Abstract
Medicine
High-Resolution Respirometry to Assess Mitochondrial Function in Human Spermatozoa
ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …Semen quality is often studied by routine semen analysis, which is descriptive and often inconclusive. Male infertility is associated with altered sperm mitochondrial activity, so the measurement of sperm mitochondrial function is an indicator of sperm quality. High-resolution respirometry is a method of measuring the oxygen consumption of cells or tissues in a closed-chamber system. This technique can be implemented to measure respiration in human sperm and provides information about the quality and integrity of the sperm mitochondria. High-resolution respirometry allows the cells to move freely, which is an a priori advantage in the case of sperm. This technique can be applied with intact or permeabilized spermatozoa and allows for the study of intact sperm mitochondrial function and the activity of individual respiratory chain complexes. The high-resolution oxygraph instrument uses sensors to measure the oxygen concentration coupled with sensitive software to calculate the oxygen consumption. The data are used to calculate respiratory indices based on the oxygen consumption ratios. Consequently, the indices are the proportions of two oxygen consumption rates and are internally normalized to the cell number or protein mass. The respiratory indices are an indicator of sperm mitochondrial function and dysfunction.
Erratum
Erratum: High-Resolution Respirometry to Assess Mitochondrial Function in Human SpermatozoaAn erratum was issued for: High-Resolution Respirometry to Assess Mitochondrial Function in Human Spermatozoa. The Protocol and Representative Result sections were updated.
Step 2.4.12 of the Protocol was updated from:
Finally, inject 1 µL of 5 mM antimycin A (2.5 µM final concentration). This is a complex II inhibitor to discriminate between the mitochondrial and residual oxygen consumption (non-mitochondrial respiration). For the analysis of complex I, add 1 µL of 1 mM rotenone (0.5 µM final concentration), an inhibitor of this complex, instead of AA. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal decreases and stabilizes.
to:
Finally, inject 1 µL of 5 mM antimycin A (2.5 µM final concentration). This is a complex III inhibitor to discriminate between the mitochondrial and residual oxygen consumption (non-mitochondrial respiration). For the analysis of complex I, add 1 µL of 1 mM rotenone (0.5 µM final concentration), an inhibitor of this complex, instead of AA. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal decreases and stabilizes.
Figure 3 in the Representative Results section was updated from:
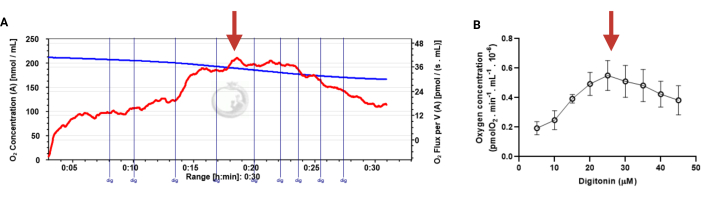
Figure 3: Determination of the optimal concentration of digitonin for the permeabilization of human sperm cells. The respiration rates were measured at 37 °C in MRM medium with glutamate, malate, and adenosine diphosphate. (A) Representative respiratory trace. The blue line is the O2 concentration, and the red line represents the O2 flow per volume correlated. (B) Mitochondria respiration rate means ± standard error, n = 4. The red arrow represents the optimal concentration. Abbreviation: dig = digitonin. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
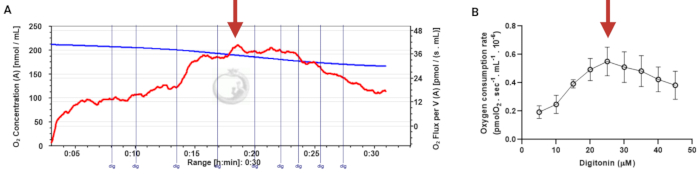
Figure 3: Determination of the optimal concentration of digitonin for the permeabilization of human sperm cells. The respiration rates were measured at 37 °C in MRM medium with glutamate, malate, and adenosine diphosphate. (A) Representative respiratory trace. The blue line is the O2 concentration, and the red line represents the O2 flow per volume correlated. (B) Mitochondria respiration rate means ± standard error, n = 4. The red arrow represents the optimal concentration. Abbreviation: dig = digitonin. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved