A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Scalable Isolation and Purification of Extracellular Vesicles from Escherichia coli and Other Bacteria
In This Article
Summary
Bacteria secrete nanometer-sized extracellular vesicles (EVs) carrying bioactive biological molecules. EV research focuses on understanding their biogenesis, role in microbe-microbe and host-microbe interactions and disease, as well as their potential therapeutic applications. A workflow for scalable isolation of EVs from various bacteria is presented to facilitate standardization of EV research.
Abstract
Diverse bacterial species secrete ~20-300 nm extracellular vesicles (EVs), comprised of lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, glycans, and other molecules derived from the parental cells. EVs function as intra- and inter-species communication vectors while also contributing to the interaction between bacteria and host organisms in the context of infection and colonization. Given the multitude of functions attributed to EVs in health and disease, there is a growing interest in isolating EVs for in vitro and in vivo studies. It was hypothesized that the separation of EVs based on physical properties, namely size, would facilitate the isolation of vesicles from diverse bacterial cultures.
The isolation workflow consists of centrifugation, filtration, ultrafiltration, and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) for the isolation of EVs from bacterial cultures. A pump-driven tangential flow filtration (TFF) step was incorporated to enhance scalability, enabling the isolation of material from liters of starting cell culture. Escherichia coli was used as a model system expressing EV-associated nanoluciferase and non-EV-associated mCherry as reporter proteins. The nanoluciferase was targeted to the EVs by fusing its N-terminus with cytolysin A. Early chromatography fractions containing 20-100 nm EVs with associated cytolysin A - nanoLuc were distinct from the later fractions containing the free proteins. The presence of EV-associated nanoluciferase was confirmed by immunogold labeling and transmission electron microscopy. This EV isolation workflow is applicable to other human gut-associated gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial species. In conclusion, combining centrifugation, filtration, ultrafiltration/TFF, and SEC enables scalable isolation of EVs from diverse bacterial species. Employing a standardized isolation workflow will facilitate comparative studies of microbial EVs across species.
Introduction
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanometer-sized, liposome-like structures comprised of lipids, proteins, glycans, and nucleic acids, secreted by both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells1. Since the early studies visualizing the release of EVs from gram-negative bacteria2, the number of biological functions attributed to bacterial EVs (20-300 nm in diameter) has constantly been growing in the past decades. Their functions include transferring antibiotic resistance3, biofilm formation4, quorum sensing5, and toxin delivery6. There is also growing interest in the use of bacterial EVs as therapeutics, especially in vaccinology7 and cancer therapy8.
Despite the growing interest in EV research, there are still technical challenges regarding methods of isolation. Specifically, there is a need for isolation methods that are reproducible, scalable, and compatible with diverse EV-producing organisms. To create a unified set of principles for planning and reporting EV isolation and research methods, the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles publishes and updates the MISEV position paper9. Moreover, the EV-TRACK consortium provides an open platform for reporting detailed methodologies for EV isolation used in published manuscripts to enhance transparency10.
In this protocol, previous methodologies used for the isolation of EVs from mammalian cell culture were adapted11,12 to enable the isolation of EVs from bacterial cell culture. We sought to employ methods that enable EV isolation from a variety of microbes, which can be scalable, and balance EV purity and yield (as discussed in the MISEV position paper9). After removing bacterial cells and debris by centrifugation and filtration, the culture medium is concentrated either by centrifugal device ultrafiltration (for a volume of up to ~100 mL) or pump-driven TFF (for larger volumes). EVs are then isolated by SEC using columns optimized for the purification of small EVs.
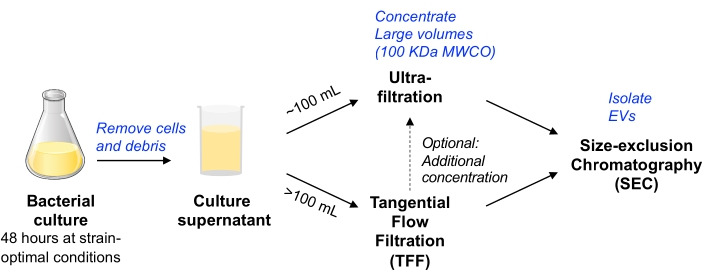
Figure 1: Bacterial EV isolation workflow schematic overview. Abbreviations: EV = extracellular vesicle; TFF = tangential flow filtration; SEC = size exclusion chromatography; MWCO = molecular weight cut-off. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
A mouse-commensal strain of Escherichia coli (i.e., E. coli MP113) was used as a model organism and modified to express EV-associated nanoluciferase by fusion to cytolysin A, as previously reported14. The methods used here can process at least up to several liters of bacterial cultures and effectively separate EV-associated from non-EV-associated proteins. Finally, this method can also be used for other gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial species. All relevant data of the reported experiments were submitted to the EV-TRACK knowledgebase (EV-TRACK ID: EV210211)10.
Protocol
NOTE: Ensure that all work involving bacteria and recombinant DNA follows best practices for biosafety containment appropriate for the biosafety hazard level of each strain. Work should be done in accordance with local, national, and international biosafety regulations.
1. Bacterial strains and culturing conditions
NOTE: Bacterial strains used in this study were Escherichia coli MP113, Akkermansia mucinophila, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bifidobacterium breve, and Bifidobacterium dentium.
- For E. coli, use a sterile loop to inoculate single colonies into 250 to 1,000 mL of Luria-Bertani (LB) broth and incubate aerobically in a shaking incubator at 300 rpm and 37 °C for 48 h before processing the culture. For recombinant E. coli MP1 strain harboring p114-mCherry-Clyluc (Supplemental Method and Supplemental Figure S1), add chloramphenicol to the LB agar and broth at a final concentration of 17 µg/mL.
- For A. mucinophila, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. breve, and B. dentium, streak on Brain heart infusion (BHI) agar plates and incubate anaerobically inside a vinyl anaerobic chamber. Inoculate single colonies into 100 mL of pre-reduced BHI broth and incubate for 48 h anaerobically.
2. EV isolation
- Clarifying bacterial culture medium by centrifugation and filtration
- Transfer the bacterial cell cultures inoculated in step 1 to clean 250 mL or 500 mL polypropylene centrifuge bottles by pouring. Centrifuge the bottles in a large-capacity, fixed-angle rotor at 4 °C and 5,000 × g for 15 min. Transfer the supernatant to clean centrifuge bottles by careful pouring, and centrifuge again at 10,000 × g for 15 min.
NOTE: Reuse the bottles after biosafety-appropriate cleaning and decontamination.- If large pellets of bacterial cells are present after the second centrifugation, repeat the centrifugation in a clean bottle to further remove cells.
- Transfer the supernatant to a 0.22 µm polyethersulfone vacuum-driven filter device of appropriate size by pouring. Filter by connecting the filtration device to a vacuum wall supply. If the filtration rate drops significantly, simply move any unfiltered material to a new device. Store the filtered medium at 4 °C overnight, and continue the protocol the following day if desired.
NOTE: The centrifugations above typically allow processing of ~2x the indicated volume of cell culture through each device. For example, a single 500 mL filter device could filter ~1,000 mL of pre-centrifuged culture. These devices are not typically reused. Using syringe filters at this step is not recommended without optimization, as significant losses were noted with the tested models. This is a potential stopping point. - Check for the complete removal of the viable cells at this point by spreading an aliquot of the filtered supernatant on suitable agar plates and ensure the absence of any colonies after incubation at optimum conditions for the bacterial strain. If bacteria are detected, further optimize the procedure above by performing additional centrifugations and/or filtrations.
- Transfer the bacterial cell cultures inoculated in step 1 to clean 250 mL or 500 mL polypropylene centrifuge bottles by pouring. Centrifuge the bottles in a large-capacity, fixed-angle rotor at 4 °C and 5,000 × g for 15 min. Transfer the supernatant to clean centrifuge bottles by careful pouring, and centrifuge again at 10,000 × g for 15 min.
- Concentration of the filtered medium
- If working with volumes significantly >100 mL, proceed to step 2.2.2. If working with volumes of ~100 mL, load 90 mL of filtered culture medium onto the reservoir of a respective capacity 100 kDa molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) centrifugal ultrafiltration device using serological pipettes. Always balance with a matching ultrafiltration device, and centrifuge in swinging bucket rotor at 4 °C and 2,000 × g for 15-30 min intervals, until the volume of the medium in the top reservoir has been concentrated to <0.5 mL.
- Top up the reservoir with any remaining filtered culture medium. If "topping up," remove the flow-through in the bottom of the device and re-balance any devices.
NOTE: It was observed that the maximum volume of filtered culture medium that can be concentrated using these devices is <2-fold the recommended volume. - If the viscosity of the concentrated medium in the reservoir is visibly increased (dark, viscous material), dilute with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and re-concentrate by centrifugation to dilute any non-EV proteins smaller than the MWCO of 100 kDa.
NOTE: This is a potential stopping point. - Transfer the concentrated medium to a low-protein-binding tube, store at 4 °C overnight, and continue the protocol the following day if desired.
- Top up the reservoir with any remaining filtered culture medium. If "topping up," remove the flow-through in the bottom of the device and re-balance any devices.
- If working with volumes significantly >100 mL, select an appropriately sized TFF device (100 kDa MWCO) to accommodate the volume to be processed.
NOTE: Filtration devices for processing 100 mL to >1,000 mL are commercially available. Local availability, cost, and compatibility with the pump and tubing/connections will dictate which particular models will be most useful. Up to 2 L of culture medium were processed with the device indicated in the Table of Materials before needing to clean the filter (see step 2.3 below for the cleaning protocol).- Assemble a filtration circuit with #16 low-binding/low-leaching tubing, 1/8 inch hose-barb to Luer adapters, the TFF device, and a peristaltic pump, as indicated in Supplemental Figure S2.
NOTE: Perform TFF within a biosafety cabinet to minimize the risk of contaminating the EV preparation with environmental bacteria. - At room temperature, begin circulating the filtered, conditioned medium at approximately 200 mL/min (minimum 100 mL/min). Determine the appropriate RPM corresponding to the desired flow rate by pumping 200 mL of PBS into a graduated vessel. When circulating filtered, conditioned medium, collect the molecules <100 kDa crossing the ultrafiltration membrane as waste in a separate vessel.
NOTE: The example below will be assuming a starting volume of 2 L of culture. - Continue to circulate the conditioned medium until its volume has been reduced to ~ 100-200 mL. Move to smaller vessels as needed. Dilute 2-fold with PBS, and continue to circulate with the pump, concentrating down to 75-100 mL. Dilute 2-fold with PBS, and continue to circulate to a final volume of 25 mL. Dilute 2-fold with PBS and continue to circulate until <10 mL.
- Lift the feed tubing out of the sample reservoir, and continue to pump to purge the filter and recover the maximum amount of sample.
NOTE: This is a potential stopping point. - Transfer the concentrated sample to a conical tube and store overnight at 4 °C if desired. Alternatively, continue with the protocol.
- Move the concentrated sample to a 15 mL capacity 100 kDa MWCO centrifugal ultrafiltration device. Centrifuge in a swinging bucket rotor at 4 °C and 2,000 × g for 15-30 min intervals until the volume of the medium in the top reservoir has been concentrated to <2 mL.
NOTE: This is a potential stopping point. - Transfer the concentrated medium to a low-protein-binding tube, and store at 4 °C overnight, continuing the protocol the following day if desired.
- Assemble a filtration circuit with #16 low-binding/low-leaching tubing, 1/8 inch hose-barb to Luer adapters, the TFF device, and a peristaltic pump, as indicated in Supplemental Figure S2.
- If working with volumes significantly >100 mL, proceed to step 2.2.2. If working with volumes of ~100 mL, load 90 mL of filtered culture medium onto the reservoir of a respective capacity 100 kDa molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) centrifugal ultrafiltration device using serological pipettes. Always balance with a matching ultrafiltration device, and centrifuge in swinging bucket rotor at 4 °C and 2,000 × g for 15-30 min intervals, until the volume of the medium in the top reservoir has been concentrated to <0.5 mL.
- Cleaning the TFF device (optional)
NOTE: The filtration rate decreases as the TFF device begins to "clog" during the process (fouling). If necessary, the filter device can be cleaned to facilitate filtration of additional samples in the same purification run. Though theoretically possible, a cleaned TFF filter has not been used for a different purification run to avoid cross-contamination.- To clean, remove all tubing and caps from the TFF device and drain any residual liquid.
- Use the peristaltic pump and tubing to flood both the inner and outer compartments of the TFF device (i.e., via the parallel and perpendicular ports in the model listed in the Table of Materials) with ~100 mL of distilled water. Remove all tubing/caps and drain the TFF device.
- Cap the outer (perpendicular, filtrate) ports and circulate 250 mL of 20% ethanol in distilled water at >200 mL/min for 10 min through the inner compartment. Drain, flood with distilled water, and drain again as above.
- Circulate 250 mL of 0.5 N fresh NaOH solution for 30 min through the inner compartment and drain again.
- Reconnect all tubing and caps to the inlet, outlet, and filtrate ports, as in Supplemental Figure S2, and circulate 0.5 N NaOH solution again until a volume of NaOH > 1 mL/cm2 filter surface area permeates through the filter membrane and is collected as filtrate/waste.
- Rinse the TFF device with distilled water as above. Use the TFF device immediately or flood the device with ~100 mL of 20% ethanol and store overnight at 4 °C.
NOTE: If stored in ethanol, be sure to drain, rinse with water, drain, and circulate 250 mL of PBS through the device until a volume of >1 mL/cm2 filter surface area permeates through the filter membrane and is collected as filtrate/waste to remove residual ethanol prior to sample processing.
- Size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
NOTE: SEC is used to increase the purity of EVs and remove non-vesicular protein.- Use a small SEC column (10 mL bed volume) for the isolation of EVs from <100 mL of starting material and a larger column (47 mL bed volume) for the isolation of EVs from >100 mL of starting material.
NOTE: The example below will list volumes for the larger column, with volumes for the smaller column in parentheses. - Bring the SEC column and PBS to room temperature over several hours. Stabilize the SEC column in a vertical position using a standard laboratory stand and holder. Alternatively, use commercial chromatography column stands.
- Before connecting to the SEC column, hydrate the sample reservoir by allowing 5 mL of PBS to flow through the frit and into a waste container. Unscrew the inlet cap of the SEC column, add 2 mL of PBS to the sample reservoir, and carefully connect the reservoir to the column as the PBS is dripping out through the frit (not applicable for small SEC columns).
NOTE: This previous step prevents any air bubbles from getting trapped at the top of the SEC column. If air is trapped, remove the reservoir, tap the column to get the air bubble out, and repeat the connection procedure. For the smaller column, simply uncap the top of the SEC column, and attach the sample hopper. - Add 47 mL (10 mL) of PBS to the sample reservoir and uncap the bottom of the SEC column. Allow all the loaded sample buffer to flow through the column for equilibration. Discard the flow-through.
- Load a maximum of 2 mL (0.5 mL) of sample onto the sample reservoir, discard the flow-through, and allow the sample to enter the column completely.
- Immediately add PBS to the sample reservoir or hopper at a volume of 14.25 mL minus the sample volume (3 mL minus the sample volume, for the small column). Allow the solution to flow through the column and discard this amount equal to the column void volume.
NOTE: For a typical 2 mL sample, the amount of PBS to be added to the sample reservoir or hopper will be 12.25 mL. - Position a 2 mL low-binding microtube directly below the SEC column. Immediately add 2 mL (0.5 mL) of PBS to the sample reservoir and allow it to enter the column. Label this first 2 mL (0.5 mL) of flow-through as Fraction 1. Continue to add 2 mL (0.5 mL) at a time to the sample reservoir to collect each subsequent fraction.
NOTE: Most bacterial EVs elute in the first 5 fractions. During optimization, the first 12 fractions were collected. - Store the fractions at 4 °C for short-term storage (days) or -80 °C for long-term storage.
- Cleaning and storage of the reusable SEC columns
NOTE: The SEC columns described in this protocol can be reused up to 5 times according to the manufacturer. If the flow rate of the SEC columns decreases after <5 uses, the manufacturer recommends centrifuging the concentrated samples at 10,000 x g for 10 min to clear any aggregates before SEC. Then load the supernatant of this centrifugation onto the SEC column for EV isolation.- To clean and store SEC column after each use, add 2 mL (0.5 mL) of 0.5 M NaOH and allow it to enter the column completely. Run 100 mL (20 mL) of 20% ethanol through the column and store it at 4 °C until the next use. Before the next use, equilibrate the ethanol to room temperature as above, and exchange it with PBS buffer by running another 150 mL (30 mL) of PBS through the column.
- To clean and immediately re-use SEC column after each use, add 2 mL (0.5 mL) of 0.5 M NaOH and allow it to enter the column completely. Run approximately 150 mL (30 mL) of PBS buffer to wash away NaOH. When pH of eluate is equal to PBS (~7), a new sample may be loaded.
- Use a small SEC column (10 mL bed volume) for the isolation of EVs from <100 mL of starting material and a larger column (47 mL bed volume) for the isolation of EVs from >100 mL of starting material.
3. EV preparation quality control
- Sterility testing
NOTE: As these EVs come from bacterial cultures, it is critical to ensure sterility prior to downstream use.- Obtain 100 µL (20 µL) of the fractions to be used in assays and inoculate 3 mL of the medium used to grow the source bacteria. Culture under the respective optimal conditions for at least 3 days and observe for turbidity. Alternatively, apply the fraction samples to agar plates containing the medium used to grow the producing bacteria and look for colony formation.
NOTE: If bacterial contamination is detected, it is not recommended to use the EV preparation for experimentation. Instead, repeat the isolation, taking care to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination by (a) performing sufficient centrifugation/filtration of conditioned bacterial cell culture medium, (b) using clean bottles, tubing, filters, and chromatography columns, and (c) employing appropriate aseptic techniques.
- Obtain 100 µL (20 µL) of the fractions to be used in assays and inoculate 3 mL of the medium used to grow the source bacteria. Culture under the respective optimal conditions for at least 3 days and observe for turbidity. Alternatively, apply the fraction samples to agar plates containing the medium used to grow the producing bacteria and look for colony formation.
- Protein quantification
NOTE: A high-sensitivity, fluorescence-based protein quantification kit was used (see the Table of Materials). The kit works with a matching proprietary fluorimeter at excitation/emission wavelengths of 485/590 nm.- Bring all reagents, standards, and samples to room temperature.
- Prepare a master mix of protein reagent and buffer by adding 1 µL of the reagent to 199 µL of buffer for each sample and standard to be assayed. Using thin-walled 0.5 mL PCR tubes, add 10 µL standard + 190 µL of master mix to each standard tube.
NOTE: To be within the range of the assay, the amount of each fraction to be added to each sample tube depends on the expected protein yield of the purification. Typically, 5 µL of each fraction + 195 µL of master mix were used. The final volume of sample + master mix must be 200 µL. - Vortex the assay tubes, and incubate for at least 15 min at room temperature in the dark.
- Measure the standards on the appropriate proprietary fluorimeter (see the Table of Materials) by selecting the Protein assay option using the arrow buttons and pressing the GO button to confirm. Follow the on-screen instructions, inserting each standard tube and pressing GO.
- Insert the experimental sample tube; press GO to read; and note the result displayed, which is the actual protein concentration in the assay buffer/sample mixture. To obtain the protein concentration in the sample, use the arrow keys to select the Calculate sample concentration option, press GO, and use the arrow keys to select the sample volume added to the assay buffer for the given sample. Press GO and record the sample protein concentration. Repeat this step for each sample to be analyzed.
- Particle counting and size distribution
NOTE: Microfluidics resistive pulse sensing (MRPS) was used to quantify EV concentration and size distribution.- Dilute the samples in PBS supplemented with 1% Tween-20 that has been filtered through a 0.02 µm syringe filter to a protein concentration of approximately 0.1 µg/mL.
NOTE: The goal of dilution is to reach an expected particle concentration in the range of 1010 particles/mL in EV-containing fractions. The optimal dilution may need to be determined empirically. Few EVs are expected for later fractions (beyond Fraction 6). Thus, the particle concentration will likely be <1010 particles/mL despite analyzing at low dilutions. - Load 3 µL of each sample into the disposable microfluidics cartridge with a micropipette, insert the cartridge into the MRPS instrument, and push the metal button with a blue illuminated rim.
- Click Go! on the acquisition software and wait for the sample to be analyzed by the instrument. Acquire 1,000 to 10,000 particle events to minimize the technical statistical error of analysis. At this point, click Stop and End Run to complete the sample acquisition.
NOTE: Together with the raw data files, the instrument outputs a summary spreadsheet listing the particle concentration in the sample. Correct this value according to the sample dilution made. - Using analysis software, load the raw data and generate customized graphs of size distribution.
- Dilute the samples in PBS supplemented with 1% Tween-20 that has been filtered through a 0.02 µm syringe filter to a protein concentration of approximately 0.1 µg/mL.
4. EV storage
- Aliquot individual or pooled fractions to 25-50% of the individual fraction size (depending on the size of column used) in low-protein-binding tubes and store at -80 °C to avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
NOTE: Different applications may require smaller or larger aliquots depending on the expected amount utilized in each experiment. This will need to be determined empirically. The non-EV-containing fractions can be discarded if not applicable to the research objectives.
5. Transmission electron microscopy
- Negative staining
- Add 5 µL of the EV sample to the carbon-coated copper 400 mesh grid and incubate at room temperature for 10 min. Wash the specimen side with 5 drops of 5 mM Tris buffer (pH 7.1) and then with 5 drops of distilled water.
- Stain specimen side with 5 drops of 2% uranyl acetate. Blot away any extra amount of stain with filter paper, and allow the grid to dry completely for several hours or overnight. Visualize the specimens with an electron microscope operated at 80 kV.
- Immunogold labeling
- Apply 10 µL of the EV suspension to a formvar/carbon 400 mesh grid and incubate at room temperature for 1 h. Wash the grid in PBS three times, and then apply 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min to fix the sample. Wash the grids five times with PBS.
- Block the grid with three washes of PBS containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). Then, apply 10 µL of a primary antibody for 40 min at room temperature (here, 1 µg/mL of nluc antibody). Wash three times again with PBS containing 0.1% BSA.
- Add 10 µL of secondary gold-labeled antibody to the grid and incubate for 40 min at room temperature. Wash the grids three times with PBS.
NOTE: Here, a goat anti-mouse antibody conjugated with 10 nm gold nanoparticles was used after diluting 1:10 in blocking buffer. If gold labeling obscures EV visualization, secondary antibodies with smaller gold nanoparticles (e.g. 5 nm) can be used instead. - Post-fix the grid with 10 µL of 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 10 min at room temperature. Wash three times in PBS. Perform negative staining with 2% uranyl acetate (10 µL) for 15 min. Embed the samples in 10 µL of 0.5% uranyl acetate and 0.13% methyl cellulose solution for 10 min.
- Allow the sample grids to dry overnight at room temperature before imaging on the electron microscope.
- On the microscope acquisition software, determine the exposure empirically to obtain the optimal quality of the image (e.g., 0.80851 s in this particular setup) and adjust it by typing this value into the exposure time option box. Select the 80 kV option, and click Start Acquisition to capture the image.
Results
To assess which SEC chromatography fractions were enriched for EVs, the SEC column was loaded with 2 mL of E. coli MP1-conditioned culture medium that had been concentrated 1,000-fold by TFF, and sequential fractions were collected. Using MRPS, it was found that Fractions 1-6 contained the most EVs (Figure 2A). Subsequent fractions contained very few EVs, comprising instead of EV-free proteins (Figure 2B). EVs were primarily <100 nm in diameter (
Discussion
In the protocol above, a method is described that is scalable and reliably isolates EVs from various gram-negative/positive and aerobic/anaerobic bacteria. It has several potential stopping points throughout the procedure, although it is better to avoid taking longer than 48 h to isolate EVs from conditioned bacterial culture media.
First, it consists of culturing bacteria to generate conditioned bacterial culture medium. It was found that increasing the culture time to at least 48 h and using...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
The research described above was supported by NIH TL1 TR002549-03 training grant. We thank Drs. John C. Tilton and Zachary Troyer (Case Western Reserve University) for facilitating access to the particle size analyzer instrument; Lew Brown (Spectradyne) for technical assistance with analysis of the particle size distribution data; Dr. David Putnam at Cornell University for providing pClyA-GFP plasmid14; and Dr. Mark Goulian at the University of Pennsylvania for providing us with the E. coli MP113.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.5 mL flat cap, thin-walled PCR tubes | Thermo Scientific | 3430 | it is important to use thin-walled PCR tubes to obtain accurate readings with Qubit |
| 16% Paraformaldehyde (formaldehyde) aqueous solution | Electron microscopy sciences | 15700 | |
| 250 mL Fiberlite polypropylene centrifuge bottles | ThermoFisher | 010-1495 | |
| 500 mL Fiberlite polypropylene centrifuge bottles | ThermoFisher | 010-1493 | |
| 65 mm Polypropylene Round-Bottom/Conical Bottle Adapter | Beckman Coulter | 392077 | Allows Vivacell to fit in rotor |
| Akkermansia mucinophila | ATCC | BAA-835 | |
| Amicon-15 (100 kDa MWCO) | MilliporeSigma | UFC910024 | |
| Avanti J-20 XPI centrifuge | Beckman Coulter | No longer sold by Beckman. Avanti J-26XP is closest contemporary model. | |
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI 5482 | ATCC | 29148 | |
| Bifidobacterium breve | NCIMB | B8807 | |
| Bifidobacterium dentium | ATCC | 27678 | |
| Brain Heart infusion (BHI) broth | Himedia | M2101 | After autoclaving, Both BHI broth and agar were introduced into the anaerobic chamber, supplemented with Menadione (1 µg/L), hematin (1.2 µg/L), and L-Cysteine Hydrochloride (0.05%). They were then incubated for at least 24 h under anaerobic conditions before inoculation with the anaerobic bacterial strains. |
| C-300 microfluidics cartridge | Spectradyne | ||
| Chloramphenicol | MP Biomedicals | ICN19032105 | |
| Escherichia coli HST08 (Steller competent cells) | Takara | 636763 | |
| Escherichia coli MP1 | Dr. Mark Goulian (gift) | commensal bacteria derived from mouse gut | |
| Fiberlite 500 mL to 250 mL adapter | ThermoFisher | 010-0151-05 | used with Fiberlite rotor to enable 250 mL bottles to be used for smaller size of starting bacterial culture |
| Fiberlite fixed-angle centrifuge rotor | ThermoFisher | F12-6x500-LEX | fits 6 x 500 mL bottles |
| Formvar Carbon Film 400 Mesh, Copper | Electron microscopy sciences | FCF-400-CU | |
| Glutaraldehyde (EM-grade, 10% aqeous solution) | Electron microscopy sciences | 16100 | |
| Hematin | ChemCruz | 207729B | Stock solution was made in 0.2 M L-histidine solution as 1.2 mg/mL |
| Infinite M Nano+ Microplate reader | Tecan | This equibment was used to measure the mCherry fluorescence | |
| In-Fusion HD Cloning Plus | Takara | 638909 | For cloning of the PCR fragements into the PCR-lineraized vectors |
| JS-5.3 AllSpin Swinging-Bucket Rotor | Beckman Coulter | 368690 | |
| Lauria Bertani (LB) broth, Miller | Difco | 244620 | |
| L-Cysteine Hydrochloride | J.T. Baker | 2071-05 | It should be weighed and added directly to the autoclaved BHI media inside the anaerobic chamber |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Female Luer to Hose Barb Adapter, 1/8" ID; 25/PK | cole-parmer - special | HV-30800-08 | connection adapters for filtration tubing circuit |
| Masterflex Fitting, Polypropylene, Straight, Male Luer to Hose Barb Adapter, 1/8" ID; 25/PK | cole-parmer - special | HV-30800-24 | connection adapters for filtration tubing circuit |
| Masterflex L/S Analog Variable-Speed Console Drive, 20 to 600 rpm | Masterflex | HV-07555-00 | |
| Masterflex L/S Easy-Load Head for Precision Tubing, 4-Roller, PARA Housing, SS Rotor | Masterflex | EW-07514-10 | |
| Masterflex L/S Precision Pump Tubing, PharmaPure, L/S 16; 25 ft | Cole Palmer | EW-06435-16 | low-binding/low-leaching tubing |
| Menadione (Vitamin K3) | MP | 102259 | Stock solution was made in ethanol as 1 mg/mL |
| MIDIKROS 41.5CM 100K MPES 0.5MM FLL X FLL 1/PK | Repligen | D04-E100-05-N | TFF device we have used to filter up to 2 L of E. coli culture supernatant |
| Nano-Glo Luciferase Assay System | Promega | N1110 | This assay kit was used to measure the luminescence of the nluc reporter protein |
| NanoLuc (Nluc) Luciferase Antibody, clone 965808 | R&D Systems | MAB10026 | |
| nCS1 microfluidics resistive pulse sensing instrument | Spectradyne | ||
| nCS1 Viewer | Spectradyne | Analysis software for particle size distribution | |
| OneTaq 2x Master Mix with Standard Buffer | NEB | M0482 | DNA polymerase master mix used to perform the routine PCR reactions for colony checking |
| Protein LoBind, 2.0 mL, PCR clean tubes | Eppendorf | 30108450 | |
| Q5 High-Fidelity 2x Master Mix | NEB | M0492 | DNA polymerase master mix used to perform the PCR reactions needed for cloning |
| qEV original, 35 nm | Izon | maximal loading volume of 0.5 mL | |
| qEV rack | Izon | for use with the qEV-original SEC columns | |
| qEV-2, 35 nm | Izon | maximal loading volume of 2 mL | |
| Qubit fluorometer | ThermoFisher | Item no longer available. Closest available product is Qubit 4.0 Fluorometer (cat. No. Q33238) | |
| Qubit protein assay kit | ThermoFisher | Q33211 | Store kit at room temperature. Standards are stored at 4 °C. |
| Sorvall Lynx 4000 centrifuge | ThermoFisher | 75006580 | |
| SpectraMax i3x Microplate reader | Molecular Devices | This equipment was used to measure the nanoluciferase bioluminescence | |
| Stericup Quick-release-GP Sterile Vacuum Filtration system (150, 250, or 500 mL) | MilliporeSigma | S2GPU01RE S2GPU02RE S2GPU05RE | One or multiple filters can be used to accommodate working volumes. In our experience, you can filter twice the volume listed on the product size. |
| Uranyl acetate | Electron microscopy sciences | 22400 | |
| Vinyl anaerobic chamber | Coy Lab | ||
| Vivacell 100, 100,000 MWCO PES | Sartorius | VC1042 | |
| Whatman Anotop 10 Plus syringe filters (0.02 micron) | MilliporeSigma | WHA68093002 | to filter MRPS diluent |
References
- Yanez-Mo, M., et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 4, 27066 (2015).
- Chatterjee, S. N., Das, J. Electron microscopic observations on the excretion of cell-wall material by Vibrio cholerae. Journal of General Microbiology. 49 (1), 1-11 (1967).
- Ciofu, O., Beveridge, T. J., Kadurugamuwa, J., Walther-Rasmussen, J., Hoiby, N. Chromosomal beta-lactamase is packaged into membrane vesicles and secreted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 45 (1), 9-13 (2000).
- Yonezawa, H., et al. Outer membrane vesicles of Helicobacter pylori TK1402 are involved in biofilm formation. BMC Microbiology. 9, 197 (2009).
- Mashburn, L. M., Whiteley, M. Membrane vesicles traffic signals and facilitate group activities in a prokaryote. Nature. 437 (7057), 422-425 (2005).
- Kato, S., Kowashi, Y., Demuth, D. R. Outer membrane-like vesicles secreted by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans are enriched in leukotoxin. Microbial Pathogenesis. 32 (1), 1-13 (2002).
- Petousis-Harris, H., et al. Effectiveness of a group B outer membrane vesicle meningococcal vaccine against gonorrhoea in New Zealand: a retrospective case-control study. Lancet. 390 (10102), 1603-1610 (2017).
- Kim, O. Y., et al. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles suppress tumor by interferon-gamma-mediated antitumor response. Nature Communications. 8 (1), 626 (2017).
- Thery, C., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 7 (1), 1535750 (2018).
- Consortium, E. -. T., et al. EV-TRACK: transparent reporting and centralizing knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nature Methods. 14 (3), 228-232 (2017).
- Watson, D. C., et al. Efficient production and enhanced tumor delivery of engineered extracellular vesicles. Biomaterials. 105, 195-205 (2016).
- Watson, D. C., et al. Scalable, cGMP-compatible purification of extracellular vesicles carrying bioactive human heterodimeric IL-15/lactadherin complexes. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 7 (1), 1442088 (2018).
- Lasaro, M., et al. Escherichia coli isolate for studying colonization of the mouse intestine and its application to two-component signaling knockouts. Journal of Bacteriology. 196 (9), 1723-1732 (2014).
- Kim, J. Y., et al. Engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles with enhanced functionality. Journal of Molecular Biology. 380 (1), 51-66 (2008).
- Beveridge, T. J. Structures of gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. Journal of Bacteriology. 181 (16), 4725-4733 (1999).
- Reimer, S. L., et al. Comparative analysis of outer membrane vesicle isolation methods with an Escherichia coli tolA mutant reveals a hypervesiculating phenotype with outer-inner membrane vesicle content. Frontiers in Microbiology. 12, 628801 (2021).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved