Quantifying Intermembrane Distances with Serial Image Dilations
In This Article
Summary
The purpose of this algorithm is to continuously measure the distance between two 2-dimensional edges using serial image dilations and pathfinding. This algorithm can be applied to a variety of fields such as cardiac structural biology, vascular biology, and civil engineering.
Abstract
A recently-described extracellular nanodomain, termed the perinexus, has been implicated in ephaptic coupling, which is an alternative mechanism for electrical conduction between cardiomyocytes. The current method for quantifying this space by manual segmentation is slow and has low spatial resolution.We developed an algorithm that uses serial image dilations of a binary outline to count the number of pixels between two opposing 2 dimensional edges.This algorithm requires fewer man hours and has a higher spatial resolution than the manual method while preserving the reproducibility of the manual process.In fact, experienced and novice investigators were able to recapitulate the results of a previous study with this new algorithm.The algorithm is limited by the human input needed to manually outline the perinexus and computational power mainly encumbered by a pre-existing pathfinding algorithm.However, the algorithm's high-throughput capabilities, high spatial resolution and reproducibility make it a versatile and robust measurement tool for use across a variety of applications requiring the measurement of the distance between any 2-dimensional (2D) edges.
Introduction
The following algorithm was developed to measure the intermembrane distance between two structurally coupled cardiomyocytes at the point they separate from each other at the edge of a gap junction plaque in a nanodomain called the perinexus1, which has been implicated in ephaptic coupling2,3,4,5. In the process of analyzing hundreds of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of perinexi using a manual segmentation method in a previous study6, the need was identified for a higher-throughput method that sampled perinexal width in higher spatial resolution while preserving the accuracy of the previous manual segmentation process During manual segmentation, lines are drawn at 15 nm intervals, approximately orthogonal to the centerline, in order to measure perinexal width.The new algorithm takes a one pixel thick binary outline of two parallel lines and uses serial image dilations to count the number of pixels between the two membranes.While image dilations have commonly been used in a myriad of image processing applications, including contour or edge detection7,8, this algorithm uses dilations as a counting mechanism. The centerline is then isolated using a pathfinding algorithm9 and perinexal width is then measured at a resolution along the length of perinexus equal to the resolution of the image. The difference in resolution in this case is 1 measurement per 15 nm for manual segmentation and 1 measurement per 0.34 nm with the new algorithm, a 44-fold increase in spatial sampling frequency.Furthermore, this increased sampling frequency is accomplished in approximately 1/5th the time needed for manual segmentation.
This algorithm will be used in its current form to measure perinexal width at the conventional 0-150 nm from the edge of a gap junction plaque5 (GJ) as well as within a specified region of interest, where the perinexus plateaus between 30 and 105 nm2,3,10. The increased sampling frequency reduces the variability in individual perinexus measurements compared to manual segmentation and significantly shortens analysis time, allowing for efficient processing of large data sets.However, this program is not limited to nanoscale TEM images of cardiac intercalated disks.The same approach could be used to quantify vascular diameter, ventricular ejection fraction, or even non-biological phenomena such as river erosion or flooding. This algorithm is appropriate for quantifying the distance between any two quasi-parallel edges.
Protocol
NOTE: Software required are ImageJ (or similar image-modifying software) and Matlab R2015. The user may encounter compatibility issues with other versions of Matlab.
1. Pre-Processing Images
- For any grayscale image, ensure the maximum intensity value of any given pixel is <255. This is typically done by subtracting a value of 1 from the image in the custom Matlab program "ImageSub.m", included in supplemental file S1.
2. Outlining the Perinexus
- Outline the perinexus in ImageJ or other image-processing software.
- Ensure that the outline is one pixel thick and is set to the highest intensity value in an image (255 in a grayscale image from 0 to 255).
- Identify the GJ by its pentalaminar structure11,12, and define the beginning of the perinexus as the point at which the two opposing cell membrane bilayers diverge, as shown in Figure 1A. Begin ~200 nm from the edge of the GJ, tracing along the inner membrane of the first cell and back along the inner membrane of the second cell. In ImageJ, release the pen to automatically close the outline. This artificial closing will be cropped out later.
NOTE: It is crucial to outline the perinexus with great care at as high a magnification as possible, as even small mis-applications of the outline can result in several nanometers of error in the final measurement.
3. Setting up Algorithm and Selecting Perinexus of Interest
NOTE: The pathfinding algorithm requires the AutoGraph, Edge, Graph, Node , and Pathfinding functions9 to be in the same directory as the MembraneSepDist m-file. All files can be found in supplemental file S1.
- Select save locations for data and figures. These are currently hard-coded into the m-file.
NOTE: The first line of the program is a function to clear all variables, close all windows and clear the command window. Save any desired variables or figures before running the m-file.
NOTE: Software screenshots are included in supplemental file S2 for all hard-coded values. - Run the program "MembraneSepDist.m".
- Set Parameters.
NOTE: A GUI will pop up with default parameters for the gradient threshold, scale, region of interest, and manual start. The default values can be changed in the m-file, or they can be changed for each individual image.- Set spatial derivative gradient threshold.
NOTE: Higher values result in more points selected in centerline isolation. Values that are too high or too low (outside of a range of approximately 3.0-7.9) may result in computational inefficiency or an imprecise selection of centerline points yielding imprecise centerline isolation (See Figure 2A-C). - Set scale in pixels/scale units.
- Set the spatial lower and upper limits for the region of interest.
NOTE: By our laboratory's convention, the defined region of interest is between 30 and 105 nm from the edge of the GJ2,3,10. - Set automatic/manual start. In the majority of cases, the algorithm accurately detects the starting point where the gap junction ends and perinexus begins. However, in some cases of irregularly-shaped perinexi, the user must identify the start point manually. Set this value to 0 for automatic, 1 for manual.
- Set spatial derivative gradient threshold.
- Select desired image.
NOTE: The file select folder can be changed in the m-file. - Crop the image to select the perinexus of interest.
- When the image comes up, the cursor will automatically change to a crosshair. Crop the image by dragging a box around the perinexus of interest (See Figure 3). The crop box can be adjusted by using the squares on the corners and sides to make it larger or smaller.
- When cropping, ensure the "open" end of the perinexus (furthest from the GJ, see Figure 3) is cropped so that the two membrane outlines reach the edge of the cropped image.
NOTE: It is recommended to make the image full-screen to more easily see the perinexus of interest and crop appropriately.
- Select the final crop by double-clicking with the curser in between the opposing edges to be measured.
NOTE: It is critical that the double-click be performed inside the perinexus. If the program fails to identify a centerline, restart the program and make sure the click occurs within the perinexus. - Observe the final centerline after all dilations and erosions pop up for a final user evaluation of the program's efficacy.
NOTE: A dialog box will appear on the screen while the program is running to inform the user that Matlab will be unable to process any additional commands until the program has finished. How long this process takes depends on array (image) size and computer processing power. - If manual start point is enabled, observe the image of the centerline pop up over the original anatomical image, along with a cross-hair cursor (see Figure 2E). Select a point outside of the perinexus near the desired start point.
NOTE: The program will find the centerline point closest to the selected pixel and use that as the start point. - Record data.
NOTE: Once the program has finished, the program will return a mapped centerline, plot of perinexal width as a function of distance from the edge of the GJ. Additionally, the program will return the average perinexal width up to 150 nm from the edge of the GJ as well as the average from within the defined region of interest at the Matlab command line. Wp values and distances from the GJ are stored in the variable "WpList" or the user can manually record them separately.
4. Algorithm Troubleshooting
- If the centerline is not properly identified (Figure 2A), open the figure "Gmag" and use the Index to identify an appropriate gradient threshold (Figure 2C).
- If the start point is not properly identified, set the start point manually (See Protocol 3.8).
Results
Statistical Methods: Comparisons were made between experimental groups using Student's t-tests. A p-value < 0.05 is considered significant and all values are represented as mean ± standard deviation.
Manual Segmentation. The quantification of the GJ-adjacent perinexus nanodomain width (Wp) is typically accomplished by manual segmentation. This manual segmentation process is demonstrated in Figure 1A and was described previously6. The observer identifies the edge of the GJ (Figure 1, red dot), measures 5nm along the center of the perinexus, and measures the distance between the membranes at that point. The process is then repeated at 10, 15, 30, and every 15 nm up to 150 nm. This technique, while effective, has limitations of time and spatial under-sampling along the length of the perinexus.
Mean Wp measurements from previous studies can vary from approximately 10 to 20 nm2,3,10, and 3 nm appears to be the mean difference needed to detect statistical significance, which is well above the spatial Nyquist frequency of 0.7 nm per measurement based an interpixel resolution of 0.34 nm. Therefore, while manual segmentation is time consuming, the method is sufficient to measure differences in Wp associated with an intervention or disease state.
Serial Image Dilations. In order to measure the perinexus in a faster, reproducible manner with appropriate spatial resolution, we developed a program based on serial image dilations to count the pixels between two manually-traced membranes, which can be seen in Figure 1B.
The serial dilation process is illustrated in Figure 4. As the binary image is dilated (Figure 4A-4D), that dilation is then inverted and added to a working image - the non-binary form of the original outline (Figure 4E-4H). The process is repeated until the outline is entirely filled in (Figure 4D). At this point, the final working image (Figure 4H) is a count of the number of times a particular pixel has remained un-dilated. As such, the values near the outline of the cell membranes are very low, while the values at the center are highest. By counting the number of dilations to fill the area at each point, the distance between the membrane edges can be calculated. The next challenge is to identify and isolate the centerline in order to quantify perinexal width as a function of distance from the GJ, which is done by first applying a spatial derivative to the final working image (Figure 2-last image, and Figure 5A). A second example of a more irregularly-shaped perinexus can be found in supplemental file S3.
Centerline Identification. The gradient of the final working image can be quantified by a spatial derivative, as dilation count values from edge to edge change from high to low to high again (Figure 5A left to right). Considering only the magnitude of the spatial derivative (Figure 5B), the outline and centerline, highlighted with white arrows, are immediately identifiable as areas of discontinuity. At these locations, the gradient direction changes from increasing to decreasing or vice versa. Applying a threshold (Figure 5C) produces a binary image of the centerline and outline, and subtracting the original outline yields the isolated centerline (Figure 5D). While this method of isolating the centerline is computationally efficient, the threshold applied to the spatial derivative creates gaps in the resulting centerline. These gaps (Figure 5D, insert) must be filled to provide an accurate measurement of the distance from the GJ and to ensure the perinexus is measured in its entirety. First, the centerline is dilated to fill in any gaps (Figure 5E), followed by an erosion (Figure 5F) and a "bwmorph" function (operation = 'skel', n = inf) to eliminate as many points as possible while leaving a continuous centerline, thereby increasing the computational efficiency of a subsequent pathfinding algorithm developed by Wasit Limprasert and available on MATLAB Central9. This dilation-erosion function produces the completed centerline, which is combined with the final working image (Figure 5G). However, this centerline is often more than one pixel thick and therefore is not a precise isolation of the centerline.
The Wasit Limprasert pathfinding algorithm is used to determine the perinexus centerline. The pathfinding algorithm is able to track the highest values - in this case the values closest to the center which remained un-dilated through the most iterations along the centerline (Figure 5G, insert). The result is an automatic trace of the centerline, as shown in Figure 6. By isolating the centerline, perinexal width can be presented as a function of distance from the end of the GJ, as shown in Figure 6B (top), or as the average width of a specified region of interest.
Kernel Analysis. It is important to note that digitized images are based on square arrays and dilation kernels are likewise based on square matrices. This means that dilation distance across a diagonal is greater than orthogonal. Therefore, we next sought to determine whether the kernel affected the results of the algorithm. In order to quantify kernel-specific variability, five different kernel shapes were analyzed: "Plus" (the shape used in the above analyses), "X", "Box", and "Line", as described in Figure 7A. The kernel is applied at each non-zero point of a binary image. The star in each kernel of Figure 7A represents the center, where white is a value of 1, and black is a value of 0 for the dilation kernel.
Each kernel's influence on the mean Wp measurement of a single approximately horizontal perinexal image (Figure 7B, top), quantified by an experienced user, was determined by rotating the image with Matlab's "imrotate" command and computing Wp in steps of 10°. The Wp measurement values (Figure 7B, bottom) fluctuate with image orientation in a rectified sinusoidal fashion with a Plus shaped kernel. The lowest values occur when a relatively straight perinexus is oriented vertically or horizontally. Neither the X, Box, nor Line kernels provided any advantage over the plus-shaped kernel. The X and Box kernels produced identical results, but the values of mean Wp were out of phase with the Plus kernel by 45°. The Line kernel failed to fully dilate the image at certain angles as can be seen by the absence of data in the green trace for images rotated less than 30 or more than 145°. Thus, the orthogonal Plus dilation kernel overestimated membrane separation when dilating a perinexus with an axis oriented diagonally for example at approximately 45°, and the X and Box kernels underestimated mean Wp when the long axis of the perinexus was also at 45°. Based on this analysis, we developed a correction factor applied to the values generated from dilating with the plus-shaped kernel. To account for the overestimation of membrane separation associated with image orientation, this correction factor multiplied by the measured width value depending on the orientation of the image (Equation 1).
If θ <45°
Wp corrected = cosd(θ) * Wp measured
If θ ≥45°
Wp corrected = cosd(θ) * Wp measured (Equation 1)
In this equation, Wp measured is the original Wp value generated by the above algorithm and θ is the calculated angle from horizontal, in degrees. θ is calculated by taking the inverse tangent of the total change in the horizontal direction divided by the total change in the vertical direction of the perinexal centerline. The above correction approximates the average angle, relative to horizontal, of the perinexus (Figure 8A, left-top) and results in a measurement as if obtained from a horizontal perinexus (Figure 8A, left-bottom). The rationale behind this equation comes from the fact that the plus-shaped kernel (Figure 7A) is essentially two line-shaped kernels arranged orthogonally to each other. As such, below 45° (closer to horizontal), the dilations occur vertically and therefore multiplying by the cosine of the angle gives the correct measurement. Conversely, for angles above 45° (closer to vertical), dilations occur horizontally and the sine is used to determine the correct measurement. At precisely 45°, the sine and cosine are equal. Supplemental file S4 provides a depiction of this concept. Note that this correction is based on the average angle and caution should be used when analyzing substantially non-linear shapes. This process was repeated on 20 randomly-selected perinexi and the corrected measurements correlated strongly with measurements obtained by manually rotating and re-analyzing the images (Figure 8A, right). To confirm the accurate correction for image orientation, two sets of phantom edges were generated (Figure 8B, left) and rotated 180°. With the trigonometric correction, the algorithm accurately returned the correct value at each orientation, regardless of spatial resolution or image size (Figure 8B, right).
Analytical Application and Reproducibility with Orientation Correction. Recalling that previous studies using manual segmentation report statistically significant mean Wp differences greater than or equal to 3 nm, it was important to determine whether to the algorithm could be used to recapitulate previous findings using a complete dataset. Using the new algorithm, two observers - one experienced and one unexperienced with perinexal analysis (Obs. 1 and Obs. 2, respectively) - analyzed the same images from a previous study6 that included 12 patients who were diagnosed with atrial fibrillation (AF) prior to tissue collection and 29 patients that did not have pre-existing AF (No-AF). The experienced user found that Wp was significantly wider in patients with AF than without AF (21.9±2.5 and 18.4±2.0 nm, respectively, Figure 9A). These values with the correction factor applied are similar to those reported previously (24.4±2.2 nm and 20.7±2.4 nm, respectively)6. Importantly, the inexperienced user found the same significant difference (22.1±2.8 nm and 20.1±2.6 nm, respectively) between disease states with the automated program. Additionally, the standard deviation of the Wp values did not change with the correction factor, indicating the standard deviation of 2-3 nm is not an artifact of the algorithm but of the structure itself and tissue processing. These results demonstrate that the proposed automated method is capable of recapitulating the results of previous studies.
Importantly, the perinexus is a recently-defined structure and no consensus has been reached on the range of absolute values of membrane separation adjacent to the GJ2,3. Since outer-membrane-to-outer-membrane GJ width has been previously estimated at 20 nm13, we sought to determine the algorithm's efficacy by also measuring GJ width. Both observers found no significant difference between gap junction widths (GJW) of patients with or without pre-existing AF (Figure 9B). Absolute GJW values for AF and non-AF patients were 20.5 ± 2.5 nm and 20.3 ± 1.9 nm, respectively, for the experienced observer and 21.0 ± 3.1 nm and 20.0 ± 2.2 nm for the inexperienced observer, similar to what has been reported previously.
To determine whether the automated algorithm required less time to analyze data than manual segmentation, both the experienced and inexperienced user recorded the time needed to quantify a 10-image training set (Supplemental file S5). Table 1 demonstrates that the experienced and inexperienced user decreased analysis time by 4.7- and 8.3-fold respectively using the automated algorithm relative to the manual segmentation approach, with an approximately 43-fold increase in spatial resolution along the perinexus.
Algorithm Troubleshooting. The most common error when running the algorithm occurs when the final centerline does not end at the edge of the image. In such cases, not enough points were selected from the spatial derivative map, causing the program to fail and produce an error message advising the user to select a larger crop area or increase the spatial derivative threshold. Drawing a larger crop box will improve the reliability of the program in some cases as the spatial derivative changes drastically near the edges of the figure, which can disrupt the pathfinding or edge detection algorithms.
It is also possible for the pathfinding algorithm to fail to properly identify the centerline, even if the centerline reaches the edge of the image, particularly if the gradient threshold is too low (Figure 2A). If the gradient threshold is set too high, there will be more unnecessary points incorporated into the pathfinding algorithm (Figure 2B), decreasing computational efficiency. If the user is unable to determine an appropriate threshold, the image array "GMag" (Figure 2C), which is generated by the program and can be found in the Workspace, can help the user determine the threshold. Find points along the centerline and set the threshold slightly above their Index value to ensure these points are selected. In the given example, an appropriate threshold would be above ~5.1 (Figure 2C, insert).
The start point may also fail to reach the beginning of the perinexus (Figure 2D). In this case, re-run the program and set the Manual Start value to 1. After the centerline has been isolated, the user selects a point outside the perinexus and the centerline point closest to the selected pixel (Figure 2E, red square) will be set as the start point. The result is the full centerline (Figure 2F).
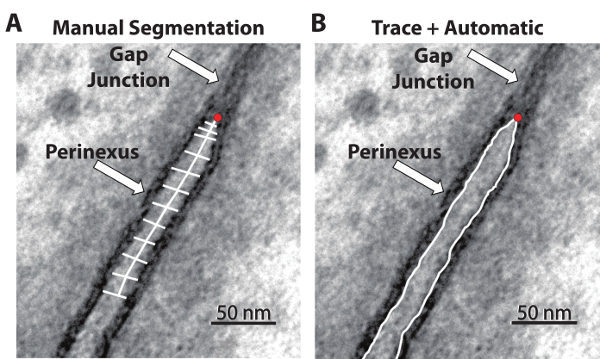
Figure 1: TEM images with quantification processes. The manual segmentation process (A) requires the user to perform 12 individual intermembrane measurements while estimating the centerline. The automatic process (B) requires a manual, continuous trace of the outline of the perinexus. The red dot in each image represents the user-identified end of the GJ and the beginning of the perinexus. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
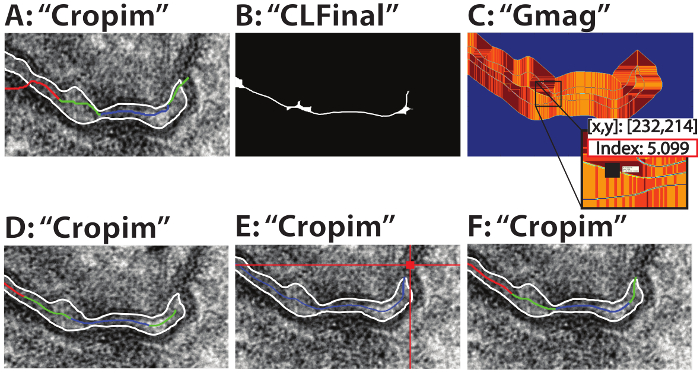
Figure 2: Centerline troubleshooting. Two primary modes of failure for the centerline identification and their solutions: Each image is labelled with the array name in Matlab. If the gradient threshold is too low (A, threshold 0.2) the centerline algorithm can fail. Setting the threshold too high (B, threshold 70) can reduce the computational efficiency of the pathfinding algorithm. An appropriate gradient threshold can be determined from the GMag array (C, insert). If the centerline fails to reach the beginning edge of the perinexus (D), the user can opt to manually select the start point. After the "Start Point" option is set to 1 in the opening GUI, the user then selects a point outside the perinexus of interest (E). The end result should be a centerline that accurately depicts the entirety of the perinexus (F). All labels in quotations (A-F) correspond to the variable names in Matlab. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
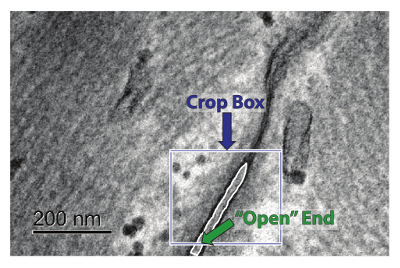
Figure 3: Perinexus Selection. To crop the perinexus, click-and-hold to drag a box around it (the crop tool is selected automatically) as shown by the blue arrow. This box can be adjusted by using the squares on the sides and corners to make it larger or smaller. The green arrow represents the end of the perinexus, which the user should ensure remains "open." Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
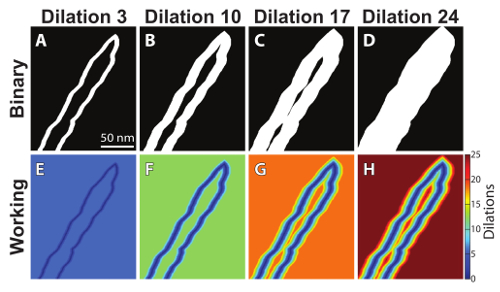
Figure 4: Serial image dilations. The binary outline is repeatedly dilated in one-pixel increments (A-D) and added to the working image (the non-binary form of the image, E-H) after each dilation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
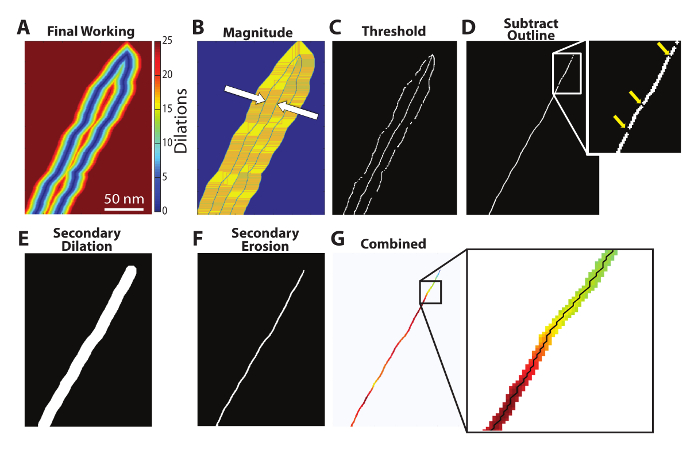
Figure 5: Centerline isolation and pathfinding. A spatial derivative is calculated from the final working image (A) and the magnitude of that spatial derivative (B) is used to isolate the outline and centerline (white arrows). A user-defined threshold identifies the outline and centerline and subtracting the original outline yields the centerline (D). However, gaps appear in the centerline as a result of the threshold (D - insert). In order to produce a continuous centerline, a secondary dilation is performed on the isolated centerline (E), followed by a secondary erosion to increase the computational efficiency of a subsequent pathfinding algorithm. This eroded image (F) is then combined with the final working image, allowing for the identification of a continuous, one-pixel-thick centerline (G - insert). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
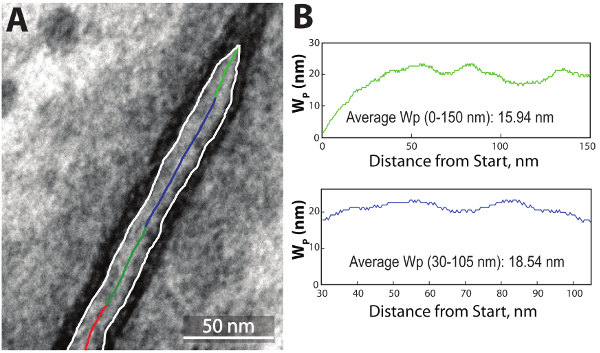
Figure 6: Final data presentation. The program outputs the final outline on top of the original TEM image (A). The line is color-coded green for 0-150 nm, blue for the user-defined region of interest and red for the area beyond 150 nm. Additionally, the program outputs a similarly color-coded chart representing Wp as a function of distance from the start of the perinexus and for the region of interest (B), as well as the average Wp (inset in respective graph). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
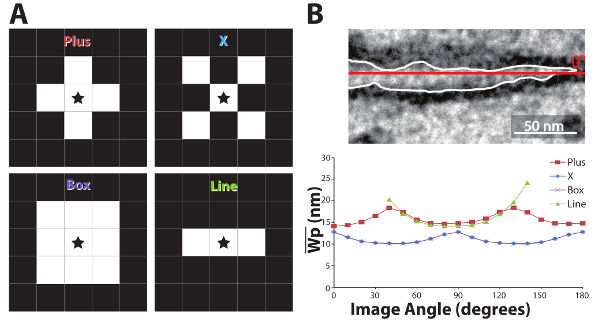
Figure 7: Dilation kernel shape analysis. Shapes for dilation kernels (A): the star in the middle represents the dilated pixels. White boxes are pixels affected by the dilation, in the shape of a plus, X, box or line. An approximately horizontal perinexus (B, top, with a red line indicating 0°) was rotated clockwise from 0 to 180° in steps of 10° and repeatedly dilated using the different kernel shapes (B, bottom). Plus- and line-shaped kernels produce similar results, although the line kernel fails at certain orientations, while the box- and X-shaped kernels are out of phase by 45°. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
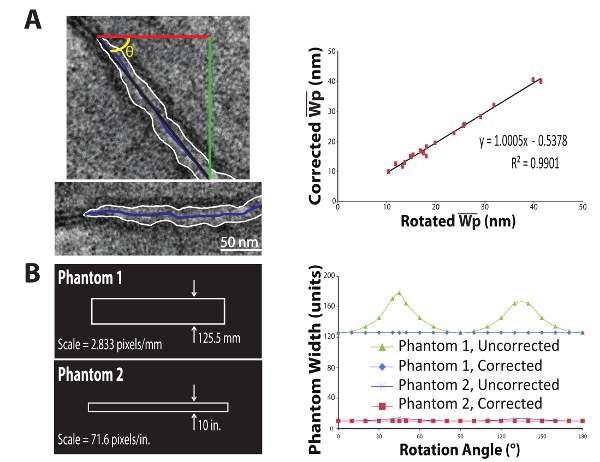
Figure 8: Image Orientation Correction. To correct for the orientation of the image, the average angle of the perinexus is calculated from the positions of the start- and end-points (A, left, beginning and end of black line). The inverse tangent of the change in the y-direction (A, left, green line) divided by the change in the x-direction (A, left, red line) yields the correction angle, θ (A, left, yellow). The goal is to then correct the average Wp value to give the minimum distance between the edges, as if the perinexus had been imaged approximately horizontally (A, left below). The application of the correction factor described by Equation 1 was compared to manually rotating each of 15 randomly-selected images by the calculated θ before analysis. The corrected values strongly correlated with the rotated-image values (R2 = 0.991, A, Right), indicating Equation 1 is a valid correction factor for image orientation. To confirm the correction factor is appropriate, two phantoms were generated of perfectly-parallel edges with a known distance between them (B, Left). Phantom 1 and Phantom 2 have spatial resolutions of 2.833 pixels/mm. and 71.6 pixels/in., respectively. As shown by the blue diamonds and red squares in B, Right, the algorithm accurately calculates their widths across 180 degrees of image rotation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
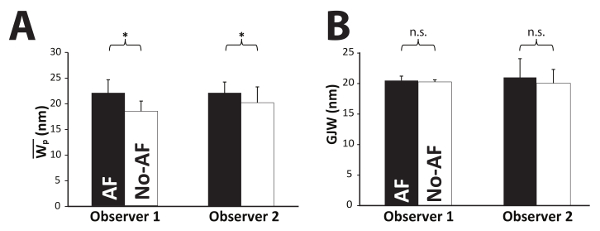
Figure 9: Algorithm reproducibility. Using the automatic process with image orientation correction, both an experienced and inexperienced observer found significant differences between AF and No-AF groups (A), consistent with a previous study, detecting a minimum difference of 2.6 nm. Additionally, neither observer found a significant difference in GJW (B). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Manual | Automatic | |
| Time - Obs. 1 (s) | 205±11 | 44±14 |
| Time - Obs. 2 (s) | 248±18 | 30±5 |
| Spatial Resolution (measurements/nm) | 0.08 | 3.45 |
Table 1: Comparison of manual and automatic processes. Both observers required less time per image to trace the outline than to perform the manual segmentation process for a 10-image training set. Additionally, the automatic process has a higher sampling frequency, recording 3.45 measurements per nm, compared to an average of 1 measurement every 12.5 nm for the manual process. The training set images can be found in Supplemental File S5, along with outlines and measurements as performed by an experienced user.
Discussion
The algorithm uses serial image dilations to count the number of pixels between two opposing 2D edges in a binary image, which in this case is the inter-membrane separation of the perinexus2,3,14. A spatial derivative and a pathfinding algorithm are then used to isolate the centerline, followed by a secondary dilation and erosion sequence to fill gaps in the centerline, similar to what has been done before15. The centerline is then combined with the final dilation-count image to represent perinexal width as a function of distance from the beginning of edge separation, in this case the end of the GJ and the beginning of the perinexus16.
Four primary parameters are user-defined in a GUI at the start of the program:
- Gradient threshold
- Scale
- Region of interest range
- Start point selection method (automatic or manual)
The most common mechanism of failure for the algorithm is the failure of the centerline to reach the edge of the image, which is how the endpoint is determined for the pathfinding algorithm. In order to fix such an issue, the user can increase the gradient threshold described in step 3.3.1, which will cause the program to select more points out of the spatial derivative image, which will increase the computation time required by the pathfinding algorithm. Therefore, this algorithm requires a compromise between computation speed and centerline integrity. It is important to note that so long as all the points of the centerline are identified from the spatial derivative, along with an appropriate start point, the spatial derivative threshold will have no effect on the edge separation measurement.
Image orientation appears to affect dilation values, because the kernel dilates in 90 degree steps, which can introduce an error if the majority of the region of interest is at an angle 45° to the axes of dilation matrices. Therefore, the dilation count may not always be an accurate representation of the space between the edges. This limitation has been addressed by a trigonometric correction factor, but could potentially be ignored if all images in a dataset are aligned at the same orientation. Furthermore, caution should be used in interpreting results, as it is possible that section planes are not perfectly perpendicular to the two membranes. In Figure 9B, we use GJW to suggest that our perinexus images were in-plane. Still, it is imperative that sample sizes be sufficiently large to account for any sectioning variations between images. Additionally, our perinexal width measurements should not be interpreted to reflect in vivo spaces, but this approach is used to measure mean differences in perinexal width relative to some intervention or disease state.
The current algorithm also requires a manually-traced outline of the edges as an input. It is important to note that so long as the scale is set correctly, spatial resolution has no effect on the algorithm's measurements, as demonstrated by the varying resolutions of images in Figure 6 and an additional low-resolution image in supplemental file S6. The next step in improving the algorithm is removing human intervention from outline generation along with a tool that can select the area of interest. These features would likely enhance the precision of the measurement and reduce user bias.
This computationally efficient algorithm provides a faster method, requiring approximately one fifth the man-hours, of quantifying the perinexus with no detectable penalty to reproducibility when compared to the manual segmentation process. Additionally, the manual segmentation process utilizes one measurement every 15 nanometers to quantify perinexal width, which can lead to under sampling as the membrane separation of the perinexus can change substantially within that 15 nm range. In contrast, the automated program has a spatial resolution equal to that of the imaging modality, in this case 2.9 pixels per nanometer along the length of the perinexus, therefore delivering a more finely resolved average of perinexal width.
While the applications in the field of cardiac structural biology are promising and exciting, this algorithm's uses are not confined to TEM images. Any field requiring a precise, high-resolution measurement of two quasi-parallel 2D edges can make use of this algorithm. The algorithm could be used to track anything from riverbank erosion and flood patterns from satellite images to vascular development with brightfield or fluorescent microscopy. One of the most promising potential applications is in the field of cardiology and measuring ventricular ejection fraction (EF) with point-of-care cardiac echocardiography. Currently, the standard technique is the biplane method of disks17, though a newer algorithm, AutoEF, is currently the cutting edge EF-quantifying method18,19. For biplane method of disks, the chamber in question is manually traced and quantified using a modified Simpson's method, whereby overall volume is automatically calculated by the summation of stacked elliptical disks. The main limitation with this method is that it can only return the total cross-sectional area of the desired chamber, with no resolution to identify specific regions of interest, and also requires substantial human input and expertise. The newer method, AutoEF, identifies and outlines the edge of the ventricle using a 2D speckling algorithm and then computes the ventricular cross-sectional area. This process, while precise and efficient for measuring gross ventricular area, also has a similar inherent limitation of only measuring total cross-sectional area. This primary drawback limits clinicians' diagnostic and treatment abilities. In contrast, the algorithm presented in this manuscript can identify a midline and has a resolution equal to the resolution of the imaging modality to pinpoint specific regions of interest. This is important because ultrasound scanners with micrometer spatial resolution are commercially available20,21, implying that this algorithm could detect localized wall motion abnormalities at the resolution of micrometers instead of centimeters. While this application needs to be experimentally validated, it is one of the most immediately promising applications of this algorithm. In fact, it could easily be combined with the speckle tracking capabilities of AutoEF or the manual traces utilized in manual planimetry to provide higher-resolution information in parallel with conventional EF data.
As versatile and applicable as the current algorithm is, it was developed for 2D images. However, as imaging technologies continue to improve, there is an increasing demand for 3 and 4D quantification technologies. Therefore, the next iteration of the algorithm is to adapt the same approach, serially dilating a binary image, to a 3-dimensional object, where automatically defining a centerline is currently beyond the capabilities of current imaging programs. Such an algorithm would have wide applications both clinically and experimentally in the cardiac field alone, including 3D cardiac echocardiograms22,23, 3D electron microscopy24,25,26, and 3D magnetic resonance imaging27,28,29.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Kathy Lowe at the Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine for processing and staining TEM samples.
Funding:
National Institutes of Health R01-HL102298
National Institutes of Health F31-HL140873-01
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Touchscreen Monitor | Dell | S2240T | Needs soft-tipped stylus |
| Desktop | Dell | Precision T1650 | 8GB RAM |
| Operating System | Microsoft | Windows 7 Enterprise | 64-bit OS |
| Program platform | Mathworks | Matlab R2015b | Program may be incompatible with newer/older versions of Matlab |
References
- Rhett, J. M., Gourdie, R. G. The perinexus: a new feature of Cx43 gap junction organization. Heart Rhythm. 9 (4), 619-623 (2012).
- Veeraraghavan, R., et al. Sodium channels in the Cx43 gap junction perinexus may constitute a cardiac ephapse: an experimental and modeling study. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. , (2015).
- George, S. A., et al. Extracellular sodium dependence of the conduction velocity-calcium relationship: evidence of ephaptic self-attenuation. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 310 (9), 1129-1139 (2016).
- Veeraraghavan, R., et al. Potassium channels in the Cx43 gap junction perinexus modulate ephaptic coupling: an experimental and modeling study. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. , (2016).
- Rhett, J. M., et al. Cx43 associates with Na(v)1.5 in the cardiomyocyte perinexus. Journal of Membrane Biology. 245 (7), 411-422 (2012).
- Raisch, T. B., et al. Intercalated Disc Extracellular Nanodomain Expansion in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Frontiers in Physiology. , (2018).
- Yan, J., et al. Novel methods of automated quantification of gap junction distribution and interstitial collagen quantity from animal and human atrial tissue sections. PLoS One. 9 (8), 104357 (2014).
- Papari, G., Petkov, N. Adaptive pseudo dilation for gestalt edge grouping and contour detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 17 (10), 1950-1962 (2008).
- George, S. A., et al. Extracellular sodium and potassium levels modulate cardiac conduction in mice heterozygous null for the Connexin43 gene. Pflugers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. , (2015).
- Revel, J. P., Karnovsky, M. J. Hexagonal array of subunits in intercellular junctions of the mouse heart and liver. Journal of Cell Biology. 33 (3), 7-12 (1967).
- Huttner, I., Boutet, M., More, R. H. Gap junctions in arterial endothelium. Journal of Cell Biology. 57 (1), 247-252 (1973).
- Makowski, L., et al. Gap junction structures. II. Analysis of the x-ray diffraction data. Journal of Cell Biology. 74 (2), 629-645 (1977).
- Entz, M., et al. Heart Rate and Extracellular Sodium and Potassium Modulation of Gap Junction Mediated Conduction in Guinea Pigs. Frontiers in Physiology. 7, 16 (2016).
- Sild, M., Chatelain, R. P., Ruthazer, E. S. Improved method for the quantification of motility in glia and other morphologically complex cells. Neural Plasticity. 2013, 853727 (2013).
- Rhett, J. M., et al. The perinexus: Sign-post on the path to a new model of cardiac conduction. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. , (2013).
- Lang, R. M., et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography. 28 (1), 1-39 (2015).
- Kawai, J., et al. Left ventricular volume and ejection fraction by the axius auto ejection fraction method: comparison with manual trace method and visual assessment of ejection fraction. Journal of Cardiology. 49 (3), 125-134 (2007).
- Frederiksen, C. A., et al. Clinical utility of semi-automated estimation of ejection fraction at the point-of-care. Heart, Lung and Vessels. 7 (3), 208-216 (2015).
- Foster, F. S., et al. A new ultrasound instrument for in vivo microimaging of mice. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 28 (9), 1165-1172 (2002).
- Moran, C. M., et al. A comparison of the imaging performance of high resolution ultrasound scanners for preclinical imaging. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 37 (3), 493-501 (2011).
- Papademetris, X., et al. Estimation of 3D left ventricular deformation from echocardiography. Medical Image Analysis. 5 (1), 17-28 (2001).
- Hosny, A., et al. Unlocking vendor-specific tags: Three-dimensional printing of echocardiographic data sets. Journal of Thoracic Cardiovascular Surgery. 155 (1), 143-145 (2018).
- Cretoiu, D., et al. Human cardiac telocytes: 3D imaging by FIB-SEM tomography. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 18 (11), 2157-2164 (2014).
- Risi, C., et al. Ca(2+)-induced movement of tropomyosin on native cardiac thin filaments revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 114 (26), 6782-6787 (2017).
- Dhindwal, S., et al. A cryo-EM-based model of phosphorylation- and FKBP12.6-mediated allosterism of the cardiac ryanodine receptor. Science Signaling. 10 (480), (2017).
- Reddy, V. Y., et al. Integration of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging with three-dimensional electroanatomic mapping to guide left ventricular catheter manipulation: feasibility in a porcine model of healed myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 44 (11), 2202-2213 (2004).
- van Heeswijk, R. B., et al. Three-Dimensional Self-Navigated T2 Mapping for the Detection of Acute Cellular Rejection After Orthotopic Heart Transplantation. Transplant Direct. 3 (4), 149 (2017).
- Valinoti, M., et al. 3D patient-specific models for left atrium characterization to support ablation in atrial fibrillation patients. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 45, 51-57 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved