Laser-Induced Fluorescence Emission (L.I.F.E.) as Novel Non-Invasive Tool for In-Situ Measurements of Biomarkers in Cryospheric Habitats
In This Article
Summary
Carbon fluxes in the cryosphere are hardly assessed yet but are crucial regarding climate change. Here we show a novel prototype device that captures the phototrophic potential in supraglacial environments based on laser-induced fluorescence emission (L.I.F.E.) technology offering high spectral and spatial resolution data under in situ conditions.
Abstract
Global warming affects microbial communities in a variety of ecosystems, especially cryospheric habitats. However, little is known about microbial-mediated carbon fluxes in extreme environments. Hence, the methodology of sample acquisition described in the very few studies available implies two major problems: A) high resolution data require a large number of samples, which is difficult to obtain in remote areas; B) unavoidable sample manipulation such as cutting, sawing, and melting of ice cores that leads to a misunderstanding of in situ conditions. In this study, a prototype device that requires neither sample preparation nor sample destruction is presented. The device can be used for in situ measurements with a high spectral and spatial resolution in terrestrial and ice ecosystems and is based on the Laser-Induced Fluorescence Emission (L.I.F.E.) technique. Photoautotrophic supraglacial communities can be identified by the detection of L.I.F.E. signatures in photopigments. The L.I.F.E. instrument calibration for the porphyrin derivates chlorophylla (chla) (405 nm laser excitation) and B-phycoerythrin (B-PE) (532 nm laser excitation) is demonstrated. For the validation of this methodology, L.I.F.E. data were ratified by a conventional method for chla quantification that involved pigment extraction and subsequent absorption spectroscopy. The prototype applicability in the field was proven in extreme polar environments. Further testing on terrestrial habitats took place during Mars analog simulations in the Moroccan dessert and on an Austrian rock glacier. The L.I.F.E. instrument enables high resolution scans of large areas with acceptable operation logistics and contributes to a better understanding of the ecological potential of supraglacial communities in the context of global change.
Introduction
The cryosphere harbors sea ice, glaciers, high mountain lakes, snow areas, lake ice, melt water streams, and permafrost. These areas cover approximately 11% of the earth’s landmasses1,2 and are overarched by the atmosphere as a recognized cryospheric environment. Recent studies show that massive areas of the cryosphere are quickly retreating3,4. The Antarctic5,6, the Alps7, the Arctic8, and other regions show negative ice mass balances. The retreat of ice caps and glaciers leads to the depletion of our largest freshwater reservoir on Earth. In some areas, glacier retreat is unstoppable5.
For a long time, ice ecosystems were considered sterile environments. However, despite harsh conditions, the presence of active life in the earth’s cryosphere is evident9,10,11,12,13,14,15. Due to the trend towards massive losses of ice by melting, the cryosphere is going through a shift in biological activity, affecting adjacent habitats. To understand those partially irreversible changes we require methods to investigate biological activity in ice under in situ conditions with high spatial and temporal resolution.
In supraglacial environments, life can be found in cryoconite holes, snow covers, melted water, streams, and on bare ice surfaces. However, the most obvious supraglacial habitats are cryoconite holes. They appear globally in glaciated environments and were first described by the Swedish explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskjold during an expedition to Greenland in the 1870’s16,17. The name originates from the Greek words “kryos” (cold) and “konia” (dust). Aeolian-derived dark organic and inorganic debris attach on the ice surface and reduce the albedo locally. Solar radiation promotes melting of the debris into deeper ice layers, forming cylindrical basins with sediment (cryoconite) in the bottom9. Cryoconite holes cover 0.1–10% of glacial ablation zones11.
Cryoconite communities consist of viruses, fungi, bacteria, cyanobacteria, microalgae, and protozoa. Depending on the region, metazoan organisms such as rotifers, nematodes, copepods, tardigrades, and insect larvae can also be found. Edwards and others18 describe cryoconite holes as “ice-cold hotspots”. They also traced functional genes in cryoconite holes that are responsible for N, Fe, S, and P cycling. The mini lake ecosystems respire and photosynthesize at rates found in much warmer and more nutrient-rich habitats11. These findings emphasize the important role of microbial sequestration in supraglacial environments. Beside living communities in cryoconite holes, bare ice surfaces are inhabited by ice algae. Their physiology is well studied19 but their spatial distribution has not been assessed20. Their presence in supraglacial environments decreases the albedo and hence promotes melting that leads to a nutrient outwash and nutrient input into downstream habitats9. Increasing temperatures and hence, a higher availability of liquid water, affects the net ecosystem productivity in these icy ecosystems.
In supraglacial environments, photosynthetically active organisms transform inorganic carbon and nitrogen into organic, available sources for the microbial food web21,22. Until now there are few studies that estimate supraglacial carbon fluxes11,20,23. The discrepancy in proposed rates of carbon flux results from a low spatial and temporal data resolution. Further, the spatial distribution of supraglacial communities outside cryoconite holes is barely assessed. Cook and others20 predicted in their models that supraglacial algal communities fix up to 11x more carbon than contemporary cryoconite holes due to their large surface coverage. The detection of supraglacial algal communities securing sample integrity is still impeded due to missing tools for in situ detection and quantification.
In response to difficulties in logistics, ice ecosystems are less frequently studied than habitats in temperate areas. Data resolution depends on the number of samples assessed and depend on the accessibility of the study sites. Standard sampling methods such as sawing, coring, and subsequent melting involve manipulation of the microbial community. For example, chlorophylla (chla) assessment in solid ice samples is impossible with standard methods without substantial interference. Hence, melting-induced temperature changes within the investigated microbial communities are unavoidable. In response to the thermolability of the photosystem II and other cellular structures in psychrophiles22, laboratory analyses of melted ice samples will always lead to a falsification of in situ conditions.
Non-destructive in situ measurements are the only reasonable way to obtain reliable data. This goal can be achieved using fluorescence-based methods. Due to their light harvesting function, chla and B-phycoerythrin (B-PE) are present in organisms that contribute to the carbon cycle in supraglacial environments, as has been proved by Anesio and others11. Hence, these fluorescent molecules are suitable biomarkers for the quantification of microbial mediated carbon fluxes in ice ecosystems.
In this study, we present the development, calibration, and applicability of a novel non-invasive tool for in situ quantification of chla and B-PE molecules in terrestrial and ice ecosystems. The prototype device is based on laser-induced fluorescent emission, also known as L.I.F.E. The optical instrument (Figure 1) captures fluorescent biomarker signatures after laser-induced fluorescence excitation. The procedure is nondestructive and can be performed at the study site or in a laboratory.
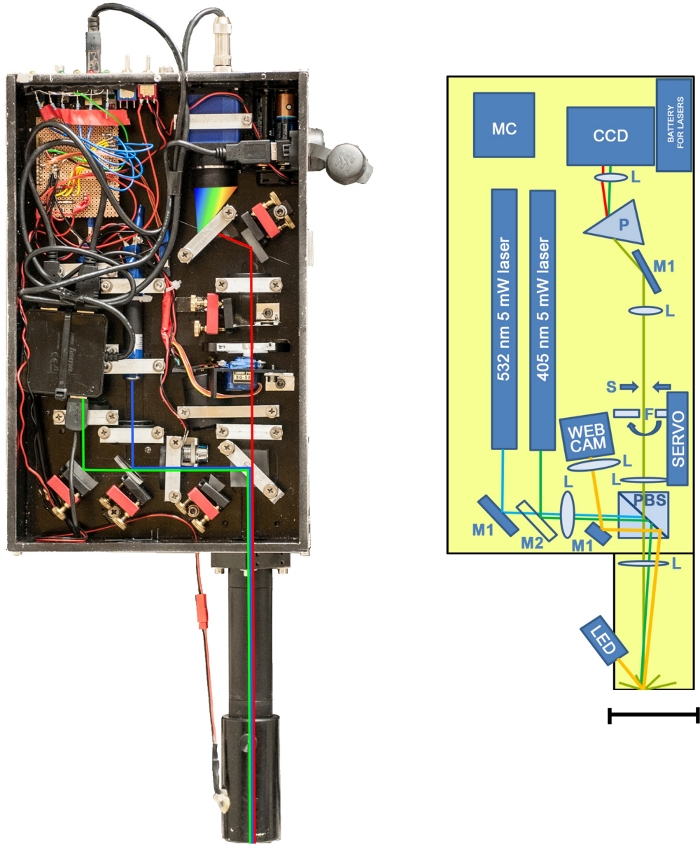
Figure 1: The L.I.F.E. prototype. Left: Photo of the instrument without a protective lid. Right: Schematic illustration of the instrument. Total mass = 5.4 kg (laser and optics = 4.025 kg, laptop = 1.37 kg). Aluminum frame = 32.5 cm x 20.3 cm x 6.5 cm. Optical tube: 18.4 cm x 4 cm (diameter). CCD: bluefox mv220g sensor; F: servo-steered long-pass filters (450 nm and 550 nm); L: optical lenses; M1: mirrors; M2: dichroic mirror; MC: microcontroller; P: prism; PBS: polarizing beam splitter; S: slit aperture made of adjustable razor blades. Scale bar = 70 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The portable dual-wavelength kit weighs 4.5 kg and is used on a tripod in combination with an external computer. The field setup is quick and easy. The instrument is attached to the tripod, and the lens tube is attached to the device along with a USB cable and the camera cable. The external computer is connected to the instrument using a USB cable. The tripod legs are adjusted in such a way that the lens tube is directed towards and covers the specimen. Then, a 5 mW green laser hits the sample after passing a polarizing beam splitter that redirects polarized light towards the optical axis of the spectrometer. The specimen exhibits a fluorescent light, illustrated in red in Figure 1. Half of the collimated light passes the polarizing beam splitter and is focused through a servo-steered long-pass filter that removes the laser signals. Next, the signal hits an aperture slit that consists of two adjustable razor blades. A prism spectrally separates the fine line of light orthogonal to the slit aperture before the signal is captured by the sensor. The procedure is repeated with a blue laser. The raw data are transferred automatically to a portable computer that is also used for the software operation.
The instrument is controlled by an external computer using a LabVIEW environment that synchronizes the picture-taking with the CCD camera, switching on/off lasers, and rotating the long-pass filter wheel. The graphical user interface (GUI) is divided into three main sections. The exposure adjustment is done manually. Although the correction between exposure time and signal intensity is linear (Figure 2B), the maximum exposure time is limited to 10 s because longer integration times lead to a significant decrease in the signal-to-noise-ratio. The comment field is used for the description of the sample (Figure 2A). In the right section, raw images are displayed as soon as the measurements are finished. This feature is crucial for immediate data evaluation in the field (Figure 2C–E). Red areas indicate overexposed pixels, which can be avoided by reducing the exposure time.
The subsequent raw data reduction process is decoupled from the image acquisition procedure and can be done at any time after image acquisition.
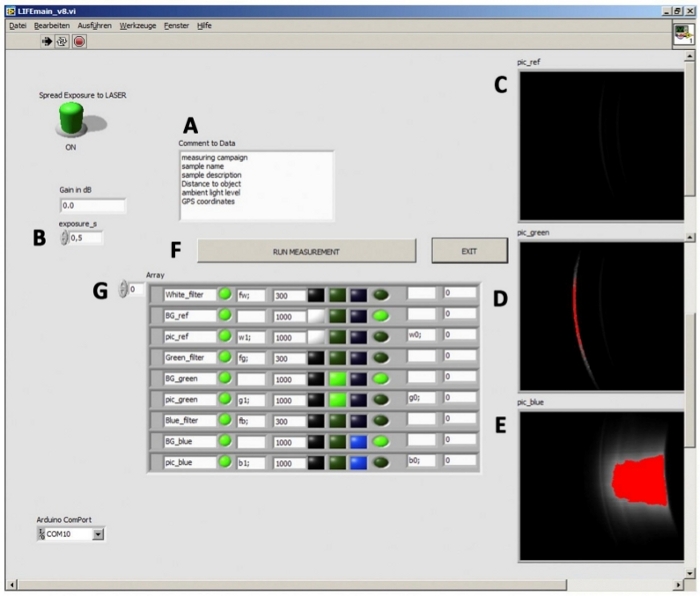
Figure 2: L.I.F.E. graphical user interface for the data acquisition and raw data evaluation. (A) The software enables manual text input for sample descriptions. (B) The exposure time can be adjusted before the measurement. (C−E) The raw images are displayed on the right side of the interface. (E) Red colors indicate a saturation of the sensor. (F) The activation of the RUN MEASUREMENT button triggers the data acquisition process. In the array (G), all commands executed automatically during data acquisition are displayed. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 3: Example of a raw image. Left: Raw data of chla standard in acetone solution, recorded with the L.I.F.E instrument. Due to the optical properties of the device, the signal is displayed as a warped line. Right: Interpretation of the raw image per pixel (px). The spectral axis (5 nm/px resolution) is plotted against the spatial axis (30 µm/px resolution). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The 12-bit gray-scale raw images show a spatial component due to the one-dimensional aperture slit and a spectral component due to the prism in front of the CCD (Figure 3). In response to optical constraints the raw images are distorted. Therefore, they need to be cropped and dewarped by applying a code that recognizes the degree of distortion. This is done with a software wizard (Figure 4). Next, the wavelength calibration is done with the 532 nm laser. The green light is produced by frequency doubling of a 1,064 nm infrared laser. Both wavelengths can be detected by the CCD and therefore, the spectral position of each pixel can be calculated in dewarped images automatically (Figure 4).
The picture is then cropped down to a given wavelength range (550–1,000 nm for green laser measurements and 400–1,000 for blue laser measurements). Gray values from each pixel in a selected pixel line are counted and summed up. A gray value can range from 0–255. After that, every pixel line accounts for one number. Further on-screen software instructions lead to the generation of a plot showing the gray value counts from each pixel line plotted against the spatial coordinates. This allows for a quantitative spatial discrimination of chla and B-PE simultaneously in the sample. Additionally, the spectral properties of a sample can be plotted from selected pixel lines automatically.
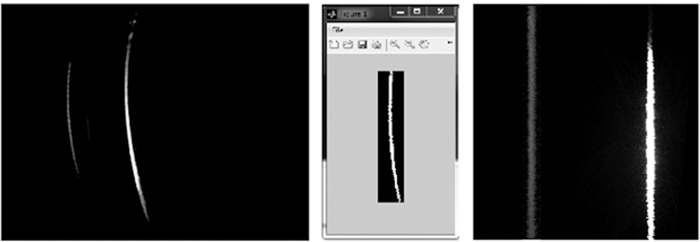
Figure 4: Dewarping raw images. Left: Raw image captured with a green laser. No filter was used. Signals are displayed at 532 nm and 1,064 nm. Exposure time = 0.015 s. Center: The cropped 532 nm signal is used as a reference line to dewarp a set of images. Right: The dewarped image from the raw image source. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
1. Calibration and validation
NOTE: For the pigment calibration, prepare dilution rows from stock solutions of chla and B-PE. The chla stock solution is diluted with acetone and B-PE is diluted with distilled sterile water. Later, 15 mL of each dilution step will be needed. Protect the pigments from light by wrapping them with aluminum foil. Store the chla in a freezer and the B-PE in a refrigerator until further use. A detailed protocol for the dilution row follows in sections 1.1 for chla and 1.2 for B-PE. Both the chla and the B-PE laboratory calibration for pigment detection and quantification with the L.I.F.E. instrument is described below. A previous calibration24 was made with the same pigments as in this study.
- Chlorophylla dilution row
- Dissolve 1 mg of chla (purified from A. nidulans algae) with acetone in a 50 mL sample tube and dilute this chla stock solution with acetone to the following final concentrations: 1,000; 800; 640; 320; 160; 80; 40; 20; 10; 5; 1; and 0.5 ng/mL.
- Transfer 15 mL of each dilution into 50 mL sample tubes and cover them in aluminum foil due to light sensitivity. Store the tubes in a -20 °C freezer until the calibration measurements are taken.
NOTE: The protocol can be interrupted here. - Measure the chla absorption features from each dilution in a double-beam spectrophotometer as triplicates and calculate the chla content as described by Lorenzen25, which will be described in detail in section 2.2.2.
- PE dilution row
- Dilute a 4 mg/mL B-PE stock solution with sterile filtered water (pH = 7) to the following final concentrations: 1,000; 800; 640; 320; 160; 80; 40; 20; 10; and 5 ng/mL B-PE. Transfer 15 mL of each dilution in a 50 mL sample tube and cover it with aluminum foil. Store at 4 °C until further use.
NOTE: The protocol can be interrupted here.
- Dilute a 4 mg/mL B-PE stock solution with sterile filtered water (pH = 7) to the following final concentrations: 1,000; 800; 640; 320; 160; 80; 40; 20; 10; and 5 ng/mL B-PE. Transfer 15 mL of each dilution in a 50 mL sample tube and cover it with aluminum foil. Store at 4 °C until further use.
- Setup for calibration
- Build a rack as shown in Figure 5 to establish three measurement platforms, each 1.5 cm higher than the next.
NOTE: The rack and column height play an important role for the measurements because the surface of the liquids should remain in the focal point of the L.I.F.E. instrument as indicated in Figure 5. - Add 5 mL of the highest concentrated dilution in a polyscintillation plastic vial and put it on the highest point of the rack. Measure the fluorescence intensity.
- Place the vial in the middle position of the rack and add another 5 mL (10 mL total volume). Measure the fluorescence intensity. Repeat the procedure at the lowest position on the rack with another 5 mL (15 mL total volume; total of 45 mm in column height).
NOTE: Adapt the exposure time for each dilution step to prevent detector saturation (gray values over 255 in 12-bit images) and for a sufficient signal-to-noise ratio of the weak fluorescence signals. - Repeat steps 1.3.2 and 1.3.3 with all dilutions (steps 1.1.1 and 1.2.1) of chla and B-PE.
- Load the generated data files into the data reduction wizard to automatically count and sum up the gray values from each pixel line along the Y-axis (spatial distribution).
NOTE: Varying exposure times are compensated automatically by normalizing the fluorescence intensity to an integration time of 1 s. - Calculate the pigment area density with a Poisson regression analysis using the known concentrations from the dilution series and the normalized fluorescence intensities that were calculated. Then normalize the fluorescence counts from the three different column heights to 1.5 cm (5 mL) by multiplying the counts from each column height with a factor (factors 1, 0.5, and 0.33, for the 5 mL, 10 mL, and 15 mL concentration solutions, respectively).
- Build a rack as shown in Figure 5 to establish three measurement platforms, each 1.5 cm higher than the next.
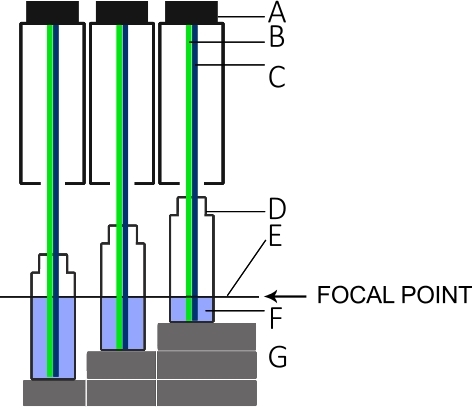
Figure 5: Setup for the L.I.F.E. calibration with chla and B-PE under laboratory conditions.
(A) Lens tube of the instrument. (B) Green laser for B-PE excitation. (C) Blue laser for chla excitation. (D) Scintillation vial. (E) Focal point of the L.I.F.E. instrument. (F) B-PE/water or chla/acetone solution with 5 mL, 10 mL, and 15 mL. (G) Spacers that keep the surface of each solution at the focal plane for three different volumes. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Sampling and sample processing
- Collection of snow and ice
- Collect snow and supraglacial ice from a glacier into sterile polyethylene bags and store them frozen until further processing.
NOTE: For this study, the samples were collected at Midtre Lovenbreen (MLB), a polythermal glacier near the research village Ny-Ålesund in the high Arctic Archipelago of Svalbard (78°53’ N, 12°03’ E). - Sample bacterial mats from the glacier forefield into sterile polyethylene bags and transport all samples to a laboratory for further processing.
- Melt frozen material slowly in the dark at 4 °C. Filter liquid samples on GF/F filters (47 mm diameter) and note the filtered volume. Keep the filters frozen until further processing.
- Collect snow and supraglacial ice from a glacier into sterile polyethylene bags and store them frozen until further processing.
- Chlorophylla measurements
- Using the L.I.F.E. instrument, measure the filter in four random areas, each in triplicates using the green and blue laser. Calculate the overall pigment concentration by multiplying the area density with the filtered area and filtered volume. Normalize the pigment concentration (µg/L) to a volume of 1 L.
- Assess the chla contents of the GF/F filters with a laboratory standard according to the protocol by Lorenzen25. To do so, put each of the filters in a vial with 13 mL of acetone and store them in the dark at 4 °C overnight. Next, take a vial and place it on ice before sonication for 2 min at 50% power in continuous mode. Squeeze and remove the filter from the vial.
- Attach tygon tubing to a syringe and remove the chla extraction-acetone mix from the vial. Replace the tygon tubing with a GF-5 filter holder. Transfer the solution into a quartz cuvette.
- After calibrating the absorbance spectrometer for acetone, place the sample in the cuvette into the spectrometer and measure the absorbance features between 400–750 nm. Next, remove the cuvette from the spectrometer and add 200 µL of 2 M HCl to the sample. Then, repeat the absorbance measurement to measure the phaeophytin content in the sample.
- Measurement of microbial activity via radiolabelled markers and impact of laser intensity and exposure time on productivity rates
CAUTION: Beware of the marker radioactivity (β-radiation). Use a laboratory coat, gloves, and goggles, and work under a fume hood in a licensed isotope lab.- For bacterial production transfer five aliquots of bacterial mats into sterile polyethylene bags. Inactivate the controls with formaldehyde to a 4% final concentration.
NOTE: Three aliquots are used for the 3H-labeled leucine uptake and two aliquots are used as controls. - Expose the mats with a blue laser (405 nm, 5 mW) and with a green laser (532 nm, 5 mW) for 10 s and 30 s each. Repeat the procedure with 50 mW lasers. Then, inactivate the samples that were not treated with formaldehyde.
NOTE: One mat is used for only one laser exposure. Use non-exposed microbial mats as controls. - After the laser treatment, estimate the bacterial and primary production by incorporating 3H-leucine and NaH14CO3, respectively. For bacterial production measurements, use five aliquots per sample (20 mL) and add formaline (4% final concentration) to two of the parallels, which serve as controls for the abiotic incorporation of the marker. Add 3H-leucine (40 nM) to all samples of the various treatments and incubate them for 4 h under in situ conditions (0.1 °C). Terminate the reaction by adding formaline to the remaining live samples.
- For bacterial production of bacterial mats, transfer labelled samples into cryovials. Extract cells with 5% trichloroacetic acid and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 5 min according to the protocols by Kirchman26 and Bell27. Add scintillation liquid and put the cryovial into a polyscintillation vial. Analyze the samples with a liquid scintillation counter and calculate the uptake rates.
NOTE: Three aliquots are used for the 3H-labeled leucine uptake, two aliquots are used as controls. - For primary production, prepare five replicates of various treatments (100 mL), wrap two of them into aluminum foil to mimic the dark samples, and add NaH14CO3 (1 µCi) to all. Incubate for 4 h in the ambient light and in situ temperature (0.1 °C). Terminate the reaction by darkening the remaining three replicates and filter the sample onto GF/F filters (25 mm diameter).
- Add 100 µL of 2 N HCl to the filters to remove all excess carbon and let it air out under the fume hood. Dry the samples on a heating plate at 80 °C and place samples into polyscintillation vials.
- To measure radioactive disintegrations per minute (dpm) of all treatments of primary and bacterial production, place the cryovials into polyscintillation vials and add 5 mL of scintillation cocktail. Measure dpm with a liquid scintillation counter and calculate the uptake rates.
- For bacterial production transfer five aliquots of bacterial mats into sterile polyethylene bags. Inactivate the controls with formaldehyde to a 4% final concentration.
Representative Results
Laboratory calibration for B-PE
The response signals of the B-PE dilution row were measured with the L.I.F.E. instrument in a dark room at 20 °C (Figure 6). The count rate depended on both the concentration and the column height of the measured sample. Low concentration and low column height B-PE specimen fluoresced stronger compared to samples of the same concentration and higher column height.
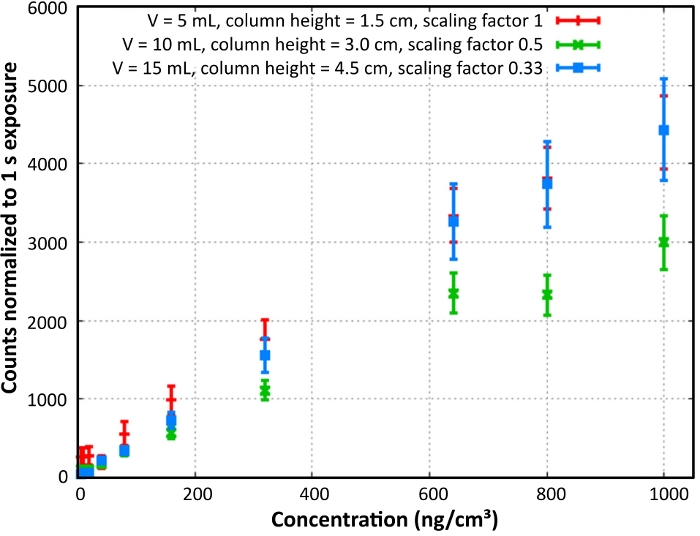
Figure 6: B-PE laboratory calibration. B-PE content and column density calibration is shown. Normalized count rates were calculated for a column height of 1.5 cm. Reprint with permission28. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
A Poisson regression was used for the final calibration line fit. There was a linear correlation between the area densities and pixel gray value counts. The function of the curve was y = 81.04x (Figure 7), which means that a gray value count rate of 8,104 in a 1 s exposed sample equaled an area density of 100 ng/cm2 B-PE. The chla calibration is set up in an analogue manner. The function was y = 8.94x.
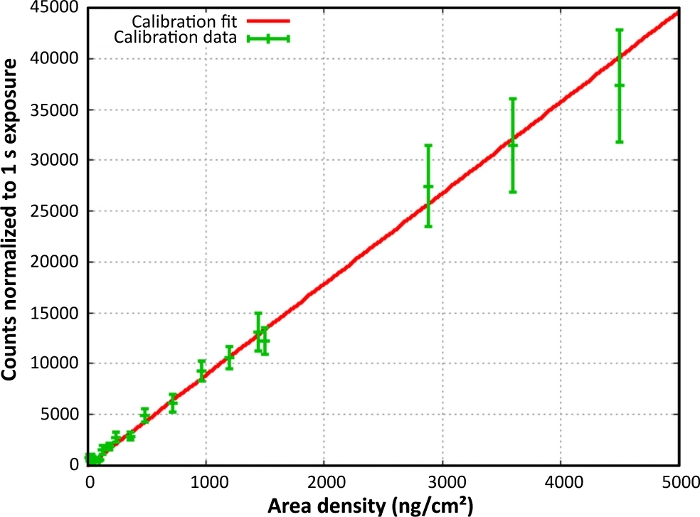
Figure 7: Final calibration curve for B-PE. The gray value counts were normalized to an exposure time of 1 s and plotted against the area density. Reprint with permission28. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Application on cryoconite samples from Svalbard and laboratory validation of data
The mean values of the L.I.F.E. measurements and the single measurements of the same samples derived from conventional extraction using acetone and subsequent analysis with a spectrophotometer are illustrated in Figure 8.
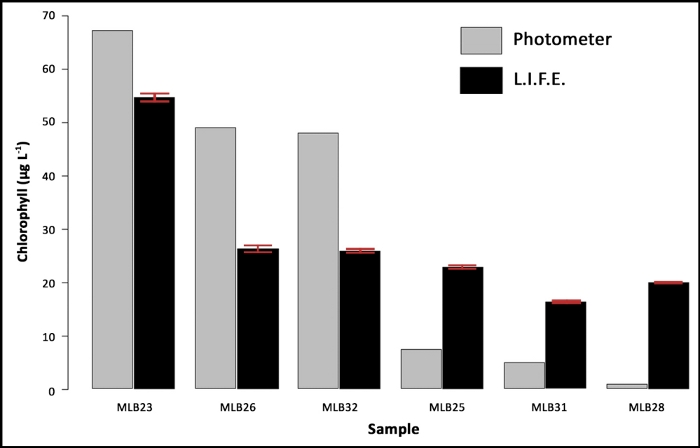
Figure 8: Data validation with natural samples. The samples (MLB) are ranked by chla content, based on the results of a laboratory spectrophotometer (single values) and compared with the chla fluorescence data measured on four random areas per filter. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the L.I.F.E. measurements. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Chla contents ranging from 48 µg/L–67 µg/L were underestimated, and lower chla contents ranging from 0.7 µg/L–7 µg/L were overestimated by the L.I.F.E. prototype. The standard deviations from the L.I.F.E. measurements were low.
Comparison of spectral data from in situ measurements with laboratory standards
Chla spectra were comparable between cryoconite samples and those from purified from A. nidulans algae. The fluorescence peaks in all samples were located at 700 nm–710 nm. However, spectra derived from cryoconite samples showed higher noise signals between 400 nm–650 nm and from 800 nm–1,000 nm compared to spectra of the chla pigment standard (Figure 9).
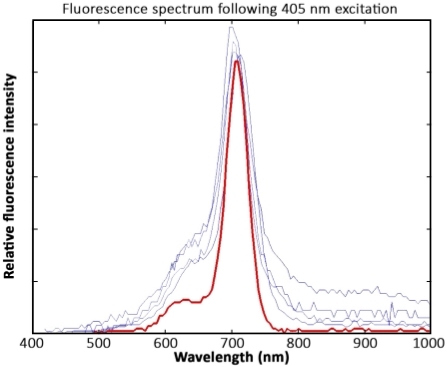
Figure 9: Spectral data interpretation. Measurements of four cryoconite granules (blue) and a chla standard pigment solution (red) after excitation with 405 nm lasers. The spectra were recorded 1 year after sample collection. The samples were kept frozen and were not exposed to light prior to the measurement. In response to wavelength calibration issues, the fluorescence peak is located at 700 nm–710 nm instead of 680 nm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Automated cryoconite grain analysis
In an example of an automated analysis of a cryoconite hole (Figure 10), the highest pigment area densities were observed at pixel line 50. The sample spectrum after excitation with a 532 nm laser showed a peak with a cut off at a gray value of 255 in response to oversaturation of the sensor. This peak derived from the green laser and not from the fluorescent signal.
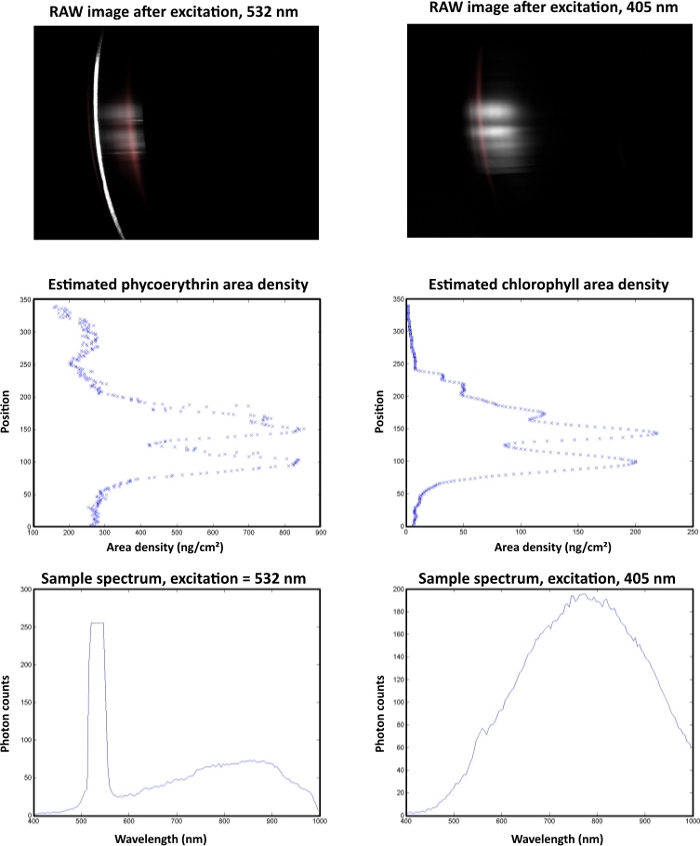
Figure 10: Automated data analysis of a single cryoconite granule with a diameter of 1 mm. The sample was collected at Vestre Brøggerbreen (VBB) and measured within 4 h after sampling in a dark laboratory room at the Arctic Station (GB) facility in Ny-Ålesund. The left column shows B-PE measurements and the right column represents chla data. The raw images are displayed on top. Laser-induced fluorescence responses are displayed in gray. Red areas indicate the response from standard pigments. The middle section illustrates the spatial distribution of the target pigments. The spectral properties of the fluorescence signal are displayed in the lower images. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Impact of laser excitation on productivity in bacterial mats
Neither primary nor bacterial productivity were affected when increasing the power of the laser and/or the exposure time (Figure 11). No significant differences were detected under laser treatments with increased power.
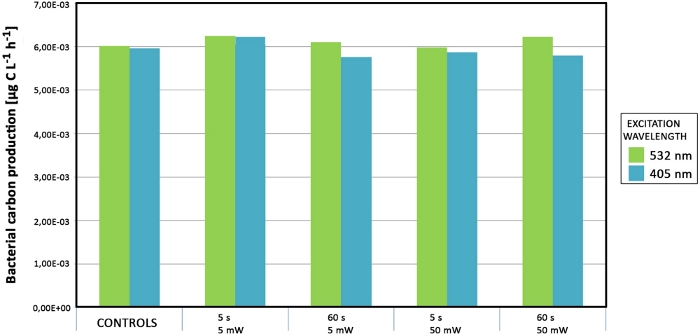
Figure 11: Productivity measurements of samples from Svalbard. Bacterial mats were exposed with green and blue lasers of varying laser intensities and exposure times. The data are colored according to the laser wavelength source (green and blue). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
Calibration
There was a linear correlation between pigment concentration and fluorescence intensity after normalizing photon counts to an exposure time of 1 s. Samples with low column height and low pigment concentrations led to an overestimation of the target pigments, compared to higher column heights with the same pigment concentration. Further, weak fluorescence signals required long exposure times for sufficient photon counts on the sensor. However, long integration times also increased the amount of stray light on the sensor, resulting in a decrease of the signal-to-noise ratio. In its current version, the software cannot distinguish between noise and signal during the data reduction process. Hence, low fluorescence intensity measurements led to a pigment overestimation because noise was counted as a signal that derived from the target pigments. Further, fluorescence intensities from more concentrated pigment solutions showed a greater variability than low concentration solutions. This effect could be explained by absorption processes within the pigment solutions that were used for the calibration curve.
Data validation for chlorophylla quantification
After filtering ice and snow samples, the three-dimensional samples almost appeared as a two-dimensional specimen on the filter. This justified a direct comparison between L.I.F.E (area density) and spectrophotometric data (volumetric measurement).
The data set (Figure 8) indicated that high pigment concentration leads to an underestimation, whereas low pigment concentration leads to an overestimation of the actual value. This effect can be explained by the thickness of the filter cake and hence, the volumetric character of the sample. The laser penetration depth depended on the optical density and thickness of the specimen. High pigment contents were underestimated because the laser could not induce pigment fluorescence in deeper layers. However, in thin filter cakes, low fluorescence signals were captured due to low area densities of pigments. Apparently, the filter itself showed laser-induced signals after passing the 450 nm long-pass filter (Figure 12). This signal was misleadingly counted as fluorescence signal derived from chla. Thus, thin and too thick filter cakes are difficult to measure with the L.I.F.E. instrument.
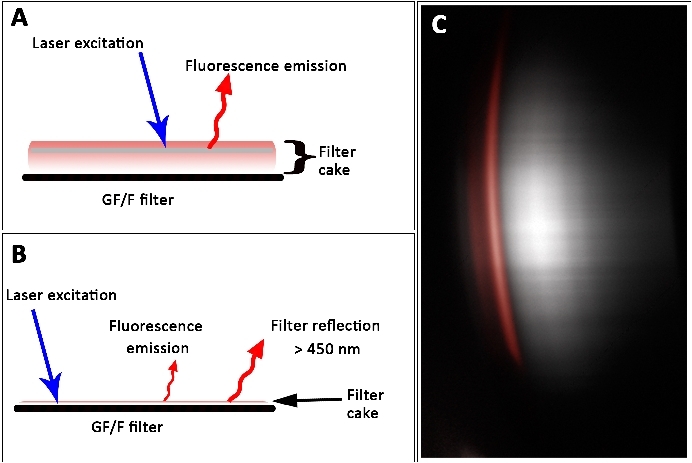
Figure 12: Fluorescence signals from thick (A) and thin (B) filter cakes on a GF/F filter. (A) Self-shading prevents laser-induced fluorescence from deeper layers, which results in an underestimate of the actual pigment concentration. (B) Fluorescence emission from filter cake with overlay by filter reflections. (C) Raw data show filter reflection (gray). The spectral property of a laboratory derived chla fluorescence pattern is illustrated in red. Scale bar = 45 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Limitations of the L.I.F.E. prototype
During data reduction, the MATLAB coded software interpreted the raw images by summing up pixel lines within a given wavelength range. The current version of the software did not distinguish between organic and inorganic derived signals. The presence of multiple signals might lead to an overestimation of the actual pigment content. Long exposure times due to low fluorescence intensities led to a decrease of the signal-to-noise ratio, promoting the effect as described above (see Figure 8 and Figure 12).
A geode rock shown in Figure 13 exhibited red fluorescent light when exposed with green and blue light. Currently, it is not clear whether the fluorescence resulted from minerals or from porphyrin-based molecules. Hence, an overlay of biological and nonbiological signals may limit the application of this method and require the establishment of a fluorescence database specifically made for the L.I.F.E. prototype.
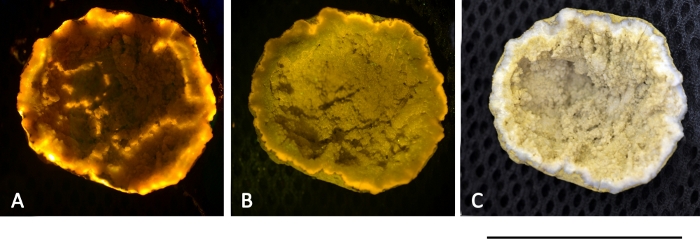
Figure 13: Mineral fluorescence from a geode rock, found in Ny-Ålesund. The rock was excited with a 532 nm 50 mW laser (A) and a 405 nm 50 mW laser (B). Both pictures were captured with a polarization filter attached on the lens, which led to a falsification of the actual fluorescence colors. (C) True color image without the use of a polarization filter under daylight conditions. Scale bar = 40 mm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Beutler and others29 concluded that characteristic emission spectra of cyanobacteria in marine ecosystems depend on environmental conditions. Also, the metabolic state has an impact on the fluorescence properties in phototrophic organisms30. The L.I.F.E instrument may distinguish between the algal and cyanobacterial fluorescence pattern by using bio-fingerprint libraries that contain spectral information of the specimen correlated with environmental conditions.
In dark-adapted chla molecules, all reaction centers are fully oxidized and available for photochemistry and no fluorescence yield is quenched31. Using the L.I.F.E. procedure, a specimen is first excited by a 532 nm laser (green) and then with a 405 nm laser (blue). During the second excitation by the blue laser, chla might show a decreased fluorescence response due to prior excitation by the green laser. Chla absorbs energy at 532 nm wavelength, despite its distance from its absorption maximum wavelength32. Before the actual chla measurement at 405 nm, the green laser may cause photochemical reactions, activating quenching mechanisms in the target pigments. Further, pre-illumination of marine phototrophic organisms did not lead to a change in spectral norm curves between 450 nm–600 nm while the standard deviation in fluorescence intensities increased by 25%29. Depending on the species, fluorescence intensities even increased in response to prior excitation. This topic requires further investigation.
Applicability
We tested the L.I.F.E. instrument in various habitats with an emphasis on cryoconite holes. The laser was successfully applied in soil and biofilm habitats because of the absence of ambient light during the measurement. Cryoconite granules could be measured when sediment layers blocked light from beneath the hole (Figure 14A,C). Thin sediment cryoconite holes were permeable for stray light from beneath (Figure 14B). Stray light interferes with the measurement. Thus, pigment concentration in bare ice surfaces is not measurable under daylight conditions yet. Signal processing efforts are currently underway to enable operation of the system in high ambient light conditions.
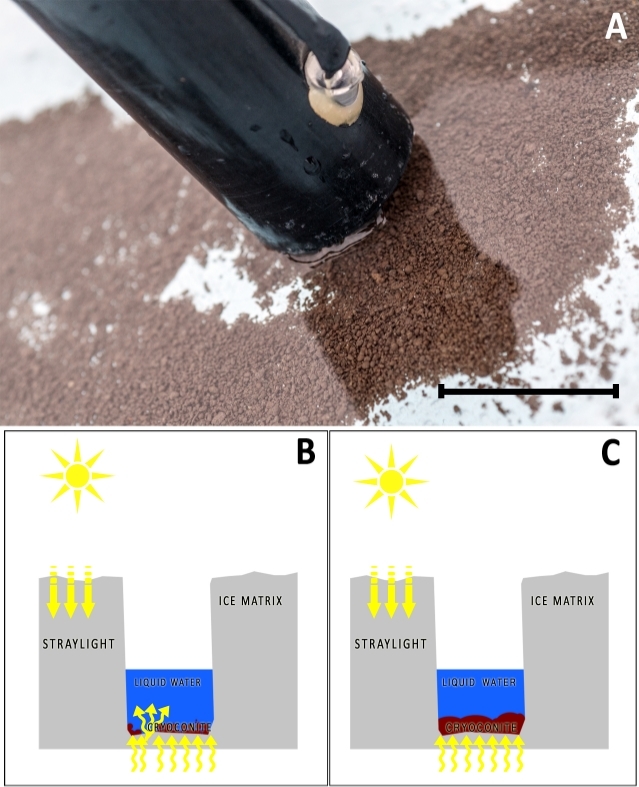
Figure 14: Cryoconite hole with liquid water on top. (A) Cryoconite on glacier with L.I.F.E. lens tube. Scale bar = 70 mm. (B) The sediment layer (red) is very thin. Stray light bleeds through the cryoconite layer. (C) The sediment layer is thick enough to block the stray light from beneath. This type of cryoconite hole is measurable with the L.I.F.E. instrument. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
In conclusion, our L.I.F.E. instrument detected photoautotrophic organisms in terrestrial habitats such as soils, bacterial mats, biofilms, and in cryoconite holes on glacial surfaces. The target molecules were chla and B-PE. The spatial resolution was 30 µm/px. The detection limit for chla was 250 pg/mL and 2 ng/mL for B-PE. After a laboratory calibration we were able to quantify pigment content in samples that were collected at our study site in the Arctic. We applied self-programmed software for an automated data reduction process. The effects of the presence of minerals and changing light conditions during the measurements require further investigation.
With climate warming, increasing temperatures lead to enhanced availability of liquid water, which results in higher biological activity on icy surfaces of autotrophic and heterotrophic nature. Vigorous efforts should be made to detect heterotrophic organisms in situ to give a full picture of active life in the cryosphere. This could be tested with other target pigments and appropriate laser excitation wavelengths. Hence, L.I.F.E. provides a suitable monitoring system providing high temporal and spatial resolution for supraglacial conditions in context with global change as well as possible astrobiological applications.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank Colonel (IL) J.N. Pritzker, the Tawani Foundation, USA, the Austrian Federal Ministry of Science, Research and Economy (Sparkling Science SPA04_149 and SPA05_201), Alpine Forschungsstelle Obergurgl (AFO), Austrian Space Forum (ÖWF), Roman Erler from the Hintertuxer Natur Eis Palast, the Austrian Federal Forestry and Base Manager Nick Cox from the Arctic Station in Ny Alesund (Svalbard). We are also indebted to Sabrina Obwegeser, Carina Rofner, and Fabian Drewes for their help during filming. Finally, we want to thank James Bradley for giving the voice for the concomitant video.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| aceton | Merck | 67-64-1 | |
| B-Phycoerythrin | Invirtrogen | P6305 | |
| Chlorophyll a standard | Sigma-Aldrich | C6144-1MG | |
| formaline | Merck | HT501128 | 36% |
| GF/C filters | Whatman | WHA1822025 | 25mm diameter |
| HCl | Merck | H1758 | 36,5-38% |
| L.I.F.E. Prototype | University of Innsbruck | built on demand | |
| LabView | National Instruments | Software, Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation Engineering Workbench | |
| Leucine, L-[4,5-3H], 1 mCi | Perkin Elmer | NET1166001MC | radioactive |
| Liquid scintillation cocktail Beckman Ready Use | Beckman | not more available, can be compensated by Ultra Gold, Packard | |
| liquid scintillation counter | Beckman | out of stock | LSC 6000 IC |
| NaH14CO3 (4 µCi/ml) | DHI Denmark | 4 μCi/ml, 1 ml | radioactive |
| Osmonics polycarbonate filters | DHI Denmark | PCTE | 25mm diameter, 0,2µm pore size |
| Polyscintillation vials | Perkin Elmer | WHA1825047 | 20ml |
| sample tubes | Sigma Aldrich | T2318-500EA | Greiner centrifuge tubes, 50ml |
| Spectrophotometer | Hitachi | NA | Model U2001, any photometer for absorption spectroscopy measuring at 664nm and 750nm would be appropriate |
| trichloric acetic acid (TCA) | Merck | T6399 | 100% |
| ultrasonic probe | nano lab | QS1T-2 |
References
- Boyd, E. S., Skidmore, M., Mitchell, A. C., Bakermans, C., Peters, J. W. Methanogenesis in subglacial sediments. Environmental Microbiology Reports. 2, 685-692 (2010).
- Sattler, B., Puxbaum, H., Psenner, R. Bacterial growth in supercooled cloud droplets. Geophysical Research Letters. 28, 239-242 (2001).
- Good, P., et al. A review of recent developments in climate change science. Part I: Understanding of future change in the large-scale climate system. Progress in Physical Geography. 35, 281-296 (2011).
- Fountain, A. G., et al. The Disappearing Cryosphere: Impacts and Ecosystem Responses to Rapid Cryosphere Loss. BioScience. 62, 405-415 (2012).
- Rignot, E., Mouginot, J., Morlighem, M., Seroussi, H., Scheuchl, B. Widespread, rapid grounding line retreat of Pine Island, Thwaites, Smith, and Kohler glaciers, West Antarctica, from 1992 to 2011. Geophysical Research Letters. 41, 3502-3509 (2014).
- McMillan, M., et al. Increased ice losses from Antarctica detected by CryoSat-2. Geophysical Research Letters. 41, 3899-3905 (2014).
- Barletta, V. R., et al. Glacier shrinkage and modeled uplift of the Alps. Geophysical Research Letters. 33, 14307 (2006).
- Nuth, C., et al. Decadal changes from a multi-temporal glacier inventory of Svalbard. The Cryosphere. 7, 1603-1621 (2013).
- Takeuchi, N., Kohshima, S., Seko, K. Structure, formation, and darkening process of albedo-reducing material (cryoconite) on a Himalayan glacier: A granular algal mat growing on the glacier. Arctic Antarctic and Alpine Research. 33, 115-122 (2001).
- Takeuchi, N. Optical characteristics of cryoconite (surface dust) on glaciers: the relationship between light absorbency and the property of organic matter contained in the cryoconite. Annals of Glaciology. 34, 409-414 (2002).
- Anesio, A. M., Hodson, A. J., Fritz, A., Psenner, R., Sattler, B. High microbial activity on glaciers: importance to the global carbon cycle. Global Change Biology. 15, 955-960 (2009).
- Anesio, A. M., et al. Carbon fluxes through bacterial communities on glacier surfaces. Annals of Glaciology. 51, 32-40 (2010).
- Storrie-Lombardi, M. C., Sattler, B. Laser-Induced Fluorescence Emission (L.I.F.E): In Situ Nondestructive Detection of Microbial Life in the Ice Covers of Antarctic Lakes. Astrobiology. 9, 659-672 (2009).
- Murray, A. E., et al. Microbial life at -13 °C in the brine of an ice-sealed Antarctic lake. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109, 20626-20631 (2012).
- Edwards, A., et al. A distinctive fungal community inhabiting cryoconite holes on glaciers in Svalbard. Fungal Ecology. 6, 168-176 (2013).
- Miteva, V., Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Marx, J. C., Gerday, C. Bacteria in Snow and Glacier Ice. Psychrophiles: from Biodiversity to Biotechnology. , 31-50 (2008).
- Yallop, M. L., et al. Photophysiology and albedo-changing potential of the ice algal community on the surface of the Greenland ice sheet. The ISME Journal. 6, 2302-2313 (2012).
- Edwards, A., et al. A metagenomic snapshot of taxonomic and functional diversity in an alpine glacier cryoconite ecosystem. Environmental Research Letters. 8, 035003 (2013).
- Remias, D., et al. Characterization of an UV-and VIS-absorbing, purpurogallin-derived secondary pigment new to algae and highly abundant in Mesotaenium berggrenii (Zygnematophyceae, Chlorophyta), an extremophyte living on glaciers. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 79, 638-648 (2012).
- Cook, J., et al. An improved estimate of microbially mediated carbon fluxes from the Greenland ice sheet. Journal of Glaciology. 58, 1098-1108 (2012).
- Mueller, D. R., Vincent, W. F., Pollard, W. H., Fritsen, C. H. Glacial cryoconite ecosystems: a bipolar comparison of algal communities and habitats. Nova Hedwigia Beiheft. 123, 173-198 (2001).
- Morgan-Kiss, R. M., Priscu, J. C., Pocock, T., Gudynaite-Savitch, L., Huner, N. P. A. Adaptation and Acclimation of Photosynthetic Microorganisms to Permanently Cold Environments. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 70, 222-252 (2006).
- Hodson, A., et al. The cryoconite ecosystem on the Greenland ice sheet. Annals of Glaciology. 51, 123-129 (2010).
- Tilg, M., et al. L.I.F.E.: laser induced fluorescence emission, a non-invasive tool to detect photosynthetic pigments in glacial ecosystems. Proceedings SPIE. 8152, Instruments, Methods, and Missions for Astrobiology XIV, 81520I. , (2011).
- Lorenzen, C. J. Determination of chlorophyll and pheo-pigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnology & Oceanography. 12, 343-346 (1967).
- Kirchman, D. Measuring bacterial biomass production and growth rates from leucine incorporation in natural aquatic environments. Methods in Microbiology. , 227-238 (2001).
- Bell, R. T., Kemp, P. F., Cole, J. J., Sherr, B. F., Sherr, E. B. Estimating production of heterotrophic bacterioplankton via incorporation of tritiated thymidine. Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology. Edited by. , 495-503 (1993).
- Groemer, G., et al. Field trial of a dual-wavelength fluorescent emission (L.I.F.E.) instrument and the Magma White rover during the MARS2013 Mars analog mission. Astrobiology. 14, 391-405 (2014).
- Beutler, M. . Spectral fluorescence of chlorophyll and phycobilins as an in situ tool of phytoplankton analysis-models, algorithms and instruments. , (2003).
- Krogmann, K. D. Discoveries in Oxygenic Photosynthesis (1727-2003): A Perspective. Photosynthesis Research. 80, 15-57 (2004).
- Corrêa, D. S., et al. Reverse saturable absorption in chlorophyll A solutions. Journal of Applied Physics B. 74, 559-561 (2002).
- Kaňa, R., et al. The slow S to M fluorescence rise in cyanobacteria is due to a state 2 to state 1 transition. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1817, 1237-1247 (2012).
Explore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved