A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Detection of Nuclear Blebbing and DNA Leakage in Mammalian Cells by Immunofluorescence
In This Article
Summary
Laminopathy disorders often lead to changes in the nuclear envelope, which may cause nuclear blebbing and leakage. This study presents an immunofluorescence method to visualize the nuclear lamina along with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), providing a means to assess nuclear structure and integrity in mammalian cells.
Abstract
The nuclear lamina is a network of filaments underlying the nuclear membrane, composed of lamins and lamin-associated proteins. It plays critical roles in nuclear architecture, nuclear pore positioning, gene expression regulation, chromatin organization, DNA replication, and DNA repair. Mutations in genes involved in the expression or post-translational processing of lamin proteins result in genetic disorders known as laminopathies. Specifically, mutations in the LMNA or ZMPSTE24 genes can lead to the accumulation of incompletely processed forms of lamin A that retain farnesyl and methyl groups, which are absent in fully processed lamin A. These incompletely processed lamin A proteins localize to the inner nuclear membrane instead of the nuclear lamina, where mature lamin A resides. Mislocalized lamin proteins profoundly disrupt nuclear function and structure, often resulting in nuclear blebbing. In severe cases, nuclear rupture can occur, causing a loss of compartmentalization and leakage of genomic DNA into the cytosol. Abnormal nuclear structure and compartmentalization loss can be identified through indirect immunofluorescence (IF) on fixed cells. This study outlines such a method, employing specific antibodies against a lamin protein and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) to simultaneously visualize the nuclear envelope and DNA. This approach enables a rapid assessment of nuclear structural integrity and the potential leakage of nuclear DNA into the cytosol.
Introduction
The nuclear lamina is a network of filaments that underlies the nuclear membrane and is made up of proteins called lamins. The nuclear lamina plays essential roles in nuclear architecture, positioning of nuclear pores, gene expression regulation, chromatin organization, DNA replication, and DNA repair1,2,3. Mutations in genes that play a role in the expression of the lamin proteins lead to genetic disorders called laminopathies3.
Restrictive dermopathy (RD) is a severe laminopathy disorder predominantly caused by compound he....
Protocol
Details of the reagents and the equipment used are listed in the Table of Materials.
1. Preparation of materials
- Autoclave at least ten 22 mm x 22 mm square glass coverslips and forceps in advance of plating cells onto the coverslips.
2. Preparation of the solutions
- Supplemented media: Prepare 500 mL of Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 units/mL of penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin.
- Antibody dilution buffer (ADB): Dissolve 2 g of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 1 g of Fish gelatin i....
Results
This study introduces an IF method for visualizing the nuclear lamina in conjunction with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). Once IF is performed, the images captured can be examined for signs of nuclear blebbing and DNA leakage.
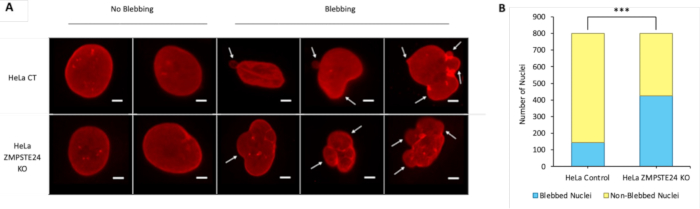
Figure 2: Nuclear blebbing in HeLa CT and ZMPSTE24<.......
Discussion
The protocol presented contains several critical steps, the most important being the treatment of the fixed cells with primary and secondary antibodies. Ensuring the use of a good quality primary antibody against the target of interest with a correct corresponding secondary antibody with fluorophores within the range of the microscope used will yield optimal results19. The quality of the antibody can greatly impact the results of this technique, as faulty antibodies can interact with nonspecific t.......
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute on Aging grant R03AG064525 to ASW. We would like to thank Dr. Jason A. Stewart for help in technique mentorship and the Hui Chen laboratory for providing the microscope used. We would also like to thank Fabio Martinon for the HeLa cell lines used in these experiments.
....Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 22 mm Square Glass Coverslips | Propper Manufacturing Company | M8710 | Any size or shape can be used as long as they can be fixed to a standard microscope slide. |
| 36.5% Formaldehyde | Sigma Aldrich | F8775 | Fixation Reagent. |
| 75 cm 2 Flasks | Corning | 430725U | For cell culture. |
| Bovine Serum Albinum (BSA) | Fisher Scientific | 9048-46-8 | Antibody dilution buffer. |
| DMEM with 1 g/L glucose, L-glutamine & sodium pyruvate | Corning | 10-014-CV | For cell culture. |
| Ethanol (200 Proof) | Decon Laboratories | 2701 | For dehydration of samples before mounting, diluted to make multiple concentrations. |
| EVOS FL Digital Inverted Fluorescence Microscope | Fisher Scientific | 12-563-460 | Imaging. |
| Fish Gelatin | Sigma Aldrich | G7041 | Antibody dilution buffer. |
| Fluoromount-G | Southern Biotech | 0100-01 | Mounting medium to prevent photobleaching. |
| Parafilm (4 in) | Fisher Scientific | 13-374-12 | Any size can be substituted, as long as the coverslips being used can fit. |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15-140-122 | For cell culture. |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) | N/A | N/A | Made and sterilized in the lab for tissue culture and solutions. |
| Premium Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Atlanta Biologicals | S11150 | For cell culture. |
| Superfrost Premium Microscope Slides | Fisher Scientific | 12-544-7 | Any standard microscope slides can be used. |
| Tissue Culture Treated 6-well Flat Bottom Plates | Falcon | 353046 | For cell culture. |
| TritonX-100 | Thermofisher Scientific | A16046.AP | For washing. |
| Trypsin-EDTA (0.5%) | Gibco | 15-400-054 | For cell culture. |
| Tween 20 | Fisher Scientific | 9005-64-5 | Cell Permeation reagent. |
References
- Navarro, C. L., et al. New ZMPSTE24 (FACE1) mutations in patients affected with restrictive dermopathy or related progeroid syndromes and mutation update. Eur J Hum Genet. 22 (8), 1002-1011 (2014).
- Dittmer, T. A., Misteli, T.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved