Pelvic Exam III: Bimanual and Rectovaginal Exam
Source:
Alexandra Duncan, GTA, Praxis Clinical, New Haven, CT
Tiffany Cook, GTA, Praxis Clinical, New Haven, CT
Jaideep S. Talwalkar, MD, Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
A bimanual exam is a thorough check of a patient's cervix, uterus, and ovaries. It can tell an experienced provider a great deal, as it may lead to the discovery of abnormalities, such as cysts, fibroids, or malignancies. However, it's useful even in the absence of such findings, as it allows the practitioner to establish an understanding of the patient's anatomy for future reference.
Performing the bimanual exam before the speculum exam can help relax patients, mentally and physically, before what is often perceived as the "most invasive" part of the exam. A practitioner already familiar with the patient's anatomy can insert a speculum more smoothly and comfortably. However, lubrication used during the bimanual exam may interfere with processing certain samples obtained during the speculum exam. Providers must be familiar with local laboratory processing requirements before committing to a specific order of examination.
This demonstration begins immediately after the end of the speculum exam; therefore, it assumes the patient has provided a history and is in the modified lithotomy position.
A rectovaginal exam is not always necessary, but it may be performed to fully assess a retroverted uterus and ovaries (this may be the only way to accomplish full assessment depending on uterine position) or to assess the rectum.
1. Bimanual Exam
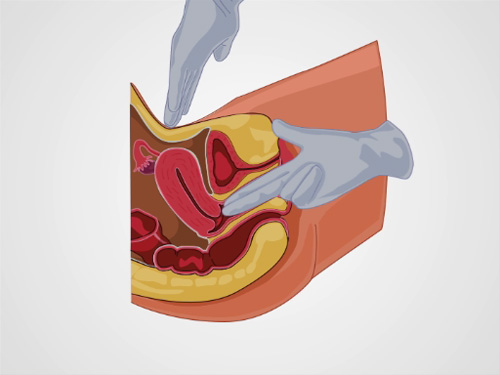
Figure 1. Bimanual exam. Correct positioning of the examiner's hands for the bimanual exam.
- Prepare the patient by saying, "I will now place two gloved fingers in your vagina and use my other hand to press on your abdomen to assess your uterus and ovaries."
- Fully coat the first two fingers of your dominant hand with lubricant.
- Sit and tell the p
This video reviewed the techniques for performing a comfortable bimanual and rectovaginal exam. When first performing the exam, it can be hard to know what both normal structures and abnormalities should feel like, but familiarity develops with practice. Experienced practitioners can determine the structure and location of the patient's anatomy and discover polyps, cysts, and malignancies; the potential of pelvic inflammatory disease; and more. The rectovaginal exam can be a good way to gather information about a retrove
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
Pelvic Exam III: Bimanual and Rectovaginal Exam
Physical Examinations II
144.8K Views

Eye Exam
Physical Examinations II
75.5K Views

Ophthalmoscopic Examination
Physical Examinations II
66.5K Views

Ear Exam
Physical Examinations II
53.4K Views

Nose, Sinuses, Oral Cavity and Pharynx Exam
Physical Examinations II
64.3K Views

Thyroid Exam
Physical Examinations II
103.1K Views

Lymph Node Exam
Physical Examinations II
379.3K Views

Abdominal Exam I: Inspection and Auscultation
Physical Examinations II
199.8K Views

Abdominal Exam II: Percussion
Physical Examinations II
244.7K Views

Abdominal Exam III: Palpation
Physical Examinations II
137.1K Views

Abdominal Exam IV: Acute Abdominal Pain Assessment
Physical Examinations II
66.1K Views

Male Rectal Exam
Physical Examinations II
111.9K Views

Comprehensive Breast Exam
Physical Examinations II
85.0K Views

Pelvic Exam I: Assessment of the External Genitalia
Physical Examinations II
297.4K Views

Pelvic Exam II: Speculum Exam
Physical Examinations II
147.6K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved
