Mouse Lumbar Vertebra Uniaxial Compression Testing with Embedding of the Loading Surface
In This Article
Summary
In this protocol, two approaches are described to make uniaxial compression testing of mouse lumbar vertebrae more attainable. First, the conversion of a three-point bending machine to a compression testing machine is described. Second, an embedding method for preparing the loading surface that uses bone cement is adapted for mouse lumbar vertebrae.
Abstract
There is increasing awareness that cortical and cancellous bone differ in regulating and responding to pharmaceutical therapies, hormone therapies, and other treatments for age-related bone loss. Three-point bending is a common method used to assess the influence of a treatment on the mid-diaphysis region of long bones, which is rich in cortical bone. Uniaxial compression testing of mouse vertebrae, though capable of assessing bones rich in cancellous bone, is less commonly performed due to technical challenges. Even less commonly performed is the pairing of three-point bending and compression testing to determine how a treatment may influence a long bone's mid-diaphysis region and a vertebral centrum similarly or differently. Here, we describe two procedures to make compression testing of mouse lumbar vertebrae a less challenging method to perform in parallel with three-point bending: first, a procedure to convert a three-point bending machine into a compression testing machine, and second, an embedding method for preparing a mouse lumbar vertebra loading surface.
Introduction
Age-related bone changes are widely recognized as problematic due to the increased risk of bone fractures associated with these changes. Bone fractures in humans can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, long-term disability, an increased risk of death, and economic burdens1. Common therapies investigated to address the symptoms of age-related bone changes include dietary supplements, hormone treatments, and drugs2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. Initial investigations of such treatments for human subjects are commonly done using small animal models (e.g., laboratory rats and mice), which possess the two major types of bones found in the human skeleton10. Appendicular long bones, such as the humerus, femur, and tibia, are rich in cortical (i.e., compact) bone, whereas vertebrae are rich in cancellous bone (i.e., woven, spongy, or trabecular bone)4. There is growing knowledge that the mechanisms of bone regulation and signaling pathways differ between cortical bone (e.g., long bone mid-diaphysis) and cancellous bone (e.g., vertebral centrum)2. Because of this, therapies may have differential effects that are bone-specific or even site-specific within the same bone2,3,4.
The application of force to an object (e.g., bone) causes the object to undergo acceleration, deformation, or both, depending on the object's boundary conditions. When the bone is constrained, an opposite force of equal magnitude resists the acceleration of the bone, and deformation occurs. As the bone sustains deformation, internal resistance called stress is generated, of which there are two basic types: Normal force, in the form of tension or compression, and shear force10. Often, a combination of the basic types of stress is generated, depending on the applied force system10. The strength of a material is its ability to withstand stress without failing. As increasingly larger forces are applied to a material, it eventually undergoes permanent deformation, at which point it is said to have transitioned from an elastic state (i.e., will return to its original shape if the force is removed) to a plastic state (i.e., will not return to its original shape if the force is removed)11. The point at which the transition from an elastic state to a plastic state occurs is called the yield point. As even larger forces are applied to the material beyond the yield point, it increasingly sustains microfractures (i.e., damage) until total fracture occurs; at this point, the material is said to have failed11,12. The fracture of a bone represents a failure at both a structural level and a tissue level10. As an example, the breakage of a vertebral bone happens because not only do multiple trabeculae fail at a structural level, but there's also a failure of extracellular matrix elements like collagen and hydroxyapatite crystals in an individual trabecula at the tissue level.
The mechanical events leading up to the failure of a material can be measured using a variety of testing methods. Three-point bending is a common method for testing the mechanical properties of long bones from the appendicular skeleton. This method is simple and reproducible, making it the preferred method of biomechanical testing for many researchers13. By lowering a crosshead beam onto the mid-diaphysis of a long bone resting on two lower support beams, this method specifically tests the mechanical properties of the mid-diaphysis region, which is densely organized cortical bone. From load-displacement curves, tensile force effects on elasticity, toughness, force to failure, and the transition from elastic to plastic behavior of bone materials, among other properties, can be determined.
In the second type of bone, referred to as trabecular, spongy, woven, or cancellous bone, bone elements are formed into an array of rods and beams called trabeculae, giving a "spongy" appearance. The main vertebral bodies (i.e., centra) are rich in cancellous bone and are often the sites of age-related compression bone fractures in humans14. Lumbar (i.e., lower back) vertebrae are the largest vertebrae, bear most of the body's weight, and are the most common site for vertebral fractures15,16. The mechanical properties of vertebral bodies can best be directly assessed using uniaxial compression testing methods since axial compression is the normal force load imposed on vertebral columns in vivo17. Compression of the vertebral bodies in vivo occurs as a result of muscle and ligament contractions, the force of gravity, and ground reaction forces18.
Ex vivo compression testing of small animal vertebra can be difficult due to their small size, irregular shape, and fragility. The shape of vertebral bodies can be estimated as a parallelogram with mild ventral tilt and slight cranial concavity17. This shape presents challenges for achieving uniaxial compression testing ex vivo because, without adequate preparation to the loading surface, compressive forces will be applied to only part of the loading surface, resulting in a "local contact"17,19. This can cause inconsistent results and premature failure19. This is not the case in vivo because the loading surface is surrounded by intervertebral discs at the vertebral joints, which allows the load to be distributed throughout the cranial end plate. The intervertebral disc-cranial end plate complex plays an important role in the application of force throughout the vertebral body and the biomechanics of fracture to the vertebral body14,20. While compression testing is not new to the field of biology, there are limitations in the current methods of mechanical testing of bones. These limitations include the lack of predictor models and simulations for bone mechanics, unique geometric spatial architecture, and even inherent sample-based biological variations21. More importantly, the field is challenged by a lack of standardization between methods and an overall lack of reported methods in the literature22.
There are two methods reported in the literature for the preparation of rodent lumbar vertebrae to achieve uniaxial compression testing: the cutting method and the embedding method17,19,23,24,25,26. The cutting method requires that the vertebral processes, cranial end plate, and caudal end plate are cut from the vertebral body. Pendleton et al.19 have previously reported a detailed method for the use of this method on mouse lumbar vertebrae. This method presents the challenges of achieving perfectly parallel cuts at both the caudal and cranial end plates while also avoiding any damage to the sample. It also has the limitation that the cranial end plate is removed. The cranial end plate contains a dense shell of cortical bone and plays an important role in distributing loads from the intervertebral discs in vivo and is involved in the failure of the bone for in vivo fractures17,20,27. In contrast, the embedding method involves removing the vertebral processes while keeping the cranial end plate of the vertebral body intact. The loading surface is then made approximately horizontal by placing a small amount of bone cement onto the cranial end of the vertebral body. This method has the advantage that it overcomes the technical challenges associated with the cutting method and may better mimic the mechanism of load application and bone failure in vivo due to the preservation of the cranial end plate. This approach has previously been documented in studies involving uniaxial compression testing on rat bones. However, as far as we are aware, it has not been previously documented in the context of smaller mouse lumbar vertebrae17,25,26. The method in question was previously detailed by Chachra et al.25 and originally used a bone specimen held in between two plates, each with a cylindrical cavity, which was then filled with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). The same research group later improved the method where one end is gently sanded (caudal), and the other end has a small spot of bone cement added (cranial)26. This method is an improvement on the previous method because it minimizes the material between the platens and is the focus of this article. Despite the challenges associated with uniaxial vertebral compression testing, it is a method that may provide valuable information regarding the effects of a proposed therapy on bone, especially when paired with three-point bending.
Here, the use of a convertible three-point bending/compression testing machine to allow for easy testing of both long bones and vertebral bodies using a single machine is presented. Furthermore, the use of an embedding method to achieve uniaxial compression testing of mouse lumbar vertebrae is presented. The present study was performed as part of a larger study that aimed to investigate the influences of dietary hempseed supplementation on the properties of skeletal bone in young, growing female C57BL/6 mice5,6. The three-point bending tester was originally constructed by faculty and students in the Engineering Dept. at Colorado State University-Pueblo and used by our research group in three-point bending tests on long bones [rat femur and tibia7 and mouse humerus, femur, and tibia5,6,8,9]. However, its modification and application for use in mouse vertebral body compression testing was not been explored. The design and construction of the three-point bending machine have been previously described7. This report will focus on methods used to modify the machine for compression testing and to correct for system displacement. Secondly, the embedding method for mouse vertebral body loading surface preparation is described, along with methods for uniaxial compression testing and the analysis of load-displacement data.
Protocol
All experiments and protocols were conducted in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals from the National Institutes of Health and received approval from the Colorado State University-Pueblo Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol Number: 000-000A-021). Detailed procedures for animal care have been previously described5,6. The mice were obtained at three weeks of age as part of a broader study aimed at investigating the effects of a hempseed-supplemented diet on young, growing female C57BL/6 mice (see Table of Materials). From 5 to 29 weeks of age, the mice were raised on one of three diets: control (0% hempseed), 50 g/kg (5%) hempseed, or 150 g/kg (15%) hempseed, with eight mice per group5,6. Throughout the study, mice had ad libitum access to their respective diets and water, were pair-housed in polycarbonate cages, and maintained on a 12 h light:12 h dark cycle (with lights on from 06:00 to 18:00 h). The mice's weight and health were assessed weekly, and all mice successfully completed the study without developing any adverse health conditions. At twenty-nine weeks of age, the mice were deeply anesthetized using isoflurane gas and euthanized via cervical dislocation5,6. A midline incision was made on the ventral surface from the sternum to the tail, and all intrathoracic, peritoneal, and retroperitoneal organs were removed from the carcasses. The eviscerated carcasses were preserved in 0.9% sodium chloride solution at -70 °C until the time of bone dissection for vertebra testing, which occurred approximately one year later.
1. Conversion of a three-point bending machine to a compression testing machine
- Unscrew the crosshead beam attached to the load sensor on the three-point bending machine7 (see Table of Materials) (Figure 1A,B).
- Screw a self-aligning top platen onto the load sensor (see Table of Materials) with threading identical to the crosshead beam (Figure 1C).
- Drill two horizontal holes into each of the lower supports, where the bottom platen will be attached later (Figure 1D).
- Tap threads into the two sides of a stainless-steel bottom platen to align with the drilled holes in the lower supports (Figure 1E).
- Secure the bottom platen to the two lower supports using threaded hex screws and tighten until secure (Figure 1F).
NOTE: Hex screws must have threads that match the tapped holes on the lower supports and top/bottom platens. The use of a self-aligning top platen may help achieve uniform contact between the top platen and the loading surface, but it is not sufficient given the concavity of the cranial end of vertebral bodies. Further preparation using a loading surface preparation method is required. When constructing a compression testing machine for small animal bones, which are smaller and weaker than many industrial/engineering materials, it is essential to consider the load capacity of the load sensor and the size of the load frame. Additionally, machines should be regularly cleaned and lubricated to ensure accurate results and smooth operation.
2. Correcting for the displacement of the compression testing machine
- With no test material between the top platen and bottom platen, lower the top platen onto the bottom platen until light contact has been made (~0.3-0.5 N preload force).
- Turn on the machine at a constant lowering speed (~1 mm/min) to begin compression testing. Collect load (N) and displacement (mm) measurements using digital data collection software (see Table of Materials) for data collection of mechanical testing.
NOTE: Since no material is between the top and bottom platen, all displacement observed will be due to displacement of the machine alone (Δxmachine) (frame, load cell, platens, couplings, etc.). - Continue to lower the top platen onto the bottom platen at a constant (i.e., monotonic) speed until forces higher than what will be obtained from all bone samples are reached.
- Repeat steps 2.1 to 2.3 for a total of three times.
- Plot the data for system displacement (Δxmachine, mm) vs. applied load (Force, N).
- Fit a regression line of best fit to the data (Figure 2A-D).
- In a spreadsheet with the data from a bone compression test, use the equation provided by the regression analysis to determine the amount of machine displacement (Δxmachine) influencing the recorded displacement (Δxtotal recorded) for a data point of a mouse lumbar vertebra compression test.
NOTE: For example, consider a data point where 18 N of force is applied, and 2.730 mm of displacement has been recorded (Δxtotal recorded). According to the example third-order polynomial regression equation (Figure 2D) [Δxmachine = (4 × 10-7 x Applied Load3) - (8 × 10-5 x Applied Load2) + (0.0044 x Applied Load)], 0.056 mm of the displacement recorded is due to machine displacement (Δxmachine).
Δxtotal recorded= Δxmachine + Δxspecimen - Correct the recorded displacement for the data point.
NOTE: For example, consider the example above. If 2.730 mm of displacement is recorded (Δxtotal recorded) and machine displacement (Δxmachine) accounts for 0.056 mm of the total, then the displacement that the specimen (i.e., bone) of interest underwent (Δxspecimen) is 2.664 mm. Thus, 2.664 mm is the actual displacement that the vertebra underwent (Δxspecimen) and is the value to be used for load-displacement curve analysis.
Δxspecimen = Δxtotal recorded - Δxmachine - Repeat steps 2.7-2.8 for every data point collected for every single specimen (bone).
NOTE: This step is important because during compression testing, the displacement observed is not only due to displacement of the specimen, but instead, the observed displacement is a combination of machine displacement (Δxmachine) (e.g., compression/displacement of the frame, load cell, platens, couplings, etc.) and the specimen (Δxspecimen). Thus, for specimens that undergo relatively small amounts of displacement, such as those of a small animal (e.g., mouse), system displacement (Δxmachine) can cause large errors. The procedures described here to correct for system displacement were previously reported by Kalidindi and Abusafieh28, who also detail two other methods in addition to the one described here. Some researchers have been noted to use more than one method for determining system displacement17. Each machine may display unique patterns and degrees of system displacement when loads are applied to it. For this reason, the system displacement correction factor must be determined for each machine and will not be the same between any two machines. In contrast to compression testing of a vertebral bone, a large force reduction will not be observed when measuring for system displacement because no material is between the top and bottom platen.
3. Dissection of the 5 th lumbar vertebra (L5) from the mouse carcass
- Thaw frozen mouse carcass at room temperature, taking care to keep soft tissues and bones hydrated by regularly applying an isotonic solution of 0.9% NaCl.
- Make a small (<0.5 cm) incision in the skin on the dorsal midline near the base of the tail, then extend the cut across each hindlimb and gently pull to remove the pelt from the base of the tail to the head of the animal.
- Cut away the abdominal wall musculature until the vertebral column is easily visible.
- Under a dissecting microscope, visualize the two sacroiliac joints and the cranial end of the sacrum.
- Using a razor blade or scalpel, make a fine cut to separate the last lumbar vertebra (L6) from the cranial end of the sacrum.
- Again, cutting between the intervertebral space, remove L6 and L5 from the vertebral column, setting aside L5 for analysis (Figure 3).
- Inspect the vertebra under a dissecting microscope and remove all soft tissues from the bone, including the intervertebral disc, using mostly gauze pads and gently with forceps where necessary.
NOTE: In the present study, the L5 was chosen as the vertebra of interest, but other lumbar vertebrae may be chosen for compression testing.
4. Preparing L5 vertebra loading surface for uniaxial compression testing using PMMA bone cement embedding method
- Using a diamond-cutoff wheel (see Table of Materials) attached to a rotary tool, make a cut at each pedicle to remove the transverse and spinous process (Figure 4). If left attached to the centrum, vertebral processes can result in local contacts with the upper/lower platens at the processes themselves as opposed to a distribution of the load throughout the centrum.
- Gently sand the caudal end of the vertebra using fine 120-grit sandpaper (see Table of Materials) to remove all intervertebral discs, soft tissue, and irregularities.
- Mark the sanded caudal end with a permanent marker for easy identification later.
- Mix the PMMA bone cement according to the manufacturer's instructions (see Table of Materials).
- With the PMMA bone cement still semi-soft, place a minimal amount onto the cranial (unmarked) end of the vertebra facing up, ensuring that the entire surface is covered while the vertebra sits in a saline bath to keep the bone sample hydrated and cool.
- With the PMMA still semi-soft, position the vertebra on the bottom platen with the caudal (marked) side facing down (Figure 5).
- Turn on the machine to engage the drive gears and slowly lower the top platen onto the vertebra + PMMA bone cement complex until contact is made with the bone cement and minimal force (<0.5 N) is applied to distribute the PMMA evenly on the bone surface. The top platen in a neutral position can be estimated as horizontal and, when pressing onto semi-soft PMMA, will cause the PMMA to fill the concavity on the cranial end of the vertebra and form a flat horizontal surface beneath the top platen.
- With the top platen gently pressing down on the PMMA bone cement, let the sample sit undisturbed until the PMMA bone cement has completely hardened (~10 min per the manufacturer's instructions for the PMMA bone cement used in the present study). Keep the sample in a saline bath or frequently mist it with saline during this period to keep the sample hydrated and cool.
- Once the PMMA bone cement has completely hardened, compression testing can begin. Collect data for load (i.e., force) (N) and displacement (i.e., deflection) (mm) from the sensors into a spreadsheet in real-time using digital software designed for data collection of mechanical testing (see Table of Materials).
- After baseline data collection for 5 s, applied at a minimal preload force of <0.5 N, begin lowering the top platen onto the sample at a single (i.e., monotonic), pre-determined lowering speed to start the compression test (~1 mm/min).
- Stop collecting data once a large reduction in load (N) has been observed, indicating material failure.
NOTE: Manufacturer instructions will specify the approximate hardening time for PMMA bone cement. Hardening time for the PMMA bone cement may differ depending on the type of PMMA bone cement used. Follow manufacturer instructions to determine the wait time for PMMA hardening. However, as an indicator that the PMMA bone cement has completely hardened, an additional sample of the PMMA bone cement can be mixed at the same time as the sample that will be placed on the vertebra but kept aside and checked to see if it is still soft or completely hardened. If completely hardened, this can indicate that the PMMA on the bone is also completely hardened without disturbing the bone + PMMA complex. The bone sample must remain well-hydrated and cool throughout the PMMA hardening and testing periods. As little as a few minutes of exposure to dry air can result in changes to the biomechanical properties. Some researchers use compression testing machines equipped with a saline bath19. The compression testing machine did not have a saline bath in the present study. Instead, a fine mist of saline was regularly applied throughout the PMMA hardening period and testing period.
5. Analysis of load-displacement curves for L5 vertebra uniaxial compression tests
- Copy and paste load (N) and corrected displacement (mm) data from the spreadsheet into a technical graphing and data analysis software (see Table of Materials).
- Generate a graph with load (N) on the y-axis and corrected specimen displacement (Δxspecimen, mm) on the x-axis (Figure 6). Do this in the software by first clicking on Windows, New Table, then Do it to make a table. Copy corrected displacement (mm) and load (N) data from the raw data spreadsheet into the new table.
- Next, generate a waveform to represent raw data by clicking on Data, then click on XY Pair to Waveform and select corrected displacement data for the X-Wave and load data for the Y-Wave. Ensure that the correct number of data points is in the "Number of Points" box, name the waveform, then click on Make Waveform. Once a waveform has been made, generate a graph by clicking on Windows, then New Graph, and place the waveform on the Y-axis and "calculated" on the X-axis.
- Use the cursor tool to mark points/regions of interest on the graph for analysis. A few of the points/regions of interest to calculate common whole-bone mechanical properties are mentioned in steps 5.4-5.8 (Figure 6), and include work-to-failure (N x mm), maximum load (N), stiffness (N/mm), yield load (N), and post-yield displacement (mm).
- For calculation of work-to-failure (N x mm), place a cursor (A) at the start of the test and a cursor (B) at the point immediately before the material fails (i.e., at the maximum load reached during the test before a large decrease in load is observed).
NOTE: Thus, cursors A-B will bracket the entirety of the test from when the material starts to withstand forces and undergo displacement to the point where the material fails. Work-to-failure (N x mm) can be measured as the total area underneath the curve (i.e., the area underneath the curve between cursors A and B). - Calculate maximum load (N) as the highest value for the load that is observed during the test (i.e., load at cursor B).
- Calculate the stiffness (N/mm) of the material as the slope of the linear elastic region (i.e., the slope between cursors C and D).
- The yield load (N) is the load at which the load-displacement curve deviates from linearity and enters the plastic region, thus sustaining permanent deformity (i.e., load at point D). Calculate this by measuring the load at cursor D.
- The post-yield displacement (mm) is an indicator of a material's ductility. Measure this as the displacement between the yield point and the point of material failure (i.e., the displacement between cursors D and B).
NOTE: The parameters listed above are only some of the common whole-bone mechanical properties reported. It is not a complete list of all whole-bone mechanical properties that can be obtained from a load-displacement curve. Other whole-bone mechanical property parameters include total displacement (mm), elastic energy absorbed (N x mm), elastic displacement (mm), plastic energy absorbed (N x mm), and plastic displacement (mm), to name a few. Furthermore, tissue-level bone mechanical properties are not listed; these require data transformations using specific anatomical measurements, such as bone diameter. Example code to make the measurements from the load-displacement curve in the software have been listed in Supplementary File 1.
Representative Results
With this step-by-step protocol that uses embedding of the L5 loading surface and a convertible three-point bending machine/compression testing machine, it is possible to perform compression testing on mouse lumbar vertebra for inter-group comparisons. A total of twenty-four mouse L5 vertebrae were prepared using the embedding method. Three of the samples, however, were damaged during the removal of the vertebral processes using a diamond cutoff wheel on a rotary tool and, thus, were not tested. Given this, the mechanical properties listed were successfully obtained from twenty-one of twenty-four samples using the embedding method. Specimens were visually inspected after each test, and the PMMA cap sustained no damage in any of the tests. As noted, the mice used in the present study were part of a larger study aiming to determine the effects of dietary hempseed on the bones of young and growing C57BL/6 female mice. Descriptive statistics of five commonly reported whole-bone mechanical properties are offered in Table 1. The load-displacement curves for all twenty-one samples are provided in Figure 7.
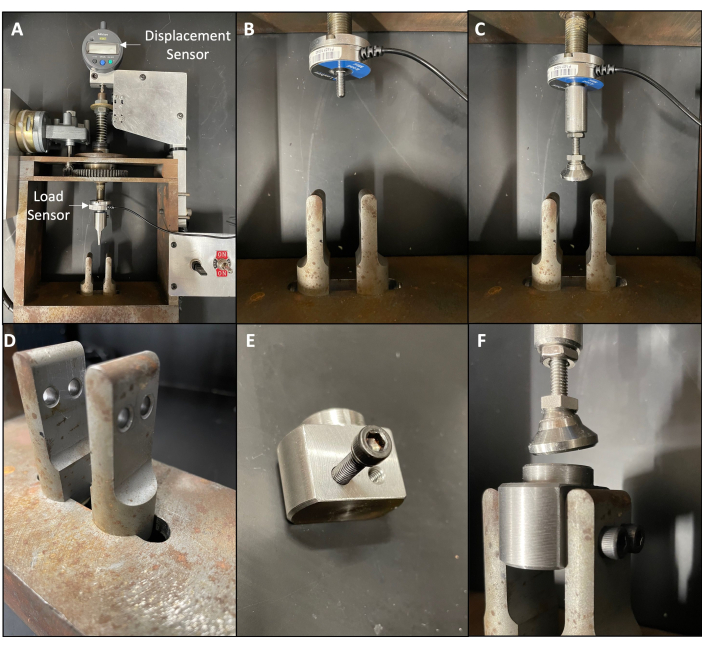

Figure 1: The conversion of a three-point bending machine to a compression testing machine. (A) The machine fully equipped to operate as a three-point bending machine with the displacement sensor and load sensor indicated (white arrows). (B) The machine after the crosshead beam has been removed. (C) The machine after a self-aligning top platen has been placed where the crosshead beam was previously placed. (D) The lower support beams with holes drilled into them. (E) The stainless-steel bottom platen with four threaded holes tapped into it, and a screw partially screwed into one of the holes. The other two holes not seen in the photo are on the opposite side. (F) The lower support beams with the bottom platen attached to them by four hex screws. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
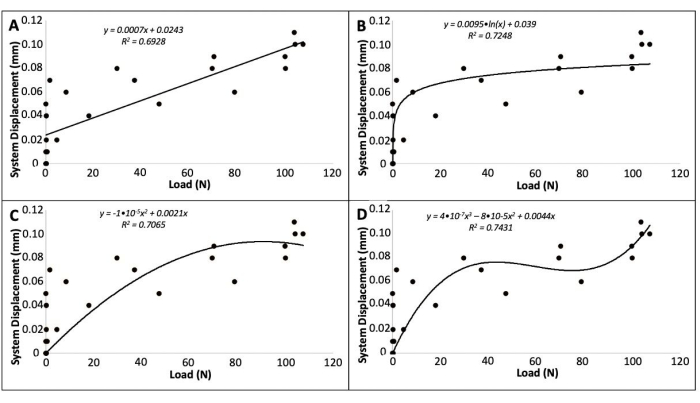
Figure 2: An example system displacement (Δxmachine) vs. load plot fitted with a linear (A), logarithmic (B), second-order polynomial (C), and third-order polynomial (D) regression. In this example, the third-order polynomial provides the best fit per R2 value, and its regression is used as the system displacement correction factor. Images represent example data to demonstrate regression fitting and will need to be obtained by researchers for individual machines. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
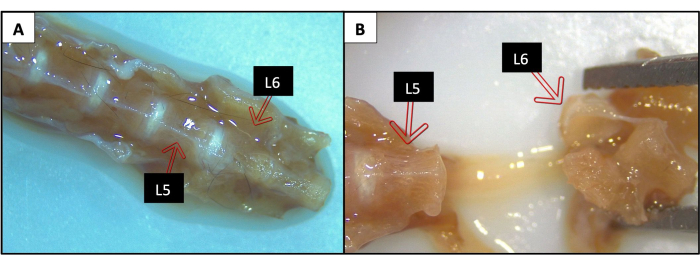
Figure 3: Mouse lumbar vertebral column. A mouse lumbar vertebral column under a dissecting microscope before L6 was removed (A), and after L6 had been removed, leaving L5 attached (B). L5 will be subsequently removed and prepared for compression testing. The white colored bands are the intervertebral discs which were dissected and removed. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
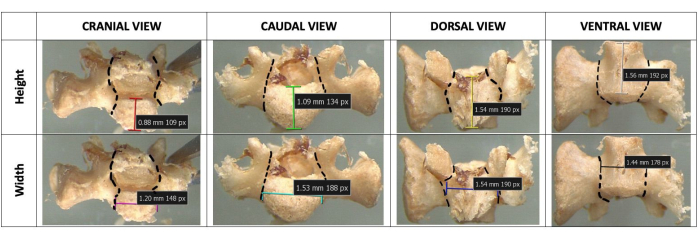
Figure 4: Anatomy of L5 vertebra. A representative mouse L5 vertebra in cranial, caudal, dorsal, and ventral views under a dissecting microscope. Important dimensions for the vertebral body include height, dorsoventral width, and lateral width, as shown by the colored lines. The black dashed lines show approximately where cuts are to be made to remove the vertebral processes. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
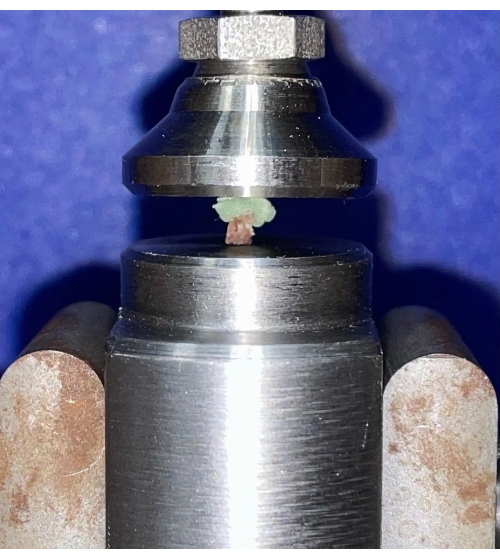

Figure 5: Hardening period of PMMA bone cement. An example L5 vertebra with PMMA bone cement (green) placed on the cranial endplate and the top platen lowered onto the PMMA bone cement + bone complex. Once PMMA bone cement has fully hardened, the compression test will begin. The top platen will be further lowered until failure of the material is observed. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
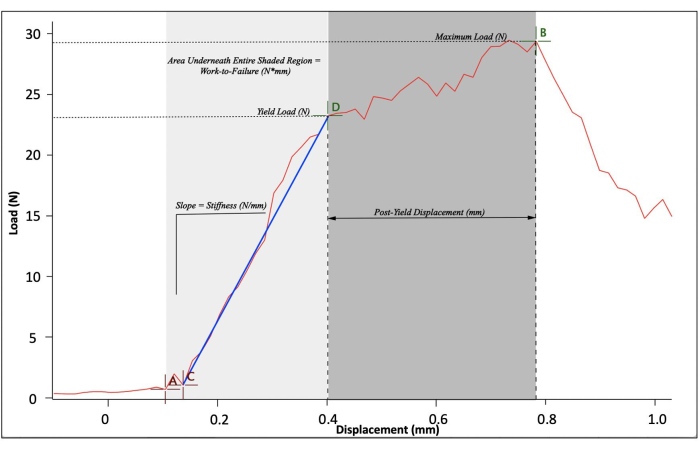
Figure 6: Mouse vertebral bone compression test load-displacement curve and data analysis. Cursor A marks the start of the compression test. Cursor B marks the point of material failure. Cursor C marks the start of the linear elastic region, whereas cursor D marks the end (i.e., the yield point). The area shaded in light gray is the linear elastic region, where the material will return to its original shape if the load is removed. The area shaded dark gray is the plastic region, where the material has undergone permanent deformity and will not return to its original shape if the load is removed. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
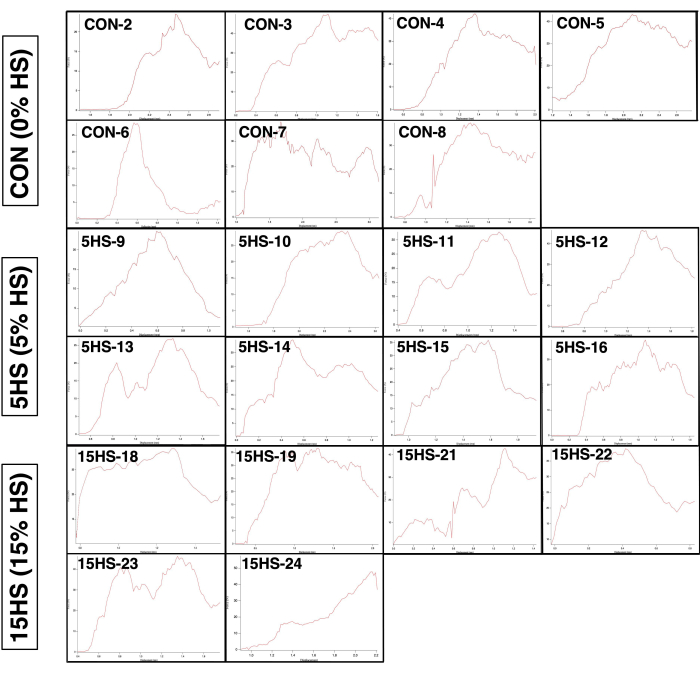
Figure 7: Load-displacement curves for all twenty-one bone samples. Patterns varied between bones. In general, the greatest variability was in post-yield displacement, with a few (n = 5) of the bones having a relatively small post-yield displacement and others (n = 16) having a relatively large post-yield displacement. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Group | Work-to-Failure (N*mm) | Maximum Load (N) | Stiffness (N/mm) | Yield Load (N) | Post-Yield Displacement (mm) |
| CON (n = 7) | 13.43 ± 2.44 A,B | 37.93 ± 3.28 | 109.14 ± 11.86 | 22.68 ± 2.04 | 0.34 ± 0.06 |
| 5HS (n = 8) | 12.12 ± 1.23 A | 33.62 ± 2.43 | 99.70 ± 16.62 | 20.88 ± 2.69 | 0.38 ± 0.08 |
| 15HS (n = 6) | 19.55 ± 2.13 B | 41.82 ± 1.85 | 134.58 ± 19.73 | 28.07 ± 3.20 | 0.51 ± 0.07 |
| Combined Groups (n = 21) | 14.68 ± 1.27 | 37.40 ± 1.63 | 121.82 ± 9.43 | 23.54 ± 1.60 | 0.40 ± 0.04 |
Table 1: Representative values for commonly reported whole-bone mechanical properties obtained using the loading surface preparation embedding method. Values were obtained using all protocols detailed in the present study. Thus, the values represent those that can be obtained using the methods described here. Values are means ± SEM. Groups represent C57BL/6 female mice fed a diet enriched with whole hempseed at concentrations of 0% (CON), 50 g/kg (5%) (5HS), or 150 g/kg (15%) (15HS) from ages 5-29 weeks. For one of the parameters (work-to-failure), it appears that the diet influenced the values per a one-way ANOVA (p < 0.05). Values sharing the same letter superscript are not significantly different (p > 0.05), while values with different letter superscripts are significantly different (p < 0.05), per Tukey-Kramer post hoc analysis.
Supplementary File 1: Example code to obtain whole-bone mechanical properties. Please click here to download this File.
Discussion
The goal of the present study was to describe the construction of a convertible three-point bending machine/compression testing machine, as well as the use of a PMMA bone cement embedding method for the preparation of mouse lumbar vertebrae samples before uniaxial compression testing. Descriptive statistics were obtained and reported for the bone samples, which will be useful for comparison in future studies. Some of the most commonly reported whole-bone mechanical properties were analyzed in the present study. However, it's worth noting that there are several additional whole-bone and tissue-level mechanical properties that were not investigated here.
It remains unclear how the mechanical properties obtained from samples prepared using the embedding method compare to those prepared using the cutting method for mouse lumbar vertebrae. Schumancher17 previously assessed the mechanical properties of rat vertebrae prepared using the two different methods and found that vertebrae prepared using the embedding method had significantly lower stiffness, higher yield displacement, and higher yield strain than samples prepared using the cutting method. Further characterization is needed to understand how the vertebral mechanical properties of mice or other animal models compare when measured using the two different methods of loading surface preparation. It's expected that some parameters differ between vertebrae prepared using different methods, given that the embedding method adds material to the sample but preserves the end plate, which is an important structure in vertebral fractures in vivo17,27. The addition of bone cement to the cranial end adds height to the sample, whereas cutting the end plates removes height, altering the aspect ratio and thereby changing mechanical properties like stiffness. Furthermore, although PMMA is stiffer than vertebral cancellous bone, it's possible that the PMMA undergoes displacement, and the extent of this displacement needs further characterization. Additionally, it's unclear how the results obtained from either the embedding method or cutting method compare to predictions of bone parameters using finite element analysis for mouse vertebrae or how the results vary under different conditions (e.g., lowering speed, different vertebral levels, PMMA compositions). Nonetheless, because all specimens are prepared in a similar manner, this method is appropriate and allows for an easy and cost-effective means of making comparisons between treatment groups in a single study where samples are prepared and tested under similar conditions.
Regarding specimen preparation before compression testing, it's essential to prepare samples in a reproducible manner. One possible limitation of the method described in the present study is the use of a rotary tool to remove the vertebral processes. Another method to remove the vertebral processes of mouse lumbar vertebrae has been described by Pendleton et al.19, which may allow for more consistent sample preparation. Furthermore, inconsistencies may arise from the application of PMMA bone cement. Therefore, it's important to apply the bone cement consistently in terms of volume, placement, and hardening time. However, the embedding method may provide a simpler means of achieving consistent sample preparation compared to the cutting method, as it can be challenging to achieve perfectly even, parallel cuts consistently between all samples due to their small size and fragility. Future studies will be needed to assess the precision of results obtained from samples prepared using the embedding vs. cutting method.
As mentioned, further characterization and investigation of the embedding method for specimen preparation of mouse lumbar vertebrae before uniaxial compression testing are needed. Nonetheless, this study demonstrates that such a method can be employed, provides a detailed description of the proposed method, and offers descriptive statistics of the parameters measured from samples prepared using the method. This protocol is valuable to the field due to the current lack of available methodology. Moreover, this method may better mimic the mechanism by which in vivo vertebral fractures occur compared to other methods17,27. The method also has the advantage of overcoming the technical difficulties associated with other currently reported methods, making uniaxial compression testing more feasible in bone research. This is particularly significant because drugs, diets, or other interventions may influence cortical-rich bones (e.g., long bone mid-diaphysis) and trabecular-rich bones (e.g., vertebral bodies) differently, yet three-point bending is the predominant method to assess the mechanical properties of bones13. The combination of three-point bending and uniaxial compression testing can become even more easily achievable through the use of a convertible three-point bending/compression testing machine. Thus, the present study proposes two possible means of making the assessment of both cortical-rich and trabecular-rich bone in the same study more available to researchers, potentially leading to a better understanding of how a given treatment affects different bone types between experimental groups.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the significant efforts that the Colorado State University-Pueblo Dept. of Engineering provided in constructing the three-point bending machine and its modification to a convertible three-point bending/compression testing machine. We are especially thankful to Mr. Paul Wallace, machine shop coordinator, for his efforts in planning and carrying out the construction and modification of the machine. Expertise and feedback from Dr. Bahaa Ansaf (Colorado State University-Pueblo, Dept. of Engineering) and Dr. Franziska Sandmeier (Colorado State University-Pueblo, Dept. of Biology) also significantly contributed to this project. The Institute of Cannabis Research Grant at Colorado State University-Pueblo funded the larger project that this experiment was a part of and allowed for the purchase of the mice, reagents, and some of the equipment used.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 120-Grit Sand Paper | N/A | N/A | For removal of caudal end plate soft tissues and irregularities |
| 24-bit Load Cell Interface | LoadStar Sensors, Freemont, California, USA | DQ-1000 | To connect load and displacement sensors to personal coputer |
| Base Mouse Diet | Dyets, Inc, Bethlehem, PA, USA | AIN-93G | Diet the mice were fed, without added hempseed |
| Diamond Cutoff Wheel w/ Rotary Tool | Dremel US, Mt. Prospect, Illinois, USA | F0130200AK | To remove vertebral proccesses |
| Displacement Sensor | Mitutoyo, Aurora, Illinois, USA | ID-S112EX | Displacement sensor with 0.001 mm resolution and 0.00305 mm accuracy |
| External Variable Voltage Power Source | Extech Instruments, Nashua, New Hampshire, USA | 382213 | To provide power to compression testing machine |
| Female C57BL/6 Mice | Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, Massachusetts, USA | 027 (Strain Code) | Mouse model used in present study |
| Hempseed | Natera, Pitt Meadows, Canada | 670834012199 | Hempseed added to Base Mouse Diet |
| Igor Pro Software (Version 8.04) | Wave Metrics, Portland, Oregon, USA | N/A | Sofware used for load-displacement curve analysis |
| iLoad Mini Force Sensor | LoadStar Sensors, Freemont, California, USA | MFM-010-050-S | Load (force) sensor with 1.0% accuracy |
| Isotonic (0.9%) Saline Solution | N/A | N/A | To keep bone sampels hydrated |
| Leica EZ4 W Miscoscope | Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany | NC1601884 | For bone dissections and vertebral process removal |
| Microsoft Excel Software | Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, Washington, USA | N/A | For data transfer from SensorVue software |
| PALACOS R Bone Cement | Hareus Medical, Wehreim, Germany | 00-1112-140-01 | PMMA bone cement for embedding of the loading surface |
| Personal Computer | N/A | N/A | For data recording (see 24-bit Load Cell Interface, SensorVue Software, Microsoft Excel Software) and analysis (see Igor Pro Software) |
| SensorVue Software | LoadStar Sensors, Freemont, California, USA | N/A | Software used for real-time data collection during compression testing |
| Small Animal Dissecting Kit | N/A | N/A | Dissecting scissors, forceps, scalpel, blades, pins, gauze pads |
| Stainless Steel Top Platen (Self-Alligning) and Bottom Platen Pair | N/A | N/A | Constructed by Colorado State University-Pueblo Dept. of Engineering |
| Three-Point Bending Machine | N/A | N/A | Constructed by Colorado State University-Pueblo Dept. of Engineering. Refer to Sarper et al. (2014) for further details regarding construction |
References
- Kemmak, A. R., et al. Economic burden of osteoporosis in the world: A systematic review. Medical Journal of The Islamic Republic of Iran. 34, 153 (2020).
- Li, J., et al. Different bone remodeling levels of trabecular and cortical bone in response to changes in Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mice. Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 35 (4), 812-819 (2016).
- Crandall, C. Parathyroid hormone for treatment of osteoporosis. JAMA Internal Medicine. 162 (20), 2297-2309 (2002).
- Ott, S. M. Cortical or trabecular bone: what's the difference. American Journal of Nephrology. 47 (6), 373-375 (2018).
- Sparks, C. A., Streff, H. M., Williams, D. W., Blanton, C. A., Gabaldón, A. M. Dietary hempseed decreases femur maximum load in a young female C57BL/6 mouse model but does not influence bone mineral density or micro-architecture. Nutrients. 14 (20), 4224 (2022).
- Blanton, C. A., Barrott, J. J., Kunz, K., Bunde, E., Streff, H. M., Sparks, C. A., et al. The Impact of Hempseed Consumption on Bone Parameters and Body Composition in Growing Female C57BL/6 Mice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 19 (10), 5839 (2022).
- Sarper, H., Blanton, C., Depalma, J., Melnykov, I. V., Gabaldón, A. M. Simulated weightlessness and synbiotic diet effects on rat bone mechanical strength. Life Sciences in Space Research. 3, 45-54 (2014).
- Choman, M. The Effect of a synbiotic diet on the structure and strength of cortical bone in aging male mice. , (2015).
- Sparks, C. A., Giltner, Z. T., Blanton, C. A., Gabaldón, A. M. The Effects of a synbiotic diet on humerus bone mineralization and mechanical strength in aging male mice. El Río. 4 (1), 3-12 (2021).
- Bilezikian, J. P., Martin, T. J., Clemens, T. L., Rosen, C. J. . Principles of bone biology (Fourth Edition). , (2019).
- Jepsen, K. J., et al. Establishing biomechanical mechanisms in mouse models: practical guidelines for systematically evaluating phenotypic changes in the diaphyses of long bones. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 30 (6), 951-966 (2015).
- Vashith, D., Tanner, K. E., Bonfield, W. Contribution, development and morphology of microcracking in cortical bone during crack propagation. Journal of Biomechanics. 33 (9), 1169-1174 (2000).
- Turner, C. H., Burr, D. B. Basic biomechanical measurements of bone: A tutorial. Bone. 14 (4), 595-608 (1993).
- Warriner, A. H., et al. Which fractures are most attributable to osteoporosis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 64 (1), 46-53 (2011).
- Donally, C. I., DiPompeo, C., Varcallo, M. . Vertebral compression fractires. , (2022).
- Alhadhoud, M., Alsiri, N. The epidemiology of spinal fractures in a level 2 trauma center in Kuwait. SAGE Open Medicine. 9, 1-11 (2021).
- Schumancher, Y. . Comparison of two loading surface preparation methods on rat vertebral bodies for compression testing. , (2013).
- Rathore, M., Sharma, D., Sinha, M., Siddiqui, A., Trivedi, S. A. Focused review - thoracolumbar spine: anatomy, biomechanics and clinical significance. Indian Journal of Clinical Anatomy and Physiology. 1 (1), 41-48 (2014).
- Pendleton, M. M., et al. High-precision method for cyclic loading of small-animal vertebrae to assess bone quality. Bone Reports. 9, 165-172 (2018).
- Lundon, K., Bolton, K. Structure and function of the lumbar intervertebral disk in health, aging, and pathologic conditions. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 31 (6), 291-306 (2011).
- Sharir, A., Barak, M. M., Shahar, R. Whole bone mechanics and mechanical testing. The Veterinary Journal. 177 (1), 8-17 (2008).
- Zhao, S., et al. Standardizing compression testing for measuring the stiffness of human bone. Bone & Joint Research. 7 (8), 524-538 (2018).
- Akhter, M. P., Jung, L. K. L. Decreased bone strength in HLA-B27 transgenic rat model of spondyloarthropathy. Rheumatology. 46 (8), 1258-1262 (2007).
- Shahnazari, M., et al. Higher doses of bisphosphonates further improve bone mass, architecture, and strength but not the tissue material properties in aged rats. Bone. 46 (5), 1267-1274 (2011).
- Chachra, D., Kasra, M., Vanin, C., MacLusky, N., Casper, R., Grynpas, M. The effect of different hormone replacement therapy regimens on the mechanical properties of rat vertebrae. Calified Tissue International. 56 (2), 130-134 (1995).
- Bushinsky, D. A., Willet, T., Asplin, J. R., Culbertson, C., Sara, C., Grynpas, M. Chlorthalidone improves vertebral bone quality in genetic hypercalciuric stone-forming rats. The Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 26 (8), 1904-1912 (2011).
- Fujiwara, T., Akeda, K., Yamada, J., Kondo, T., Sudo, A. Endplate and intervertebral disc injuries in acute and single level osteoporotic vertebral fractures: is there any association with the process of bone healing. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 20 (1), 336 (2019).
- Kalidindi, S. R., Abusafieh, A. Accurate characterization of machine compliance for simple compression testing. Experimental Mechanics. 37 (2), 210-215 (1997).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved