Intraoperative Assessment of Resection Margins in Oral Cavity Cancer: This is the Way
In This Article
Summary
The goal of this protocol is to provide a clear overview of specimen-driven intraoperative assessment of resection margins. It is encouraged to implement this protocol to improve patient care at other institutes.
Abstract
The goal of head and neck oncological surgery is complete tumor resection with adequate resection margins while preserving acceptable function and appearance. For oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OCSCC), different studies showed that only 15%-26% of all resections are adequate. A major reason for the low number of adequate resections is the lack of information during surgery; the margin status is only available after the final histopathologic assessment, days after surgery.
The surgeons and pathologists at the Erasmus MC University Medical Center in Rotterdam started the implementation of specimen-driven intraoperative assessment of resection margins (IOARM) in 2013, which became the standard of care in 2015. This method enables the surgeon to turn an inadequate resection into an adequate resection by performing an additional resection during the initial surgery. Intraoperative assessment is supported by a relocation method procedure that allows accurate identification of inadequate margins (found on the specimen) in the wound bed.
The implementation of this protocol resulted in an improvement of adequate resections from 15%-40%. However, the specimen-driven IOARM is not widely adopted because grossing fresh tissue is counter-intuitive for pathologists. The fear exists that grossing fresh tissue will deteriorate the anatomical orientation, shape, and size of the specimen and therefore will affect the final histopathologic assessment. These possible negative effects are countered by the described protocol. Here, the protocol for specimen-driven IOARM is presented in detail, as performed at the institute.
Introduction
Every year, around 350,000 new patients are diagnosed worldwide with cancer in the oral cavity; 90% of cases are squamous cell carcinoma1. The mortality rate is 175,000 worldwide per year and the 5-year survival is 50% to 64.8%1,2,3,4.
The primary treatment of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OCSCC) is surgery5. The goal of the surgery is the complete removal of the tumor with adequate margins, according to the Royal College of Pathologists6. Margins >5 mm (clear) are regarded as adequate, whereas margins from 0-5 mm are regarded as inadequate.
Adequate resection margins lead to higher survival and a reduction in local recurrence-rates of OCSCC7,8,9. Tumor resections with inadequate margins result in the need for adjuvant therapy (postoperative radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy). This brings an additional burden for the patient, increasing morbidity and reducing the quality of life10. The resection margin is the only oncological prognostic factor that the surgeon and pathologist can influence.
Recent reports have shown that adequate resections are only achieved in 15%-26% of cases7,8,11. These poor results are caused by the complex anatomy of the oral cavity and the lack of intraoperative guidance. During surgery, the surgeon can only rely on inspection, palpation, and preoperative imaging.
The final margin status follows only several days after the operation. If an inadequate margin is encountered at the final pathologic assessment, a second operation is usually not an option, because the wound bed reconstruction has usually healed by that time. Moreover, a second operation is mostly not effective, because the relocation of the inadequate margin is even more difficult in the postoperative setting.
To overcome the lack of intraoperative information about margin status, specimen-driven intraoperative assessment of resection margins (IOARM) was implemented in 20139. It became the standard of care in the institute in 2015. Described here is the IOARM method in detail to enable colleagues at other institutes to implement this protocol.
Protocol
This study was approved by the institutional Medical Ethics Committee (MEC-2015-150).
NOTE: All the patient and personnel information in the figures or examples are fictional (i.e., XXXXX and YYYYY).
1. Before surgery
- Surgery department: Request for IOARM during the planning of surgery.
- Pathology department: Ensure logistics/equipment (see Table of Materials) and the availability of personnel (pathologist/pathology resident and assistant).
2. During surgery
- Operation room (OR)
- Ensure that all involved personnel are familiar with the relocation protocol12.
- Follow the relocation protocol.
- Submerge the tags in chlorhexidine for at least 30 min before the start of the surgery.
- Place the tags paired on either side of the intended line of resection (both superficial and deep), so that one tag is on the resection specimen and the other remains at the corresponding spot in the wound bed (Figure 1A) as described by Van Lanschot et al.12.
- Cut between each pair of tags.
- Remove the specimen with the tumor (one tag from each pair remains in the wound bed, Figure 1B).
- Fill out the pathology request form with a clear indication of the anatomical location of the tags (e.g., tag 1 = anterior, tag 2 = superior).
- Record the surgical procedure-related defects of the specimen and their location in relation to the tags, on the pathology request form.
NOTE: Procedure-related defects create false resection surfaces and can lead to incorrect allocation of inadequate margins during both IOARM and final pathology. - Bring the specimen to the pathology department.
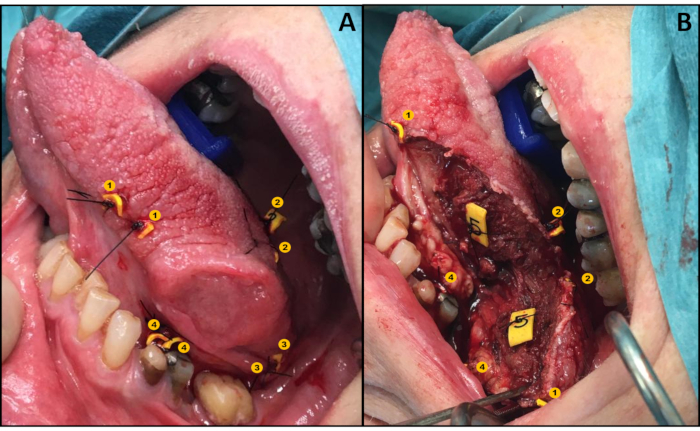
Figure 1: Illustration of the relocation protocol. (A) Application of tags in a pair-wise manner. (B) Wound bed and specimen both with one tag of each pair. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- IOARM - Grossing room (GR), pathology department
- Rinse the specimen with water and gently pat it dry with gauze or paper.
NOTE: Register every next step with photographs and store them in the Electronic Patient File (EPF). - Record the general information (date, patient id, pathology number, surgeon, pathologist, type of specimen, and tags used) on the anatomical template.
- Indicate the locations of the tags on the anatomical template (Figure 2).
- Place the specimen on the anatomical template.
- Rinse the specimen with water and gently pat it dry with gauze or paper.
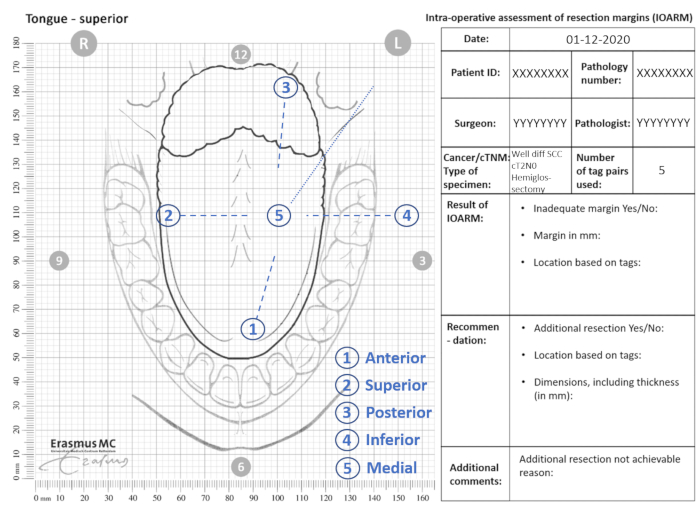
Figure 2: Example of anatomical template for IOARM. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Ink the resection surface according to standard protocol (e.g., superior blue and inferior green).
- Inspect the specimen visually and by palpation (pathologist and surgeon).
- Indicate the location of any suspicious region (i.e., margin <5 mm) on the anatomical template and relate it to the numbered tags (section Result of IOARM, Figure 2).
- Perform an incision perpendicular to the resection surface at the suspicious region (Figure 3A). Depending on the size of the specimen and/or suspicious regions, make one or more incisions with a distance of about 5 mm. In case of more than one incision, number the incisions as IOA1, IOA2, etc.
- Measure the margins (i.e., the distance between resection surface and tumor border) on the tissue sections (Figure 3B) and record the exact values in mm on the anatomical template (section Result of IOARM, Figure 3C).
NOTE: If the tumor border is macroscopically not distinguishable (e.g., the tumor cannot be distinguished from surrounding fibrotic or salivary gland tissue), microscopic analysis by frozen section is indicated.
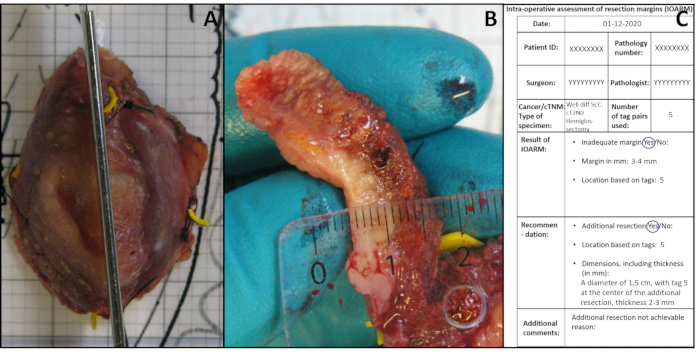
Figure 3: Illustration of IOARM. (A) Perpendicular incision performed after identification of suspicious region by palpation. (B) The margin is measured. (C) The result of IOARM and the recommendation are recorded. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Proceed with the completion of the operation, step 2.2.19. If an adequate margin is detected (i.e., additional resection is not needed).
- Indicate the exact location based on the tags if an inadequate margin is detected and record it on the template. Proceed with an additional resection if surgically/technically achievable, step 2.2.13.
- Annotate the reason on the template, if an additional resection is not achievable (section Additional comments, Figure 2).
- Recommend (pathologist/surgeon) the additional resection based on the exact location and indicate the thickness needed to achieve an adequate resection (Figure 3C).
NOTE: If the inadequate margin concerns a positive margin, a minimal thickness of 6 mm should be recommended for the additional resection. - Keep (pathologist) the main resection specimen in the refrigerator until the additional resection is received.
- Relocate (surgeon) the area of additional resection in relation to the tags, in the wound bed, based on the record of IOARM (Figure 3C).
- Perform the additional resection.
- Send the additional resection to the GR.
- Verify (pathologist) the accuracy of the additional resection regarding its location (based on tags) and its size.
NOTE: The above steps are applicable in the case of a close margin. In the case of a positive margin, an IOARM of the additional resection is necessary (pathologist). The surgeon waits for the result of the second IOARM before completing the operation. - Remove (surgeon) the remaining tags from the wound bed and complete the operation.
- Copy (pathologist) all data from the anatomical template to the EPF.
3. After IOARM - Grossing room (GR), pathology department
NOTE: To preserve the anatomical orientation and shape of the specimen the following steps are performed.
- Reassemble the specimen by the correct orientation of all tissue sections (cross-sections and the polar ends) based on the tags and the photographs recorded during IOARM.
NOTE: Cross-sections are in the middle of the specimen and the polar ends are the outer parts of the specimen. - Cut the pieces of cork slightly larger than the tissue sections.
- Place each tissue section on a piece of cork.
- Draw a line on the cork around the tissue section with a permanent marker and take a photograph (Figure 4A).
- Place another piece of cork on top of all tissue sections except the polar ends (Figure 4B).
- Keep the upper and lower cork together, with the tissue section in between, by placing pins through both corks next to the edge of the tissue section, but not through the tissue section (Figure 4B).
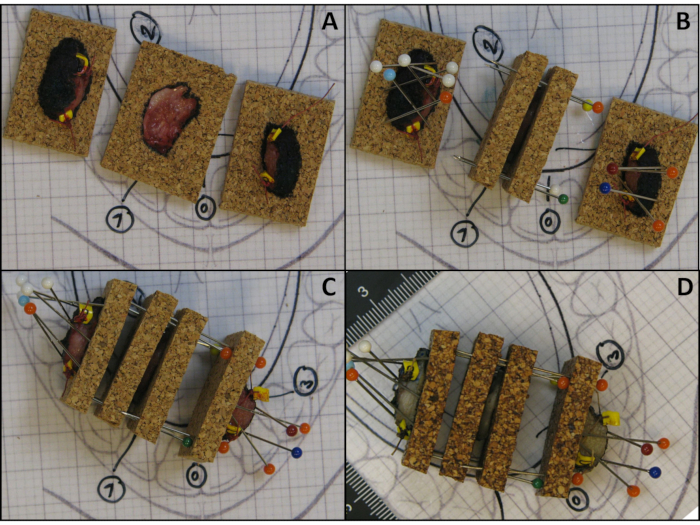
Figure 4: Illustration of the method to preserve the anatomical orientation and shape of tissue sections. (A) Tissue sections are placed on a piece of cork with a line drawn on the cork around the tissue section with a permanent marker. (B) Pins are obliquely placed over the polar ends and another piece of cork is placed over the tissue section. (C) Illustration of a reassembled fresh specimen kept together with pins that puncture the adjacent corks. (D) Illustration of a reassembled fixed specimen kept together with pins that puncture adjacent corks. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Place the polar ends on a separate piece of cork (Figure 4A).
- Keep the polar ends attached to the cork by obliquely placing pins over the tissue and piercing the cork just beside the edge of the tissue (Figure 4B).
CAUTION: Do not puncture the specimen with the pins. - Reassemble the whole specimen: put all the tissue sections including the polar ends together in the correct anatomical orientation.
- Keep all the tissue sections together by puncturing the adjacent corks (Figure 4C).
- Position the specimen with the correct orientation on the anatomical template and take a photograph.
- Place the specimen in formaldehyde solution (formalin 4%).
NOTE: For proper fixation, pieces of paper can be placed on top of the specimen to keep it submerged in formalin. - Make a clear and visible warning note on the container with the specimen (e.g., caution needles/pins), to avoid accidents.
- Store the container with the specimen for further processing, according to the standard pathology protocol.
4. Grossing of the fixed specimen after IOARM
NOTE: After formalin fixation, the specimen should be grossed preferably by the pathologist/resident/assistant, who performed the IOARM.
CAUTION: Be careful with the needles/pins when removing the specimen from the container.
- Follow the institutional grossing protocol.
NOTE: Take additional measures to ensure the correct orientation and to facilitate the comparison of the margin status between IOARM and final pathologic assessment.- Consult the pictures of the IOARM.
- Take the specimen out of the container.
- Check whether all the tissue sections are present.
- Position the specimen with the correct orientation on the anatomical template and take a photograph (Figure 4D).
- Remove the pins.
- Separate the individual tissue sections with corresponding cork.
- Take photographs of each tissue section with their corresponding corks, focusing on the lines that were drawn around the tissue section to assess possible shrinkage of tissue after fixation (Figure 5).
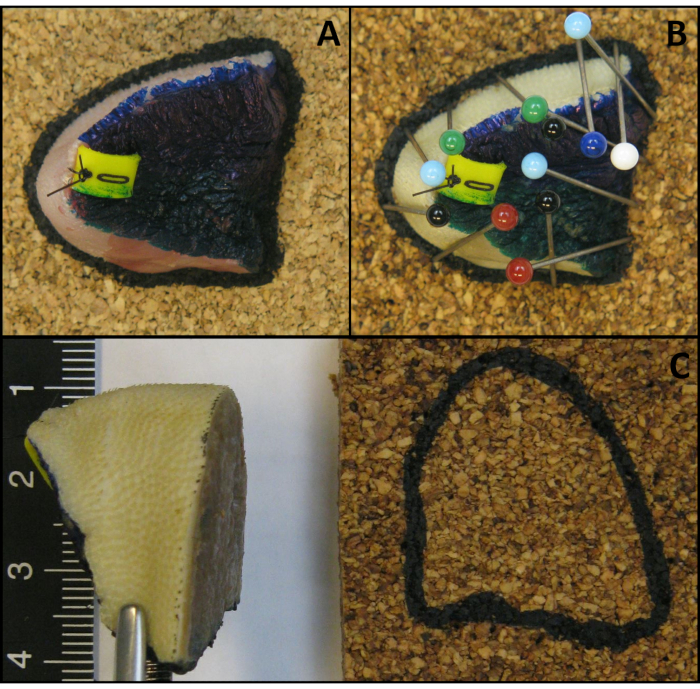
Figure 5: Illustration of a polar end with the cut surface facing the cork, held against the cork by tilted pins. (A) Fresh specimen. (B) After fixation. (C) The cut surface of the polar end is flat after fixation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Detach all tissue sections systematically from the cork (e.g., start from anterior to posterior or left to right).
- Gross the IOARM-tissue sections to the standard final tissue sections (2-3 mm thick).
- Place all final tissue sections, in the correct anatomical orientation (e.g., from anterior to posterior), on a paper on the grossing table.
- Number all the final tissue sections consecutively with a permanent marker on the paper (Figure 6).
- Annotate the location of IOARM with a permanent marker (Figure 6).
- Take photographs, including all final tissue sections and store them in the EPF (Figure 6).
- Select the relevant final tissue sections and IOARM sections to be further processed for final pathologic assessment.

Figure 6: Grossed specimen with the location of the IOARM marked. Corresponding numbers 1-5 refer to tissue sections from left to right. A-E corresponds with tissue sections included for histopathologic evaluation. Note that the remaining piece of tissue that was evaluated by frozen section (FS) is indicated to enable direct comparison with the permanent HE-stained section. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. The final pathologic assessment - Impact of IOARM on final margin status
- Follow the local standardized protocol. The protocol followed here is the PALGA (Pathologisch-Anatomisch Landelijk Geautomatiseerd Archief, the nationwide network and registry of histo- and cytopathology in the Netherlands) national Head-Neck protocol for the final standardized structured pathology report.
NOTE: This protocol is based on the up-to-date standards of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC), Union for International Cancer Control (UICC), and the World Health Organisation (WHO).- Assess all the margins in millimeters, including mucosa, submucosa, and bone.
- If an inadequate margin is found, annotate its extent (e.g., submucosal margin anterior is 3.5 mm, extending over a trajectory of 6 mm).
- Assess the presence of dysplasia and its grade for mucosal resection margins.
- Indicate the final margin by adding the dimensions of the additional resection (if performed) to the margin measured on the main specimen.
- Record the unique pathology number of the additional resection in the pathology report of the main specimen (e.g., Margins: anterior 6 mm, posterior 8 mm, superior 6 mm (including 3mm of the additional resection, H20-2021), inferior 7 mm, medial 5.3 mm).
- Verify the margins found during IOARM.
- Annotate the result of this verification (e.g., NB Margins found during the intraoperative assessment are in concordance with margins based on the final pathology).
NOTE: The time needed for IOARM should be limited in order to not interfere with the surgical workflow. At the institute, the IOARM takes about 10 min. The surgeon and pathologist perform the IOARM together. For the relocation method (placing the tags during surgery) an additional time of 5 min is needed. This will differ for each institute depending on the logistics.
Representative Results
Example of IOARM resulting in an adequate resection
The patient presents with a cT2N0M0 SCC of the left side of the tongue with no medical history. The patient undergoes hemiglossectomy supported by IOARM. The specimen is inspected and palpated; the mucosal margins are measured as >5 mm. One area in the submucosal resection surface is suspicious for an inadequate margin, located around tag 5. The submucosal margin is 3-4 mm at tag 5. All the information is recorded on the template and copied to the EPF (Figure 7A).
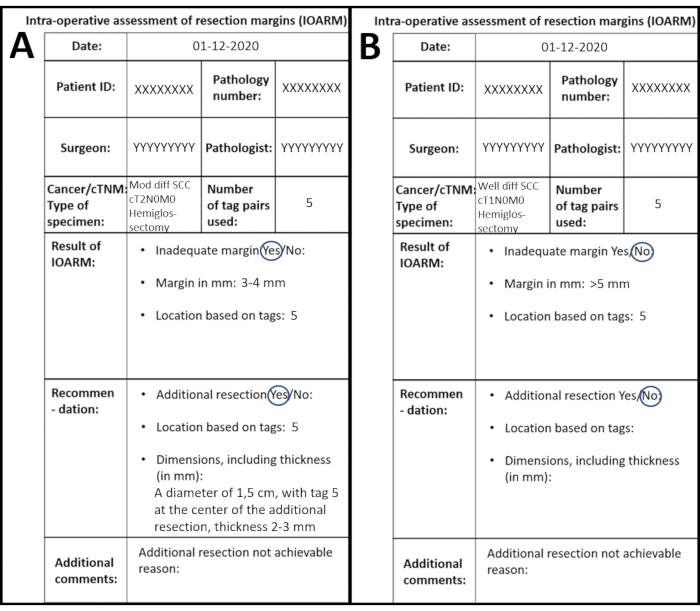
Figure 7: Examples of two different IOARMs recorded on the anatomical template. (A) IOARM resulting in an adequate resection. (B) IOARM not resulting in an adequate resection. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The surgeon returns to the OR and performs the additional resection. The pathologist verifies the accuracy and dimensions, including the thickness of the additional resection.
The final pathology report shows the presence of moderately differentiated pT2 squamous cell carcinoma on the left side of tongue. The tumor diameter is 2.5 cm and the depth of invasion is 6.0 mm. The worst pattern of invasion (WPOI) is category 3. Perineural invasion (PNI) is not present and the lymphovascular invasion (LVI) is present. The minimal margins (mucosal and submucosal) at the inferior, superior, anterior, and posterior location are 5.8 mm (including additional resection (PA number: XXXXX) of 3 mm thickness), 6.2 mm (including additional resection (PA number: XXXXX) of 3 mm thickness), 5.2 mm, and 5.5 mm, respectively. IOARM is in concordance with final pathology.
| Margins (mm) | |||
| Location | Based on IOARM | After additional resection | Based on Final pathology |
| Inferior | 3-4 | 6-7 | 5.8 |
| Superior | 3-4 | 6-7 | 6.2 |
| Anterior | >5 | 5.2 | |
| Posterior | >5 | 5.5 | |
Table 1: Example of resection margins during IOARM resulting in an adequate resection at final pathology, after additional resection.
Example of IOARM not resulting in an adequate resection
The patient presents with a cT1N0M0 SCC of the right side of the tongue with no medical history. The patient underwent a resection supported by IOARM. The surgeon takes the specimen to the pathologist at the pathology department. The mucosa is visually inspected, and the mucosal margins are measured with a transparent ruler, all mucosal margins are >5 mm. The submucosal margins are visually inspected and palpated and all margins seem >5 mm. A suspicious area is found at tag 1 (anterior resection surface) and tag 3 (posterior resection surface). A grossing knife is placed perpendicular to the resection surface from anterior to posterior (tag 1 to tag 3) and an incision is made. The pathologist measures the margin on the cross-section and the margins are >5 mm. All the information is recorded on the template and copied to the EPF (Figure 7B).
The final pathology report shows a well-differentiated pT1 squamous cell carcinoma on the right side of the tongue. The diameter of the tumor is 1.8 cm, and the depth of invasion is 3.8 mm. The worst pattern of invasion (WPOI) is category 2. Perineural invasion (PNI), lymphovascular invasion (LVI), and dysplasia are not present. The minimal margins (mucosal and submucosal) at the inferior, superior, anterior, and posterior locations are 4.0 mm, 6.1 mm, 6.4 mm, and 7.8 mm, respectively. IOARM is not in concordance with final pathology, margin inferior was missed.
| Margins (mm) | |||
| Location | Based on IOARM | After additional resection | Based on Final pathology |
| Inferior | >5 | Not recommended all margins > 5mm | 4.0 |
| Superior | >5 | 6.1 | |
| Anterior | 6 | 6.4 | |
| Posterior | 8 | 7.8 | |
Table 2: Example of resection margins during IOARM not resulting in an adequate resection at final pathology.
Discussion
The goal of surgical treatment of OCSCC patients is the complete removal of the tumor with adequate margins. This is too often not achieved, which inspired to design an adjusted approach to oral cancer surgery with a focus on intraoperative assessment of resection margins. Aside from resection margins, other adverse tumor factors such as the pattern of invasion, perineural invasion, and lymphovascular invasion also affect the local recurrence. However, of all adverse tumor factors, surgeons and pathologists can only influence the resection margins7,8,11.
The specimen-driven IOARM method was implemented in 2013; this was eventually supported by the evidence that specimen-driven IOARM is superior to defect-driven IOARM7,13,14,15,16,17. This resulted in its recommendation by AJCC in 201718. Noteworthy, the specimen-driven IOARM method became the standard of care in the institute in 2015. From 2013 until 2020 the IOARM was performed in 304 cases with a steep increase from 2018.
It is important to realize that developing and implementing an IOARM method involves many personnel (pathologists/surgeons/assistants/trainees/researchers), in order to make it standard of care. Many professionals were involved, during many years, in the development of this protocol, which is actually the strength of the method. The development of this method started in 2013 and reached a consensus in 2015. This was achieved based on the two-weekly meetings during which discussions regarding all the patients treated with surgery, including IOARM, took place. In this way, it was possible to timely adjust and refine the procedure. Besides, the two-weekly meetings enabled prospective data collection, which provides the basis for the performance and follow-up studies9. Moreover, for every case, the team ensured that the final pathology was not compromised due to IOARM. Finally, it is important to realize that this kind of assessment is a dynamic process and will always undergo changes toward improvement.
With the specimen-driven IOARM method, the margins are assessed by inspection, palpation, and perpendicular incisions (grossing). This approach provides an as accurate as possible estimation of margins in millimeters and enables feedback on whether an additional resection is needed and what the dimensions should be. Kubik et al. described several reasons (e.g., additional resection at an incorrect location, the incorrect orientation of the additional resection, incorrect dimensions of the additional resection) for additional resections to be inadequate17. The IOARM is a valuable method but only when accompanied by an as accurate as possible relocation method of inadequate margins to enable the surgeon to perform an adequate additional resection. The spatial relationship between the additional resection and the main specimen is the key factor. Therefore, a simple but elegant relocation method as shown in Figure 1 was developed and described in detail by Van Lanschot et al.12. This method allows the surgeon to perform an additional resection based on the relocation of the inadequate margin defined by the tags in the wound bed. For example, a margin of 2 mm is found between tags 1-2-3, the surgeon performs an additional resection around tags 1-2-3 with a thickness of 4 mm. This relocation method is shown to be effective by the results of Smits et al.9.
This IOARM method is supported by frozen section procedure only if the tumor cannot be distinguished macroscopically from surrounding tissue (e.g., fibrosis of tissue after radiotherapy or scar formation after previous surgery, or salivary gland tissue). Some institutes use another approach, in which frozen sections are taken from the specimen from all quadrants13,19. This method enables a more standardized protocol. However, the comprehensiveness of this method might not be always efficient. Moreover, multiple frozen sections are needed which is costly, time-consuming, and not accessible for all institutes. The described method is more efficient because the region of interest is preselected (i.e., region of suspicious inadequate margin) and is therefore cheaper, faster, and available for every institute. This is in accordance with previous findings that frozen section analysis does not improve the accuracy of specimen-driven IOARM based on grossing in most cases and is not cost-effective20,21,22.
According to the literature >93% of all inadequate margins are found at the submucosal resection margins23. This is in line with the findings of the institute. Mucosal alterations with high-grade dysplasia/CIS are often easy to detect during IOARM, only in a few cases, a frozen section is recommended. Until now in the IOARM cohort, any mucosal positive margins regarding cancer or high-grade dysplasia/CIS have not been encountered.
Even though specimen-driven IOARM significantly improves the rate of adequate resections in OCSCC patients and consequently improves patient outcome7,9,22,21, its wide implementation is lagging. The main cause of this is the fact that the grossing of fresh tissue is counter-intuitive for pathologists. The pathologists are fearful that grossing fresh tissue will deteriorate the anatomical orientation, shape, and size of the specimen, and therefore will affect the final histopathologic assessment24,25. However, the measures prescribed in the protocol prevent these possible negative effects. Since the implementation of this protocol, the anatomical orientation, shape, and size of the specimen have never been altered nor was the final pathologic assessment ever compromised (manuscript in preparation).
Although little additional time is required to perform IOARM, it is clear that no real obstacles exist to implement IOARM, but there must be a willingness to go through a learning curve, regarding the grossing of fresh tissue and identifying inadequate margins. The most important prerequisite is a dedicated and cooperative team of surgeons and pathologists. In this study, an IOARM method for head and neck cancer surgery has been described, that can easily be implemented in every institute and during any other cancer surgery. This protocol significantly improves the rate of adequate resections while concomitantly reducing the need for postoperative radiotherapy and improving the patient outcome. The specimen-driven IOARM method will help surgeons to achieve first-time-right surgery and patients will benefit.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We thank Bas J. van Brakel and Roxanna Haak for their help in performing IOARM. Klara A. Bouman-Zevenbergen, Ian Overduin, and Silvy L. Sabiran - Singoredjo for their assistance and supportive role in ensuring logistics, equipment, and availability of personnel at the pathology department.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Anatomical templates | https://www.palga.nl/assets/uploads/Protocollen/HoofdHalstumoren.pdf | ||
| Anatomical tweezers | |||
| Brush | to apply the inc to the tissue | ||
| Bucket for formalin fixation | Size of the container depends on the size fo the tissue | ||
| Buffered formalin 4% | |||
| Camera | |||
| Computer | |||
| Cork | Thin plates of cork | ||
| Ethanol 70% | |||
| Examination gloves | |||
| Gauze or Paper | That wont leave particles on the specimen | ||
| Grossing knife 15cm | |||
| Grossing knife 30cm | |||
| Grossing tabel | |||
| Inc for tissue | 3 or more different colors | ||
| Labcoat | |||
| Long pins/Sewing pins | |||
| Paper | To place the tissue sections on during the grossing | ||
| Permanent markers | Different colors (black/blue/red/green) | ||
| Relocation tags | Premier Farnell Limited BV, Utrecht, The Netherlands | Numbered froimn 0-9, cut to a size of 5 mm x 7 mm x 2 mm | |
| Scalpel | |||
| Surgical tweezers | |||
| Sutures | Ethicon | Ethilon 3.0 | To suture in the tags |
| Tap water | |||
| Transparant ruler 30 cm | 2 rulers needed |
References
- Bray, F., et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 68 (6), 394-424 (2018).
- Sharma, S. M., Prasad, B. R., Pushparaj, S., Poojary, D. Accuracy of intraoperative frozensection in assessing margins in oral cancer resection. Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery. 8 (4), 357-361 (2009).
- vander Ploeg, T., Datema, F., Baatenburg de Jong, R., Steyerberg, E. W. Prediction of survival with alternative modeling techniques using pseudo values. PLoS One. 9 (6), 100234 (2014).
- Chen, S. W., et al. Trends in clinical features and survival of oral cavity cancer: fifty years of experience with 3,362 consecutive cases from a single institution. Cancer Management and Research. 10, 4523-4535 (2018).
- Shah, J. P., Gil, Z. Current concepts in management of oral cancer--surgery. Oral Oncology. 45 (4-5), 394-401 (2009).
- Helliwell, T., Woolgar, J. Dataset for histopathology reporting of mucosal malignancies of the oral cavity. Royal College of Pathologists. , (2013).
- Varvares, M. A., Poti, S., Kenyon, B., Christopher, K., Walker, R. J. Surgical margins and primary site resection in achieving local control in oral cancer resections. The Laryngoscope. 125 (10), 2298-2307 (2015).
- Smits, R. W., et al. Resection margins in oral cancer surgery: Room for improvement. Head & Neck. 38, 2197-2203 (2016).
- Smits, R. W. H., et al. Intraoperative assessment of the resection specimen facilitates achievement of adequate margins in oral carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology. 10, 614593 (2020).
- Lin, A. Radiation therapy for oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. Dental Clinics of North America. 62 (1), 99-109 (2018).
- Dik, E. A., et al. Resection of early oral squamous cell carcinoma with positive or close margins: relevance of adjuvant treatment in relation to local recurrence: margins of 3 mm as safe as 5 mm. Oral Oncology. 50 (6), 611-615 (2014).
- van Lanschot, C. G. F., et al. Relocation of inadequate resection margins in the wound bed during oral cavity oncological surgery: A feasibility study. Head & Neck. 41 (7), 2159-2166 (2019).
- Amit, M., et al. Improving the rate of negative margins after surgery for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective randomized controlled study. Head & Neck. 38, 1803-1809 (2016).
- Maxwell, J. H., et al. Early oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: Sampling of margins from tumor bed and worse local control. JAMA Otolaryngology-- Head & Neck Surgery. 141 (12), 1104-1110 (2015).
- Hinni, M. L., Zarka, M. A., Hoxworth, J. M. Margin mapping in transoral surgery for head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope. 123 (5), 1190-1198 (2013).
- Kain, J. J., et al. Surgical margins in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Current practices and future directions. Laryngoscope. 130 (1), 128-138 (2020).
- Kubik, M. W., et al. Intraoperative margin assessment in head and neck cancer: a case of misuse and abuse. Head and Neck Pathology. 14 (2), 291-302 (2020).
- Amin, M. B., et al. The Eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 67 (2), 93-99 (2017).
- Gokavarapu, S., et al. Revision of margins under frozen section in oral cancer: a retrospective study of involved margins in pT1 and pT2 oral cancers. The British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. 53 (9), 875-879 (2015).
- Chaturvedi, P., et al. Gross examination by the surgeon as an alternative to frozen section for assessment of adequacy of surgical margin in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head & Neck. 36 (4), 557-563 (2014).
- Mair, M., et al. Intraoperative gross examination vs frozen section for achievement of adequate margin in oral cancer surgery. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology. 123 (5), 544-549 (2017).
- Datta, S., et al. Frozen section is not cost beneficial for the assessment of margins in oral cancer. Indian Journal of Cancer. 56 (1), 19-23 (2019).
- Woolgar, J. A., Triantafyllou, A. A histopathological appraisal of surgical margins in oral and oropharyngeal cancer resection specimens. Oral Oncology. 41 (10), 1034-1043 (2005).
- Umstattd, L. A., Mills, J. C., Critchlow, W. A., Renner, G. J., Zitsch, R. P. Shrinkage in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An analysis of tumor and margin measurements in vivo, post-resection, and post-formalin fixation. American Journal of Otolaryngology. 38 (6), 660-662 (2017).
- Pangare, T. B., et al. Effect of Formalin Fixation on Surgical Margins in Patients With Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. 75 (6), 1293-1298 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved