Intracerebral Transplantation and In Vivo Bioluminescence Tracking of Human Neural Progenitor Cells in the Mouse Brain
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
We describe the intraparenchymal transplantation of human neural progenitor cells transduced with a dual reporter vector expressing luciferase-green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the mouse brain. After transplantation, the luciferase signal is repeatedly measured using in vivo bioluminescence and GFP-expressing grafted cells identified in brain sections using fluorescence microscopy.
Abstract
Cell therapy has long been an emerging treatment paradigm in experimental neurobiology. However, cell transplantation studies often rely on end-point measurements and can therefore only evaluate longitudinal changes of cell migration and survival to a limited extent. This paper provides a reliable, minimally invasive protocol to transplant and longitudinally track neural progenitor cells (NPCs) in the adult mouse brain. Before transplantation, cells are transduced with a lentiviral vector comprising a bioluminescent (firefly-luciferase) and fluorescent (green fluorescent protein [GFP]) reporter. The NPCs are transplanted into the right cortical hemisphere using stereotaxic injections in the sensorimotor cortex. Following transplantation, grafted cells were detected through the intact skull for up to five weeks (at days 0, 3, 14, 21, 35) with a resolution limit of 6,000 cells using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Subsequently, the transplanted cells are identified in histological brain sections and further characterized with immunofluorescence. Thus, this protocol provides a valuable tool to transplant, track, quantify, and characterize cells in the mouse brain.
Introduction
The mammalian brain has limited regenerative capacities following injury or disease, requiring innovative strategies to promote tissue and functional repair. Preclinical strategies focus on different aspects of brain regeneration, including neuroprotection, neurogenesis, angiogenesis1,2, blood-brain-barrier repair3,4, or cell therapy5,6. Cell therapy has the advantage of being able to promote many of these pro-repair processes simultaneously. In experiments with transplantation of cells, tissue repair has occurred through (1) direct cell replacement and (2) production of cytokines leading to angiogenesis and neurogenesis7. Recent advancements in stem cell technology have further facilitated the development of scalable, well-characterized neural cell sources that are now in the pipeline for clinical trials (reviewed in 7,8,9). Although cell therapies have reached the clinical stage for a few neurological diseases (e.g., Parkinson's disease10, stroke11, and spinal cord injury12), their efficacy has been variable, and more preclinical research is needed to understand the mechanisms of graft-host interactions.
One major limitation of many preclinical studies is the continuous tracking of the transplanted cells inside the host. Often only end-point measurements are performed, omitting the dynamic migratory and survival processes in the host6,13. These limitations result in the poor characterization of the grafted cells and require high animal numbers to comprehend longitudinal changes. To overcome these limitations, in this study, we transduce induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neural progenitor cells with a commercially available dual-reporter lentiviral vector consisting of red firefly luciferase and enhanced green fluorescent protein (rFluc-eGFP). These cells are transplanted via stereotaxic intraparenchymal injection into the mouse brain and are longitudinally tracked using in vivo bioluminescence imaging over 5 weeks. After brain tissue collection, the GFP-expressing grafted cells are identified and further characterized in histological brain sections. This method can be smoothly adapted to alternative transducable cell sources and routes of transplantation for in vivo applications in the rodent brain. Overall, the procedure is valuable to obtain longitudinal information of graft survival and migration in the mouse brain and facilitates subsequent histological characterization.
Protocol
NOTE: All experiments involving mice were conducted in accordance with governmental, institutional, and ARRIVE guidelines and were approved by the Cantonal Veterinary Office of Zurich. Adult male and female non-obese diabetic SCID gamma (NSG) mice (10-14 weeks, 25-35 g) were used. Mice were housed in regular Type II/III cages in groups of at least two animals per cage in a humidity- and temperature-controlled room with a constant 12/12 h light/dark cycle. .).
1. Cell culture and viral transduction
- Differentiate neural progenitor cells (NPCs) from iPSCs using small molecule inhibitors as previously described14.
- Culture NPCs15 from passage 2 onwards in Neural Stem cell Maintenance Medium (NSMM; Table 1) supplemented with small molecules (Table 1) in 6-well plates (2 mL of medium per well) coated with poly-ornithine/laminin521 (pLO/L521). Change the medium daily.
NOTE: To passage NPCs, add 1 mL of cell dissociation reagent per well (see the Table of Materials) and incubate at 37 °C for 1 min until most cells detach.- For coating, incubate 150 µL of pLO in 1 mL of 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) per well for 2h at room temperature (RT). After three washes with PBS, incubate 10 µg of L521 in 1 mL of PBS per well for 2 h at RT.
- For viral transduction, plate 50,000 cells per well in a 24-well plate coated with pLO/L521 and add prepackaged viral vectors (pLL-EF1a-rFLuc-T2A-GFP-mPGK-Puro, LL410PA-1) to each well.
NOTE: Total infectious units (IFU) provided are >2 × 106 IFU and are enough to infect 100,000 cells at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 20. Cell counting has been performed with an automated cell counter. The transduction efficiency strongly depends on the used cell line. Work with lentivirus requires compliance with the local guidelines for biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) products. - Incubate the cells at 37 °C for 72 h, while continuing daily medium changes.
- Confirm successful transduction by checking the cells for GFP expression in a fluorescence microscope. Set the microscope magnification to 10x or 20x and use the appropriate excitation (460-480 nm) and emission range (490-520 nm) to detect transduced GFP-expressing cells.
- Quantify the ratio of GFP-transduced to total cells to estimate general transduction efficacy.
NOTE: Transduction rates of 65-95% were achieved with this protocol. A transduction efficacy of >50% is recommended as a go/no-go criterion before transplantation. If 50% transduction efficacy cannot be achieved, perform puromycin selection or sort the cells using flow cytometry to increase the yield of transduced cells. - Optional: Freezing of cells
- Spin the cells down (300 × g, 5 min) and discard the supernatant. Resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of freezing medium (see the Table of Materials) and transfer the suspension into vials to obtain 106 cells/vial. Transfer the cells to freezing boxes for 24 h at -80 °C and then to -150 °C for long-term storage.
2. Cell preparation for transplantation
- Collect a vial of cells from -150 °C storage and transfer it to the laboratory. Count the cells using an automated cell counter.
NOTE: The vial contains 1.5-2 × 106 cells. - Quickly transfer the vial to a 37 °C water bath until no ice crystals remain (2-3 min).
NOTE: It is important to thaw rapidly to minimize any damage to cell membranes. Do not immerse the vial completely in the water bath as it can increase the risk of contamination. - Transfer the vial to the biosafety cabinet and pipette the whole content (~1 mL) into a sterile 15 mL conical tube.
NOTE: Work with lentivirally transduced cells requires BSL-2. However, washing and passaging cells remove viral particles from the medium. Information about when a transfer from BSL-2 to BSL-1 is permitted should be obtained from the local authorities. - Add 9 mL of sterile 1x PBS and centrifuge for 5 min at 300 × g, RT.
- Remove the supernatant by aspiration using a pipette (1-10 mL); gently tilt the suspension towards the pipette tip and start aspirating. Be careful not to disturb the pellet.
- Wash the cells by resuspending in 10 mL of sterile 1x PBS.
NOTE: Gently tab the tube to resuspend cells in the residual volume. Slowly triturate the cell suspension using a 1 mL pipette until it does not contain clumps or aggregates. - Count the cells before the final spin using an automated cell counter.
- Centrifuge for 5 min at 300 × g, RT.
- Remove the supernatant (step 2.5) and resuspend the cell pellet in the required volume of sterile PBS to a concentration of 8 × 104 cells/µL. Place the cells on ice and use them for transplantation within the next 5h.
NOTE: A volume of 1.6 × 105 cells/2 µL of PBS was used in this protocol.
3. Transplantation procedure
- Preparation for surgery
- Clean and sterilize the surgery equipment.
- Prepare the stereotaxic device and the microinjection pump system.
NOTE: It is critical to test the Hamilton syringe and the 30 G, 2 inches needle before starting. Insert the needle into a tube containing sterile 0.9% NaCl and slowly draw the solution in and out. - Set up the anesthesia machine. Test the machine before involving any animals. Clean the induction chamber with 70% ethanol.
- Preparation of animals
- Keep the mice for at least 7 days prior to the experiments in standard conditions to acclimate them.
NOTE: The following animals were used for this protocol: female NOD/SCID/IL2rγnull (30-35 g, also known as NSG) and female C57BL/6J (20-25 g, also known as B6). The procedure can also be performed with male mice. - Measure the mouse body weight and adjust the dose of the pain killer to be injected. Administer carprofen (5 mg/kg body weight) intraperitoneally to reduce pain and/or prevent an inflammatory response.
- Anesthetize the animals using isoflurane (3% in the induction phase and 1.5-2% in the maintenance phase during surgery) vaporized in oxygen.
NOTE: Gaseous anesthesia is preferred due to a quick wake-up after the surgical procedure and because the levels of anesthetic gas can be easily adjusted. - Use nociceptive reflexes to ensure the animal is deeply anesthetized (e.g., toe pinches). When deep anesthesia is reached, transport the animal from the induction chamber to the stereotaxic frame. Maintain anesthesia using a face mask.
NOTE: The breath rate needs to be monitored visually throughout the procedure (40-60 breaths per minute). Use a warming pad to avoid hypothermia during the procedure. - Apply ophthalmic lubricant to prevent the eyes from drying out.
- Shave the mouse scalp with an electric razor and disinfect the skin with 5% betadine solution using cotton swabs.
- Secure the mouse head and insert the ear bars into the external meatus.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the eardrums. Apply lidocaine ointment to both ear canals before inserting the ear bars. To check if the animal's head is in a stable position, carefully push down on the head to see if there is movement. If movement is noted, either the ear bar, nosepiece placement, or both are incorrect and need to be readjusted.
- Keep the mice for at least 7 days prior to the experiments in standard conditions to acclimate them.
- Craniotomy
- Use a surgical blade to make a cut along the midline big enough to reveal the lambda and bregma landmarks.
NOTE: Skin retractors can be applied to keep the skull exposed. - Retract the periosteum and fascia with a scalpel and use sterile cotton swabs to dry the skull surface.
- Adjust the ear and mouth bars to standardize the head position.
NOTE: The vertical coordinates for bregma and lambda need to be identical for anteroposterior positioning. - Place the needle at the bregma and calculate the coordinates of the desired injection points (the coordinates of interest chosen for this protocol: anterior-posterior (AP): + 0.5 mm, medial-lateral (ML): + 1.5 mm). Move the needle to that point and mark it with ink.
NOTE: The coordinates were chosen based on the Franklin and Paxinos Mouse Brain Atlas 16. Distances are mm from the bregma. - Apply sterile 0.9% NaCl to the skull and drill a hole with a diameter of 2-3 mm through the skull with a surgical, dental drill.
- Move the needle to the surface of the dura and calculate the depth coordinates.
- Use a surgical blade to make a cut along the midline big enough to reveal the lambda and bregma landmarks.
- Transplantation procedure
- Resuspend the cells in the tube (step 2.9) and draw 2 µL of cell suspension into a syringe (5 µL or 10 µL).
NOTE: Make sure that no air bubbles are present in the cell suspension. The syringe needs to be kept in a horizontal position until mounted into the stereotactic device to avoid cell sedimentation. - Place the syringe above the target site (calculated coordinates: AP: + 0.5 mm, ML: + 1.5 mm) and slowly move the needle to the surface of the dura.
NOTE: If unsure about the correct coordinates, perform injections with a dye and histological evaluation of the injection site before transplanting cells (for more details, see 17). - Guide the needle at a rate of 0.02 mm/s into the brain up to the proper depth (the coordinate chosen for this protocol is dorsal-ventral (DV) - 0.8 mm). Overshoot the depth by 0.1 mm and withdraw the needle over the same distance to create a pocket for the injected cells.
- Apply tissue adhesive around the needle using forceps to prevent leakage of cells.
- Inject 2 µL of the prepared cell suspension at a constant rate of 3-5 nL/s.
NOTE: The injection procedure will last between 7 and 12 min. - Following injection, leave the needle in place for at least 5 min before slowly withdrawing it. Apply tissue adhesive to seal the hole in the skull and wait for another 2 min.
- Resuspend the cells in the tube (step 2.9) and draw 2 µL of cell suspension into a syringe (5 µL or 10 µL).
- Sutures and post-care
- Apply sterile 0.9% NaCl solution to the exposed skull to avoid dehydration.
- Close up the wound with a 5/0 silk suture thread.
- Hydrate the animal with 0.5 mL of ringer lactate solution subcutaneously injected in the lower back.
- Interrupt anesthesia delivery and carefully remove the mouse from the stereotaxic apparatus and place it back in a cage kept on a heating pad.
- Monitor the animals during the acute phase postinjury. Check the suture, the animal weight, and overall health at least twice a day.
4. In vivo imaging
- Preparation of luciferin
- Thaw D-luciferin potassium salt at RT and prepare a fresh stock solution of D-luciferin at 30 mg/mL in PBS.
- Sterilize the stock solution through a 0.22 µm syringe filter.
NOTE: Immediate use of the working solution is recommended. If necessary, dissolved luciferin can be stored at -20 °C. However, prolonged storage may result in the degradation of signal. Luciferin is a light-sensitive reagent; keep it out of direct light whenever possible. Alternative substrates may also be considered, e.g., cycluc, to improve the resolution limit18.
- Imaging
- Initial setup
NOTE: Bioluminescence imaging was performed using an in vivo imaging system (see the Table of Materials) consisting of a dark chamber and a cooled charge-coupled device (CCD) camera.- Double-click the Living Image software icon and select a user ID from the drop-down list.
- Click Initialize in the control panel that appears. Once the initialization process is completed, the temperature box in the control panel will turn green.
- In the control panel, check the Luminescent and Photograph boxes and select Auto exposure (~60 s). Select a field of view (D/12.5cm was chosen for this protocol). Enter the subject height (1.5 cm) and select the use subject height focus option. Manually set the following parameters: large binning, f/2, blocked excitation filter, and open emission filter.
- Determine the injection amount of D-luciferin at 300 mg/kg body weight.NOTE: The standard recommended dose is 150 mg/kg of D-luciferin. This procedure was adjusted according to a protocol reporting higher sensitivity using 300 mg/kg18.
- Inject the luciferin intraperitoneally (i.p.).
NOTE: If the animal needs to be sedated before injection, be aware that it may extend the peak luciferase expression time. - Wait for 5 min, then anesthetize animals with a continuous supply of isoflurane (4.5% in the induction phase and 1.5-2% in the maintenance phase during imaging procedure).
- Apply ophthalmic lubricant to the eyes, then shave the sedated animals on the head region using a conventional hair shaver. Place the animals in the imaging chamber and start imaging 15 min after the luciferin injection by clicking Acquire in the control panel.
- Initial setup
5. Perfusion
- Anesthetize the animals by an i.p. injection of sodium pentobarbital (150 mg/kg body weight). Wait until the mouse no longer responds to painful stimuli, such as toe pinches.
- Lay the mouse on its back and use tweezers and scissors to open the chest cavity.
- Use standard scissors to open the diaphragm.
- Expose the heart and insert a needle (from the tubing with ringer/4% paraformaldehyde solution (PFA)) into the apex of the left ventricle.
NOTE: Be careful to keep the tip of the needle in the lumen of the ventricle. - Cut the right ventricle using scissors.
- Perfuse with ringer solution (can be kept at RT) for 3-4 min (flow rate: 17 mL/min). Continue until the heart is clean.
- Switch the stopcock to allow for the flow of PFA (store at 4 °C; keep on ice during the procedure) and perfuse for another 5 min (~100 mL).
- Stop the pump and remove the needle from the left ventricle.
NOTE: The perfusion with PFA preserves tissue integrity uniformly. It also facilitates the preservation of GFP signal in the transplants that otherwise may be lost due to diffusion.
6. Processing
- Tissue collection
- Remove the head using standard scissors and make a midline incision in the skin.
- Turn the skin over the eyes to expose the skull.
- Start from the caudal part at the point of the parietal bone and make a small incision using spring scissors. Advance the scissors rostrally along the midsagittal suture up to a point between the eyes. Start again from the caudal part and make two cuts parallel and ~4 mm apart in the sagittal plane.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the brain by pressing the scissors against the interior surface of the skull. - Use forceps to carefully tilt one side of the parietal bone and break it off. Do the same with the other side.
NOTE: Use a microspatula to free the bone from the meninges; otherwise, they may damage the brain while breaking off the skull. If parts of the frontal bone remain, make a small cut to tilt and break off the bone plate. - To release the brain, carefully slide the microspatula under the brain (olfactory bulbs) and tilt it gently upward.
- After collecting, keep the brain in 4% PFA solution for 4-6 h at 4 °C. Transfer it to sterile 1x PBS afterward.
- Immunohistochemistry
- Transfer the brain to a 30% sucrose solution for at least 48 h at 4 °C to prevent the formation of crystals during freezing.
- Use a sliding microtome to cut coronal sections with a thickness of 40 µm. Collect and store the sections as free-floating sections (in a 24-well-plate) in a cryoprotectant solution (Table 1) at -20 °C until further processing.
- Rinse the sections with 450 µL of 1x PBS for each well (3 times, 5 min each, RT).
- Block non-specific sites with 450 µL of blocking solution for each well (Table 1) for 1 h at RT.
- Incubate each well with 450 µL of primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. Dilute the antibodies 1:200 in 3% donkey serum; 0.1% Triton-X-100 in PBS. To identify donor material in the host environment, use an antibody to human-specific nuclei (Anti-Human Nuclei Antibody, clone 235-1).
- Wash the sections with 450 µL of 1x PBS for each well (3 times, 5 min each, RT).
- Incubate each well with 450 µL of corresponding fluorescent secondary antibodies for 2-3 h (RT). Dilute the antibodies in 3% donkey serum; 0.1% Triton-X-100 in 1x PBS.
- Wash the sections with 450 µL of 1x PBS for each well (3 times, 5 min each, RT).
- Stain the nuclei with 450 µL of 0.1 µg/mL 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).
Representative Results
We aim to longitudinally track transplanted neural progenitor cells in the mouse brain using in vivo bioluminescence imaging and identify the transplanted cells in subsequent histological analysis (Figure 1A). Therefore, neural progenitor cells are transduced with a lentiviral vector consisting of EF1α-rFluc-eGFP. Before transplantation, cells were tested for successful transduction by expression of eGFP in vitro (Figure 1B). The successfully transduced cells were stereotactically transplanted in the mouse brain at the desired coordinates (e.g., in the sensorimotor cortex). Following transplantation, the mice were systemically injected with D-luciferin, the substrate for rFluc, and signal intensities of the transplanted cells were measured to confirm successful transplantation (Figure 1C).
To evaluate the detection limit of the in vivo bioluminescence imaging, a range of 6,000-180,000 cells was transplanted in the right sensorimotor cortex of the mouse (Figure 2A). We detected <6,000 cells and a bioluminescence signal proportional to the transplanted cell count directly after transplantation (Figure 2B). As human cell sources are immunogenic to immunocompetent mice, NOD scid gamma (NSG) immunodeficient mice were used to observe the long-term survival of the cell grafts. Long-term survival and detection of a bioluminescence signal for up to 5 weeks were confirmed after cell transplantation (Figure 2C,D). The transplanted cells were successfully detected ex vivo in a subsequent histological analysis through the eGFP reporter and immunostaining with anti-human nuclei and anti-human mitochondrial antibodies (Figure 2E).
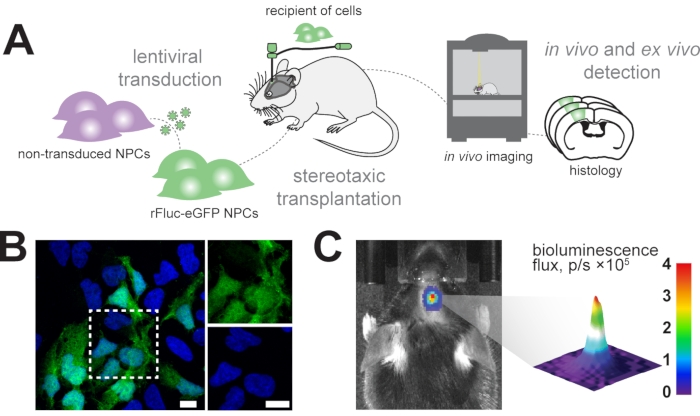
Figure 1: Transplantation of neural progenitor cells. (A) Schematic overview of generation and transplantation of rFluc-eGFP NPCs. (B) Representative immunofluorescence image of transduced NPCs (GFP reporter, green) counterstained with DAPI (blue); scale bars = 5 µm. (C) In vivo detection of bioluminescence signal in transplanted cells; color bar = blue (0, min, no signal), red (4 flux, p/s × 105, max signal) Abbreviations: NPCs = neural progenitor cells; GFP = green fluorescent protein; rFluc-eGFP = red firefly luciferase and enhanced green fluorescent protein; DAPI = 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; p/s = photons/s. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
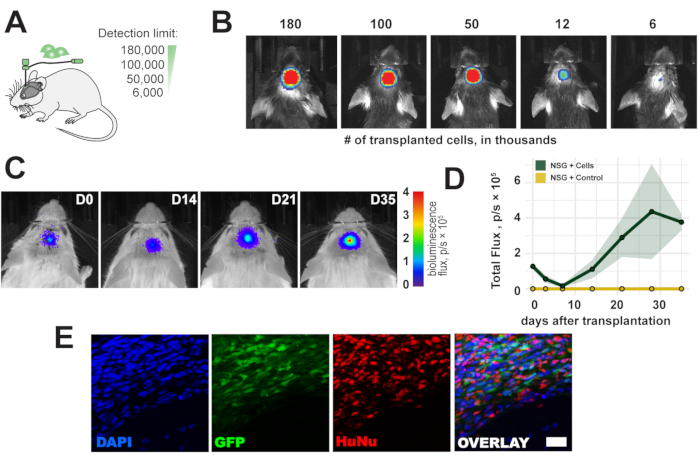
Figure 2: Time course of transplanted cells. (A) Schematic view of cell numbers for transplantation. (B) Detection limit of transplanted cells 1 h after transplantation. (C, D) Time course of transplantation (180,000 cells) for up to 35 days in NSG mice ; color bar = blue (0, min, no signal), red (4 flux, p/s × 105, max signal) Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3). (E) Representative fluorescence images of histological sections and transplanted cells 5 weeks following transplantation. Scale bar = 10 µm. Abbreviations: D = day after transplantation; NSG = immunodeficient NOD scid gamma; DAPI = 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFP = green fluorescent protein; HuNu = Anti-Human Nuclei Antibody, clone 235-1; p/s = photons/s. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
Regenerating the injured brain to allow for functional recovery remains an unmet challenge. Many innovative preclinical approaches have evolved targeting, for example, immune modulation19,20, angiogenesis1,21,22,23, blood-brain-barrier integrity2,3,24,25, and cell replacement5,26. Especially in recent years, cell-based therapies have emerged as a promising treatment strategy for the brain due to major advancements in stem cell technology and efficient differentiation protocols15,28. This paper provides a valuable protocol for transplanting and tracking neural cells in the mouse brain. The method is applicable for all transducable cell lines for in vivo applications in the mouse brain.
The presented setup uses transplants of human origin in a mouse. These transplants are not viable in the long-term in immunocompetent wild-type mice due to immunogenicity. Hence, immunodeficient NSG mice were used to overcome this limitation. Alternatively, the use of mouse transplants may be preferred to overcome the immunogenic aspects. If transplantation of human cells is required, humanized mouse models represent an emerging alternative to reduce the probability of graft rejection29.
A commercial dual-reporter viral vector consisting of firefly luciferase and eGFP under the EF1α promotor was used to visualize the transplants. This promotor was selected to achieve a high signal intensity15. However, apart from NPCs, other cell types have been shown to promote brain function after injury, including pericytes30 and astrocytes31; hence, depending on the cell line used, other promotors might be more suitable to achieve high expression levels. Additionally, the use of transgene promoters, such as CMV, may lead to downregulation, especially in long-term experiments32. The transduction efficiency of the lentiviral vector strongly depends on the used cell line and may vary between single experiments. Therefore, transduction efficiency must be evaluated before starting the in vivo experiments and to correct variations in transduction efficacy between experiments. The brain region of transplantation also influences the signal strength. Although a detection limit of <6,000 cells was achieved for cortical transplantations, it may require more cells to detect a signal in deeper brain regions, for example, striatum or hippocampus.
Transplantation volumes in the mouse brain are limited to 1-2 µL. Therefore, it is important to identify a suitable cell number for the experiments. It has been previously observed that increasing cell numbers leads to decreased survival rate, most likely due to limited availability of nutrients and oxygen in the region of transplantation33. In vivo bioluminescence imaging provides a relatively low spatial resolution compared to other in vivo imaging methods such as MRI or CT. Therefore, short migratory paths of grafted cells can only reliably be assessed in the subsequent post-hoc analysis.
The absolute signal strength of the bioluminescence is generally proportional to the transplanted cell number. However, the signal strength might be reduced if grafts are transplanted in deeper brain structures or if the signal strength is outside the linear detection spectrum of the in vivo imaging system. Currently, novel substrates are developed to ensure more efficient penetration across the blood-brain barrier than D-luciferin, including cycluc1. These substrates may further improve the detection limit of the grafted cells in the future18. Overall, this protocol allows a straightforward, minimally invasive procedure to transplant and observe grafts in the mouse brain.
Acknowledgements
The authors RR and CT acknowledge support from the Mäxi Foundation and the 3R Competence Center.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Viral Transduction | |||
| pLL-EF1a-rFLuc-T2A-GFP-mPGK-Puro (Lenti-Labeler virus) | Systembio | LL410VA-1 | |
| Consumables | |||
| Eppendorf microtubes; 1.5 mL | Sigma Aldrich | Z606340 | |
| Falcon Tubes; 15 mL | TPP | 91015 | |
| Microscope cover slips | Product of choice | ||
| Microscope slides | Product of choice | ||
| Sterlie cotton swabs | Product of choice | ||
| Sutures; 5/0 silk with curved needle | B. Braun | G0762482 | |
| Syringe filter; 0.22 µm | TPP | 99722 | |
| Syringe; 1 mL and 0.5 mL | B. Braun | 9166017V | |
| Tissue culture plate (24-well) | TPP | 92024 | |
| Equipment | |||
| Automated cell counter (Vi-CELL XR) | Beckmann Coulter Life Science | 383721 | |
| Forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11064-07 | |
| Forceps, fine | Fine Science Tools | 11412-11 | |
| Heating pad | Product of choice | ||
| High Speed Brushless Micromotor Kit | Foredom | K.1060-22. | |
| Ideal Micro Drill Burr Set Of 5 | Cell Point Specific | 60-1000 | |
| In-Vivo imaging system (IVIS Lumina III with Living Imaging 4.2 software package) | Perkin Elmer | CLS136334 | |
| Isoflurane vaporizer | Provet AG | 330724 | |
| Microinjection Syringe Pump system | World Precision Instruments | UMP3T-1 | |
| Microliter syringe; 700-Series; Volume: 5-10 µL | Hamilton | 7635-01 | |
| Microtome | Leica | HM430 | |
| NanoFill-33 G-Needle (removable and reusable) | World Precision Instruments | NF33BV-2 | |
| Needle Holder | Fine Science Tools | 12001-13 | |
| Perfusion pump and tubing | Masterflex | HV-77120-42 | |
| Scalpel | Fine Science Tools | 10003-12 | |
| Small bonn scissors, straight | Fine Science Tools | 14184-09 | |
| Small spring scissors, straight | Fine Science Tools | 15000-03 | |
| Spatula | Merck | Z243213-2EA | |
| Stereotaxic frame for rodents; motorized | World Precision Instruments | 99401 | |
| Pharmaceuticals and Reagents | |||
| Accutase | Invitrogen | A11105-01 | Proteolytic and collagenolytic; cell dissociation reagent |
| Anti-Human Nuclei Antibody, clone 235-1, Biotin Conjugate | Merck | MAB1281B | |
| B27 – Supplement (50x) | Gibco | 17504-001 | |
| Betadine (11 mg Iod als Povidon-Iod pro 1 ml Lösung) | Mundipharma Medical Company | All pharmaceuticals were provided by the cantonal pharmacy, Zurich, Switzerland | |
| Blocking solution (3% donkey serum; 0.1% Triton-X-100 in PBS) | Product of choice; can be homemade | ||
| CHIR99021 (10 mM – 2,500x) | StemMACS | 130-103-926 | |
| Cryoprotectant solution | Product of choice; can be homemade | ||
| DAPI solution (1 mg/mL) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 62248 | |
| D-Luciferin Potassium Salt | Perkin Elmer | 122799 | |
| DMEM/F12 | Gibco | 11320-074 | |
| Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-31570 | |
| Donkey serum | Product of choice | ||
| Esconarcon (Pentobarbitalum natricum 300 mg) | Streuli Pharma AG | All pharmaceuticals were provided by the cantonal pharmacy, Zurich, Switzerland | |
| Ethanol; 70% | Product of choice | ||
| FGF Basic recombinant human protein, Animal-origin free | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PHG6015 | |
| Glutamax (100x) | Gibco | A12860-01 | |
| hLif (10 µg/mL – 1,000x) | PeproTech | AF-300-05-25UG | |
| Isoflurane (Isofluran (1-Chlor-2,2,2-trifluorethyl-difluoromethylether) 99.9%) | Provet AG | All pharmaceuticals were provided by the cantonal pharmacy, Zurich, Switzerland | |
| Laminin-L521 (L-521) | Biolaminin LN | LN521 | |
| Lidocaine ointment (Lidocain: 25 mg , Prilocain: 25 mg) | Aspen Pharma Schweiz GmbH | All pharmaceuticals were provided by the cantonal pharmacy, Zurich, Switzerland | |
| Mounting Medium | Product of choice; can be homemade | ||
| N2- Supplement (100x) | Gibco | 75202-001 | |
| Neurobasal | Gibco | 21103-049 | |
| Ophtalmic lubricant (Retinol palmitat: 15,000 UI) | Bausch & Lomb Swiss AG | All pharmaceuticals were provided by the cantonal pharmacy, Zurich, Switzerland | |
| Paraformaldehyde solution | Product of choice | ||
| PBS | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10010023 | Can also be homemade |
| Poly-L-ornithine Solution (pLO) | Sigma-Aldrich | P4957 | |
| Rimadyl (Carprofen 50 mg) | Zoetis Schweiz GmbH | All pharmaceuticals were provided by the cantonal pharmacy, Zurich, Switzerland | |
| Ringer lactate | B. Braun | 3570500 | |
| Ringer solution | B. Braun | 3570030 | |
| Saline (0.9% NaCl) | B. Braun | 3570160 | |
| SB431542 (10 mM – 3,333.3x) | StemMACS | 130-106-543 | |
| Tissue Adhesive (Histoacryl) | B. Braun | 1050060 |
References
- Rust, R., et al. Nogo-A targeted therapy promotes vascular repair and functional recovery following stroke. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (28), 14270-14279 (2019).
- Rust, R., et al. Anti-Nogo-A antibodies prevent vascular leakage and act as pro-angiogenic factors following stroke. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 20040 (2019).
- Weber, R. Z., et al. Characterization of the blood brain barrier disruption in the photothrombotic stroke model. Frontiers in Physiology. 11, 58226 (2020).
- Sweeney, M. D., Sagare, A. P., Zlokovic, B. V. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nature Reviews. Neurology. 14 (3), 133-150 (2018).
- Wang, Y., et al. 3K3A-APC stimulates post-ischemic neuronal repair by human neural stem cells in mice. Nature Medicine. 22 (9), 1050-1055 (2016).
- Llorente, I. L., et al. Patient-derived glial enriched progenitors repair functional deficits due to white matter stroke and vascular dementia in rodents. Science Translational Medicine. 13 (590), (2021).
- Kokaia, Z., Llorente, I. L., Carmichael, S. T. Customized brain cells for stroke patients using pluripotent stem cells. Stroke. 49 (5), 1091-1098 (2018).
- Parmar, M., Grealish, S., Henchcliffe, C. The future of stem cell therapies for Parkinson disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 21 (2), 103-115 (2020).
- Galgano, M., et al. Traumatic brain injury: current treatment strategies and future endeavors. Cell Transplantation. 26 (7), 1118-1130 (2017).
- Schweitzer, J. S., et al. Personalized iPSC-derived dopamine progenitor cells for Parkinson's disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 382 (20), 1926-1932 (2020).
- Muir, K. W., et al. Intracerebral implantation of human neural stem cells and motor recovery after stroke: multicentre prospective single-arm study (PISCES-2). Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 91 (4), 396-401 (2020).
- Kawabori, M., et al. Cell therapy for chronic TBI: interim analysis of the randomized controlled STEMTRA trial. Neurology. 96 (8), 1202-1214 (2021).
- George, P. M., et al. Engineered stem cell mimics to enhance stroke recovery. Biomaterials. 178, 63-72 (2018).
- Sancho-Martinez, I., et al. Establishment of human iPSC-based models for the study and targeting of glioma initiating cells. Nature Communications. 7 (1), 1-14 (2016).
- Rust, R., et al. Xeno-free induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells for in vivo applications. bioRxiv. , (2022).
- Franklin, K., Paxinos, G. . Paxinos and Franklin's the Mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, compact: The coronal plates and diagrams. , (2019).
- Baker, S., Götz, J. A local insult of okadaic acid in wild-type mice induces tau phosphorylation and protein aggregation in anatomically distinct brain regions. Acta Neuropathologica Communications. 4, 32 (2016).
- Cao, J., et al. In vivo optical imaging of myelination events in a myelin basic protein promoter-driven luciferase transgenic mouse model. ASN Neuro. 10, (2018).
- Aswendt, M., Adamczak, J., Couillard-Despres, S., Hoehn, M. Boosting bioluminescence neuroimaging: an optimized protocol for brain studies. PLoS One. 8 (2), 55662 (2013).
- Roth, S., et al. Brain-released alarmins and stress response synergize in accelerating atherosclerosis progression after stroke. Science Translational Medicine. 10 (432), (2018).
- Rust, R., Hofer, A. -. S., Schwab, M. E. Stroke promotes systemic endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Trends in Molecular Medicine. 24 (7), 593-595 (2018).
- Rust, R., Gantner, C., Schwab, M. E. Pro- and antiangiogenic therapies: current status and clinical implications. FASEB Journal. 33 (1), 34-48 (2018).
- Rust, R., Grönnert, L., Weber, R. Z., Mulders, G., Schwab, M. E. Refueling the ischemic CNS: guidance molecules for vascular repair. Trends in Neurosciences. 42 (9), 644-656 (2019).
- Nih, L. R., Gojgini, S., Carmichael, S. T., Segura, T. Dual-function injectable angiogenic biomaterial for the repair of brain tissue following stroke. Nature Materials. 17 (7), 642 (2018).
- Montagne, A., et al. Pericyte degeneration causes white matter dysfunction in the mouse central nervous system. Nature Medicine. 24 (3), 326-337 (2018).
- Montagne, A., et al. APOE4 leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline. Nature. 581 (7806), 71-76 (2020).
- George, P. M., Steinberg, G. K. Novel stroke therapeutics: unraveling stroke pathophysiology and its impact on clinical treatments. Neuron. 87 (2), 297-309 (2015).
- Weber, R. Z., et al. Deep learning based behavioral profiling of rodent stroke recovery. bioRxiv. , (2021).
- Nair, R. R., et al. Uses for humanised mouse models in precision medicine for neurodegenerative disease. Mammalian Genome. 30 (7), 173-191 (2019).
- Kirabali, T., Rust, R. iPS-derived pericytes for neurovascular regeneration. European Journal of Clinical Investigation. 51 (9), 13601 (2021).
- Weber, R. Z., Perron, P., Rust, R. Astrocytes for brain repair: More than just a neuron's sidekick. Brain Pathology. 31 (5), 12999 (2021).
- Johansen, J., et al. Evaluation of Tet-on system to avoid transgene down-regulation in ex vivo gene transfer to the CNS. Gene Therapy. 9 (19), 1291-1301 (2002).
- Vogel, S., et al. Initial graft size and not the innate immune response limit survival of engrafted neural stem cells. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 12 (3), 784-793 (2018).
Explore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved