Abstract
Immunology and Infection
تفعيل وارتقاط السكريات المتعددة القابلة للذوبان باستخدام 1-سيانو-4-ديميثيلامينوبيريدين تترافلوروبورات (CDAP)
ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …اللقاحات المصاحبة هي تقدم ملحوظ في علم اللقاحات. لإعداد اللقاحات المترافقة مع السكريات المتعددة، يمكن تشغيل السكريات بشكل ملائم وربطها بالبروتينات الناقلة لللقاحات باستخدام 1-سيانو-4-ديميثيلامينوبيريدين رباعي فلوريدين (CDAP)، وهو كاشف سيانيلاتينغ سهل المعالجة. CDAP ينشط السكريات عن طريق التفاعل مع مجموعات هيدروكسيل الكربوهيدرات في PH 7-9. الاستقرار والتفاعل من CDAP تعتمد بدرجة عالية على درجة الحموضة. انخفاض درجة الحموضة من رد الفعل أيضا أثناء التنشيط بسبب التحلل المائي للCDAP، مما يجعل درجة الحموضة جيدة السيطرة على مفتاح لتنشيط استنساخها. تم تنفيذ بروتوكول تنشيط CDAP الأصلي في درجة حرارة الغرفة في حلول درجة الحموضة 9 غير المكتومة.
بسبب رد الفعل السريع في ظل هذه الحالة (<3 دقيقة) وانخفاض الرقم الحموضة السريع المصاحب من التحلل المائي السريع CDAP ، كان من الصعب ضبط درجة الحموضة المستهدفة والحفاظ عليها بسرعة في الإطار الزمني القصير. يتم تنفيذ البروتوكول المحسن الموصوف هنا عند 0 درجة مئوية ، مما يبطئ التحلل المائي CDAP ويمدد وقت التنشيط من 3 دقائق إلى ~ 15 دقيقة. كما تم استخدام Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) كمخزن مؤقت لضبط حل السكريات مسبقا إلى الرقم الحموضة لتنشيط الهدف قبل إضافة كاشف CDAP. وقت رد الفعل أطول، إلى جانب تحلل هيدروليسيس CDAP أبطأ واستخدام المخزن المؤقت DMAP، يجعل من الأسهل للحفاظ على درجة الحموضة التنشيط لكامل مدة عملية التنشيط. البروتوكول المحسن يجعل عملية التنشيط أقل المحمومة، وأكثر استنساخا، وأكثر قابلية للتوسع.
Erratum
Erratum: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP)An erratum was issued for: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP). A figure was updated.
Figure 4 was updated from:
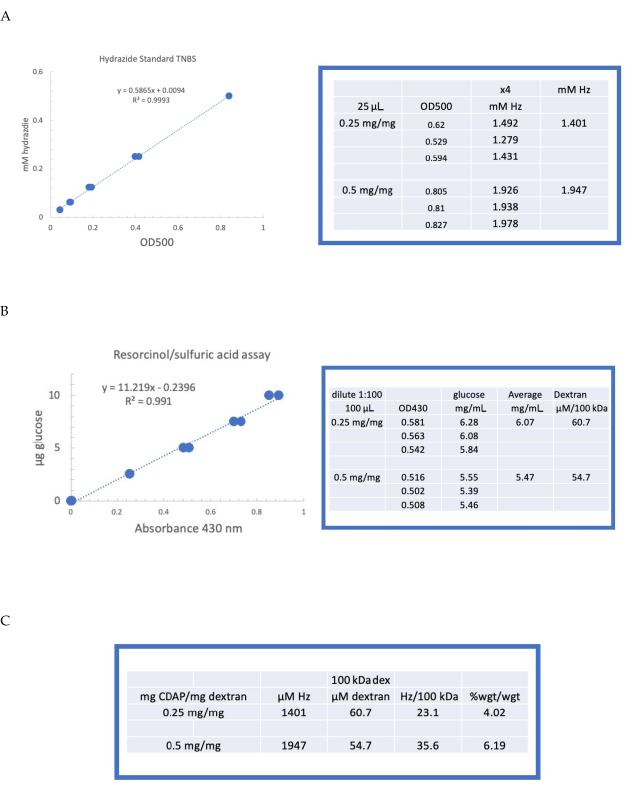
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
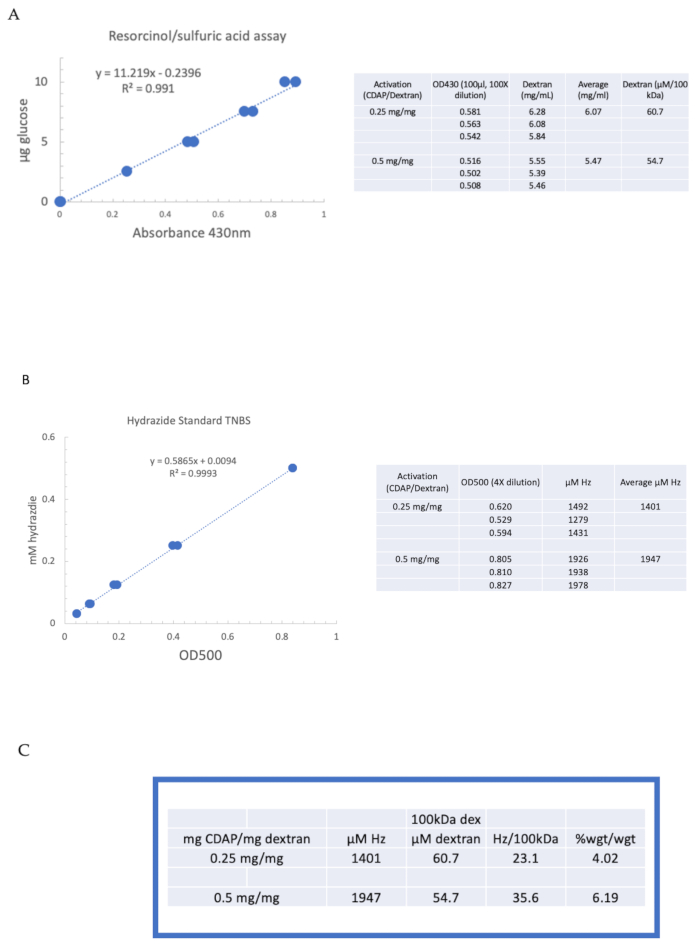
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Tags
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved