Abstract
Immunology and Infection
Attivazione e coniugazione di polisaccaridi solubili utilizzando 1-ciano-4-dimetilamminopiridina tetrafluoroborato (CDAP)
ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …I vaccini coniugati sono notevoli progressi nella vaccinologia. Per la preparazione di vaccini coniugati con polisaccaridi, i polisaccaridi possono essere comodamente funzionalizzati e collegati alle proteine portanti del vaccino utilizzando 1-ciano-4-dimetilamminopiridina tetrafluoroborato (CDAP), un reagente cianolante facile da maneggiare. CDAP attiva i polisaccaridi reagendo con i gruppi ossidrilici dei carboidrati a pH 7-9. La stabilità e la reattività del CDAP dipendono fortemente dal pH. Il pH della reazione diminuisce anche durante l'attivazione a causa dell'idrolisi del CDAP, che rende un buon controllo del pH la chiave per l'attivazione riproducibile. Il protocollo di attivazione CDAP originale è stato eseguito a temperatura ambiente in soluzioni di pH 9 non tamponate.
A causa della reazione rapida in questa condizione (<3 min) e del rapido calo del pH che accompagna la rapida idrolisi CDAP, è stato difficile regolare rapidamente e mantenere il pH della reazione target nel breve lasso di tempo. Il protocollo migliorato qui descritto viene eseguito a 0 °C, che rallenta l'idrolisi CDAP ed estende il tempo di attivazione da 3 min a ~15 min. La dimetilamminopiridina (DMAP) è stata anche utilizzata come tampone per pre-regolare la soluzione di polisaccaride al pH di attivazione target prima di aggiungere il reagente CDAP. Il tempo di reazione più lungo, unito all'idrolisi CDAP più lenta e all'uso del tampone DMAP, rende più facile mantenere il pH di attivazione per l'intera durata del processo di attivazione. Il protocollo migliorato rende il processo di attivazione meno frenetico, più riproducibile e più suscettibile di scalare.
Erratum
Erratum: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP)An erratum was issued for: Activation and Conjugation of Soluble Polysaccharides using 1-Cyano-4-Dimethylaminopyridine Tetrafluoroborate (CDAP). A figure was updated.
Figure 4 was updated from:
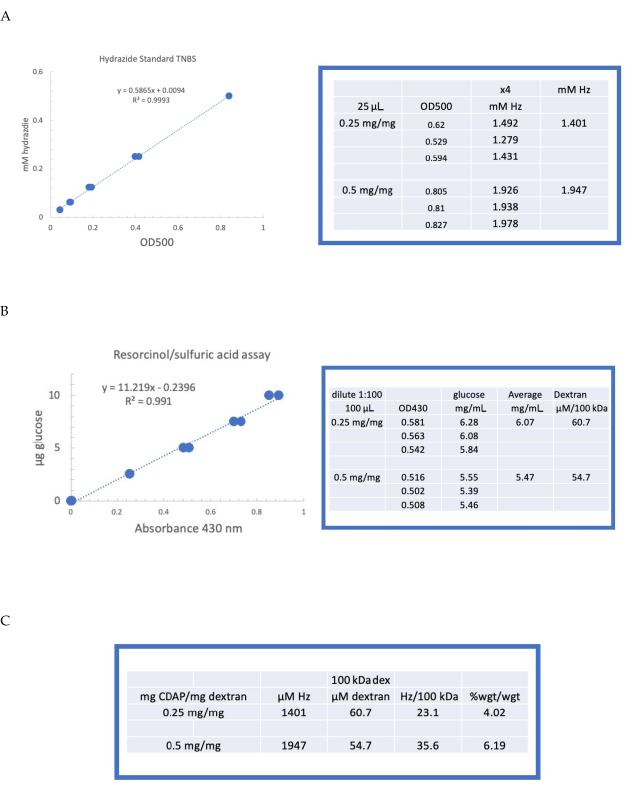
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
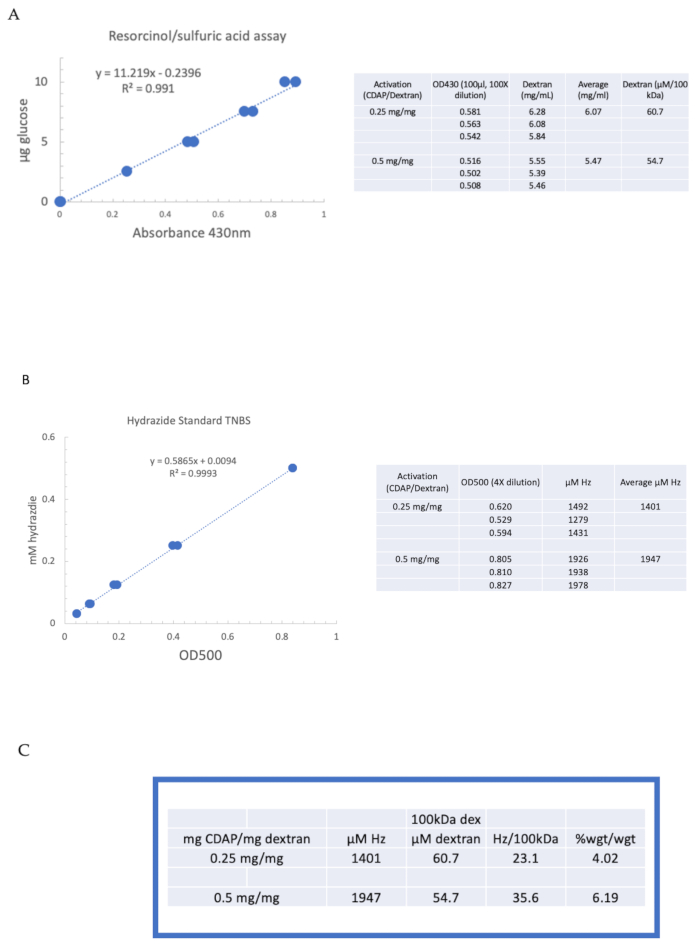
Figure 4: Representative results for CDAP activation of dextran. Typical standard curves for the (A) resorcinol/sulfuric acid and (B) TNBS assays. The assay results for dextran activated with 0.25 and 0.5 mg CDAP/mg dextran are shown. Glucose was used as the standard for the resorcinol assay. Dextran, in mg/mL, is divided by 100 kDa to give a molar concentration. The hydrazide concentration is determined using ADH as the standard and the results expressed as µM Hz. (C) Calculation of hydrazide: dextran ratios.The level of derivatization was calculated as hydrazides per 100 kDa of dextran to facilitate the comparison between polymers of different average molecular weights. The % weight ratio of g ADH/g dextran was calculated using a MW of 174 g/mole for ADH. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved