flowing through the Ubbelohde viscometer. - Calculate the PD value of the ramie fiber by the following equation:
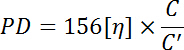
NOTE: Here [η]' is the intrinsic viscosity, the [η]×C value can be obtained from a table in Chinese standard GB 5888-86, and C' is the concentration of ramie fiber cupriethylenediamine solution.
- Linear density of the fiber
- Calculate linear density of fiber using the following equation:
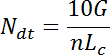
NOTE: Here Lc is the cutting length (40 mm), n is the numbers of fibers, and G (g) is weight of the fiber. Linear density of the fiber refers to the weight of a 1,000 m long fiber under official regain of ramie (12%).
- Calculate linear density of fiber using the following equation:
- Mechanical property test
- Equilibrate the fiber samples in standard atmospheric condition (T = 20 ± 2 °C, RH = 65% ± 2%) for 24 h.
- Test the tenacity, breaking elongation, and work of rupture of the fiber using the fiber strength instrument under the following setting of 20 °C, RH 65%, and pre-tension of 0.3 cN/dtex. Set the clamping distance at 20 mm and the descending speed of the bottom clamp at 20 mm/min7,15.
- COD value of degumming wastewater
- Test the COD of degumming wastewater according to Chinese standard GB/T 15456-2008 'Industrial circulating cooling water-Determination of the COD-Potassium permanganate method'7,15.
- XRD test
- Obtain crystallinity of the fiber using X-ray diffraction. Record XRD patterns 2θ = 5-60 ° with a diffractometer equipped with a graphite monochromator and Cu Kα radiation at λ = 0.154 nm (40 kV, 200 mA).
- FTIR analysis
- Obtain the FTIR pattern of fiber using spectrometer. Set the scan times at 30, the range at 4,000-400 cm-1, and the resolution at 8 cm-1. Determine the chemical functional groups in treated fiber using FT-IR analysis.
Results
The solubility of Mg(OH)2 in distilled water and degumming solution was studied (Figure 1). The effect of Mg(OH)2 substitution rate on pH value and ORP value (Figure 2) of the degumming solution was tested. The degumming yield and residual gums of fiber degummed under various Mg(OH)2 substitution rate were calculated (Figure 3). DP value, crystallinity, tensile proper...
Discussion
The setting of Mg(OH)2 substitution rate and reaction temperature was the key point of this protocol. Mg(OH)2 substitution rate can influence the pH value and thus oxidation ability of degumming solution. The best Mg(OH)2 substitution rate for ramie degumming was 20%, because cellulose cannot receive enough protection under a substitution rate below 20%, and an excessive amount of residual gums (low DP value and crystallinity) would be retained in fiber under a substitution rate above 20%...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System for Bast and Leaf Fiber Crops (grant number CARS-19), The China Academy of Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project (grant number ASTIP-IBFC07), The innovation fund for graduate students in Donghua University (grant number 16D310107), The 'Xiaoping science and technology innovation team' (industrialization integrated R & D group of bast fiber biological degumming), China Scholarship Council.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Hydrogen peroxide, 30% | Fisher Scientific | H325-100 | Chemical for degumming |
| Magnesium hydroxide, 99% | Fisher Scientific | AA1236722 | Chemical for degumming |
| Sodium hydroxide | Fisher Scientific | S318-1 | Chemical for degumming |
| Sodium bisulfite | Fisher Scientific | S654-500 | Chemical for degumming |
| Sodium tripolyphosphate | Fisher Scientific | AC218675000 | Chemical for degumming |
| Anthraquinone, >98% | Fisher Scientific | AC104930500 | Chemical for degumming |
| 1-Hydroxy Ethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid | Fisher Scientific | 50-901-10243 | Chemical for degumming |
| Degumming oil | Minglong auxiliaries limited liability company, Yiyang, Hunan,China | —— | Chemical for degumming |
| Ethyl alcohol | Fisher Scientific | A962-4 | Chemical for testing |
| Benzene | Fisher Scientific | AA43817AE | Chemical for testing |
| Copper wire,0.5mm (0.02in) dia | Fisher Scientific | AA10783H4 | Chemical for testing |
| Cupriethylenediamine solution 1mol/L | Fisher Scientific | 24991 | Chemical for testing, caution toxic |
| Nitric acid (65% ~68% ) | Fisher Scientific | A200-612GAL | Chemical for testing, caution |
| Ethylenediamine | Fisher Scientific | AC118420100 | Chemical for testing |
| Potassium permanganate | Fisher Scientific | P279-500 | Chemical for testing |
| Sulphuric acid | Fisher Scientific | A300C-212 | Chemical for testing |
| Silver sulfate | Fisher Scientific | S190-25 | Chemical for testing |
| Raw ramie | Guangyuan limited liability company, Changde, Hunan,China | —— | Raw materials |
| Electric-heated thermostatic water bath | Senxin Experiment equipment limited liability company,Shanghai,China | DK-S28 | Equipments for degumming |
| High temperature lbaorator dyeing machine | Shanghai Longda chemcials Crop. | RY-1261 | Equipments for degumming |
| Thermometer | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 100 °C | Equipments for degumming |
| Vacuum suction machine | Yukang KNET ,Shanghai,China | SHB-IIIA | Equipments for testing Mg(OH)2 solublity |
| Suction flask | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 1000mL | Equipments for testing Mg(OH)2 solublity |
| Sand-core funnels | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 35mL | Equipments for testing Mg(OH)2 solublity |
| Oxidation reduction potential meter | Dapu instrument, Shanghai, China | MODEL 421 | Equipments for testing ORP value |
| pH meter | Hanna instruments,Beijing,China | HI 98129 | Equipments for testing pH value |
| Acid burette | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 50mL | Equipments for testing H2O2 content |
| Flask | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 250 mL/500 mL | Equipments for testing H2O2 content; residual gums content |
| Electric furnace | Jiangyi Experiment instruments limited liability company,Shanghai,China | 800-2000W | Equipments for testing residual gums content |
| Reflux condensing tube | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 250mL | Equipments for testing residual gums content; COD value |
| Fiber cutter (40mm) | Changzhou No.2 Textile Machine Co.,Ltd | Y171A | Equipments for testing fiber density |
| Ostwald viscometer | Taizhou, jiaojiang, glass instruments company | 0.6mm | Equipments for testing fiber PD value |
| Spherical fat extractor | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 250mL | Equipments for testing fiber PD value |
| Soxhlet extractor | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 250mL | Equipments for testing fiber PD value |
| Torsion balance | Liangping instrucments Co.,Ltd,Shanghai, China | JN-B | Equipments for testing fiber density |
| Fiber strength instrument | Xinxian instruments, shanghai,China | XQ-2 | Equipments for testing fiber tensile property |
| Tension clamp | Depu textile technology Co.,Ltd, Changzhou, jiangsu, China | 0.3cN/dtex | Equipments for testing fiber tensile property |
| COD thermostatic heater | Qiangdao Xuyu environment protection technology Lit company | DL-801A | Equipments for testing COD value |
| FTIR | Thermo Fisher, America | Nicolet | FTIR analysis |
| XRD | Rigaku, Japan | D/max-2550 PC | XRD analysis |
| Electronic balance | Shanghai jingtian Electronic instrument Co.,Ltd | FA2004A | Generral equipments |
| Drying oven | Tonglixinda instruments, Tianjin,China | 101-2AS | Generral equipments |
| Weighing bottle | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 50x30 | Generral equipments |
| Beaker | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 500mL | Generral equipments |
| Sample sieve | Xiaojin hardware instruments Co.,Ltd, Shangyu, Zhejiang | 120 mesh | Generral equipments |
| Glass rod | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | —— | Generral equipments |
| Cylinder | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 250mL, 50mL | Generral equipments |
| Pipette | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | 5mL, 10mL | Generral equipments |
| Rubber suction bulb | Sichuan Shubo (group)Co.,Ltd | —— | Generral equipments |
| Orign | OriginLab | 8.0 | Software for figure drawing |
References
- Yuan, J. G., Yu, Y. Y., Wang, Q., Fan, X. R., Chen, S. Y., Wang, P. Modification of ramie with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid. Fiber Polym. 14, 1254-1260 (2013).
- Kipriotis, E., Heping, X., Vafeiadakis, T. Ramie and kenaf as feed crops. Ind Crop Prod. 68, 126-130 (2015).
- Rebenfeld, L. Fiber: the old and the new. J Text Inst. 92, 1-9 (2001).
- Ramamoorthy, S. K., Skrifvars, M., Persson, A. A review of natural fiber used in biocomposites: plant, animal and regenerated cellulose fiber. Polym Rev. 55, 107-162 (2015).
- Yu, H. Q., Yu, C. W. Influence of various retting methods on properties of kenaf fiber. J Text Inst. 101 (5), 452-456 (2010).
- Fan, X. S., Liu, Z. W., Liu, Z. T., Lu, J. A novel chemical degumming process for ramie bast fiber. Text Res J. 80, 2046-2051 (2010).
- Liu, G. L. . Research on the application of sodium percarbonate the degumming of ramie. , (2013).
- Meng, C. R., Yu, C. W. Study on oxidation degumming of ramie fiber. Adv Mater Res. , 881-883 (2014).
- Liu, Z. C., Duan, S. W., Sun, Q. X., Zhang, Y. X. A rapid process of ramie biodegumming by Pectobacterium sp. CXJZU-120. Text Res J. 82 (15), 1553-1559 (2012).
- Guo, F. F., Zou, M. Y., Li, X. Z., Zhao, J., Qu, Y. B. An effective degumming enzyme from Bacillus sp. Y1 and synergistic action of hydrogen peroxide and protease on enzymatic degumming of ramie fiber. BioMed Res Int. , (2013).
- Li, Z. L., Yu, C. W. Effect of peroxide and softness modification on properties of ramie fiber. Fiber Polym. 15, 2105-2111 (2014).
- Li, Z. L., Meng, C. R., Yu, C. W. Analysis of oxidized cellulose introduced into ramie fiber by oxidation degumming. Text Res J. 85 (20), 2125-2135 (2015).
- Xueren, Q. . Green bleaching technologies of pulp. , (2008).
- Erkselius, S., Karlssom, O. J. Free radical degradation of hydroxyethy cellulose. Carbohydr Polym. 62, 344-356 (2005).
- Meng, C. R., Liu, F. M., Li, Z. L., Yu, C. W. The cellulose protection agent used in the oxidation degumming of ramie. Textile Research Journal. 86 (10), 1109-1118 (2016).
- Long, X., Xu, C., Du, J., Fu, S. The TAED/H2O2/NaHCO3 system as an approach to low-temperature and near-neutral pH bleaching of cotton. Carbohydr Polym. 95, 107-113 (2013).
- Yun, N. . Studies on magnesium-based hydrogen peroxide bleaching and mechanisms of deinked pulp. , (2014).
- Zhang, W., Kong, F. Replacement of sodium peroxide bleaching by magnesium-based peroxide bleaching for pulp. Paper Sci Technol. 29, 25-28 (2010).
- Meng, C. R., Li, Z. L., Wang, C. Y., Yu, C. W. Alkali Source Used in the Oxidation Degumming of Ramie. Text Res J. 87 (10), 1155-1164 (2017).
- Gorski, D., Engstrand, P., Hill, J., Axelsson, P., Johansson, L. Mg(OH)2-based hydrogen peroxide refiner bleaching: influence of extractives content in dilution water on pulp properties and energy efficiency. Appita Journal. 63 (3), 218-225 (2010).
- Leduc, C., Martel, J., Danea, C. Efficiency and effluent characteristic from Mg(OH)2-based hydrogen peroxide bleaching of high-yield pulps and deinked pulp. Cellulose Chemistry & Technology. 44 (7-8), 271-276 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved