Fume Hoods and Laminar Flow Cabinets
Robert M. Rioux & William A. Elliott, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
Fume hoods and laminar flow cabinets are engineering controls that operate under similar principles. Both use a constant flow of air to prevent contamination of the laboratory environment and its inhabitants. Fume hoods prevent hazardous substances from exiting the hood workspace, whereas laminar flow cabinets prevent contaminants from entering the cabinet workspace.
Fume hoods are ventilation systems designed to minimize exposure to hazardous vapors, fumes, and particles. A constant flow of air is drawn into the hood opening, limiting the escape of vapors, fumes, and particles, and then is pulled out through the exhaust. Laminar flow cabinets are used to maintain a sterile/clean environment by constantly flowing high-efficiency particulate arrestance (HEPA)-filtered air outwards, minimizing contaminated air entering the cabinet workspace. The HEPA-filtered air reduces the opportunity for harmful chemicals or particles from entering the laboratory. A HEPA filter removes 99.97% or greater of 0.3 µm particles.
Fume hoods and laminar flow cabinets are engineering controls that aim to reduce exposure to hazards and contamination. Fume hoods reduce exposure to hazardous vapors, fumes, and particles for the user while laminar flow cabinets reduce workspace exposure to contaminants. Turbulent flow follows an irregular flow pattern with local flow moving in all directions relative to the bulk flow. Laminar flow moves in parallel streamlines that do not cross. Laminar flow cabinets maintain a laminar stream of air to prevent cross contamination within the workspace and to prevent backflow of contaminated air from outside the hood that would occur with turbulent flow.
1. Fume hoods
- Uses
- Fume hoods are used when a material generates harmful vapors, fumes, or airborne particles, such as fine silica powders, or volatile carcinogens, such as benzene.
- Operation
- Air is drawn in though the opening face of the hood, where the user works, and out through the exhaust. The constant flow of air inwards towards the face prevents hazardous vapors, fumes, and particles from escaping out through the hood opening, keeping the user and other laboratory workers safe.
- Facial flow velocity must be high enough for the hood to be effective. A low flow velocity allows harmful fumes, vapors, or particles to escape through the opening of the hood toward the user. One cause of low flow velocity is having the adjustable window at the hood opening, called a sash, too high. It is common for fume hoods to have low flow velocity alarms and sash height alarms. Typical flow velocities are between 0.41 and 0.51 m/s (ANSI/AIHA/ASSE Z9.5). Hoods should have the maximum safe working height of the sash clearly marked.
- There are several rules for safe use of fume hoods.
- Never put your head into the hood space, since inserting your head inside the hood can expose you to harmful materials. The hood is designed to protect users from chemical exposure only when utilized properly. Only the users' arms should be present in the hood. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) at all times, regardless of the protection afforded by the fume hood. Consult with your organization's Environmental Health & Safety (EHS) office for proper PPE recommendations, if they are unknown.
- Always work with the sash at or below the maximum safe height.
- When not in use, the sash should be closed. Closing the sash ensures a safer working environment for all laboratory occupants. Additionally, the energy costs associated with improper fume hood operation are immense. Maintaining the sash height at the minimum, non-working level is more energy efficient.
- Do not use the hood for chemical storage. Store chemicals in appropriate locations, such as a flammable cabinet, and bring them into the fume hood only when needed.
- Place all materials in the fume hood at least 6 inches away from the edge of the fume hood face. When work is carried out within 6 inches of the edge, vapors, fumes, and particles are more likely to escape.
- Just as good housekeeping principles apply on working laboratory benches, the same principles should be practiced within fume hoods.
- Perform regular maintenance on a fume hood to ensure it is operating safely. Maintenance should include testing of alarms and testing flow velocity at the design operating sash position. Many factors can affect the flow velocity, including flow patterns within the room the hood is located and obstructions at the exhaust vent. If flow velocity is low at the design operating sash position, lower the sash until the flow velocity is at the required speed. Many modern fume hoods have air flow velocity monitors that monitor the flow velocity in real time. If the sash becomes too low for effective work to be performed at the fume hood, cease operation until the root of the problem is addressed.
- Fume Hood Variations
- There are number of types of more specialized fume hoods that may be encountered. These include perchloric acid hoods, radioisotope hoods, ductless hoods, and others. More can be read about the requirements for these hoods in ANSI/AIHA/ASSE Z9.5.
2. Laminar flow cabinets
- Uses
- Laminar flow cabinets are used when a clean environment, free of particles or biological contaminants, is required. Common examples include working with tissue cultures or semiconductor wafers. Laminar flow cabinets prevent airborne contamination from entering the cabinet workspace. The laminar flow (as opposed to turbulent flow) of air minimizes cross-contamination of samples within the cabinet.
- Air is filtered by a HEPA filter and blown over the workspace, out toward the user. A constant outward flow of clean air maintains an uncontaminated workspace. Some laminar flow cabinets are fitted with a UV-C lamp to disinfect the workspace prior to use.
- There are two types of laminar flow cabinets: horizontal flow and vertical flow ( Figure 1). Horizontal flow cabinets blow clean air from the back face of the cabinet horizontally toward the user, whereas vertical flow hoods blow clean air from the ceiling of the cabinet toward the floor of the workspace where it then hits the base and flows in a horizontal direction towards the user. Vertical flow cabinets are used with the sash pulled down. Horizontal flow cabinets do not have a sash. Both types of laminar flow cabinets have their advantages and disadvantages.
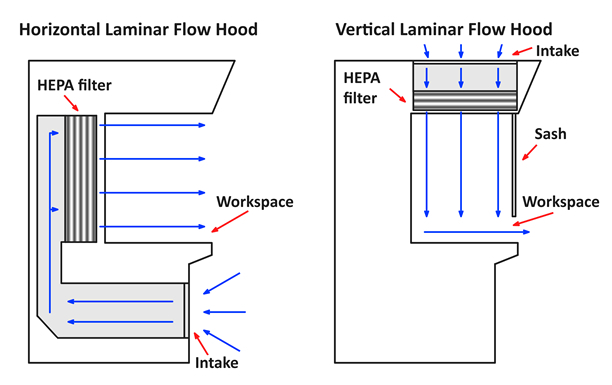
Figure 1. Diagrams of horizontal and vertical laminar flow hoods.
| Horizontal Laminar Flow Hood | |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Hands/gloves contaminate less as they are typically downwind of items in the cabinet | Air stream blows in user’s face |
| Reduced air flow turbulence | Large objects on workspace can obstruct flow of clean air, reducing effectiveness |
| Vertical Laminar Flow Hood | |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Air stream does not blow in user’s face | Cannot position hands and arms above objects |
| Less cross contamination from item in workspace | Increased air flow turbulence |
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of horizontal and vertical laminar flow hoods.
- Tips to ensure effective use of laminar flow cabinets.
- Always take care not to put items downstream of items that could lead to cross contamination. This is particularly relevant when using biological samples.
- Minimize clutter. The more items that are in the cabinet, the more likely contamination is to occur. Large items can disrupt flow.
- Ensure that hands/gloves and any items that are brought into the cabinet are free from contamination prior to entering the cabinet.
- All items must be placed 6 inches or further from the edge of the cabinet opening. The air within 6 inches of the edge is more likely to mix with the outside air, meaning objects within 6 inches are more likely to be contaminated.
- Regular maintenance should be performed on a laminar flow cabinet to ensure it is operating safely. Maintenance should include checking and replacing the HEPA filter, checking for leaks in the cabinet, and testing airflow velocity. The integrity of the HEPA filter should checked by testing the number of particles that pass through the filter. The filter should remove 99.97% or greater of 0.3 µm particles. If the flow velocity is too low, the cabinet will be ineffective in keeping out contaminants. If the flow velocity is too great, the flow will be turbulent, with contamination becoming more likely.
Fume hoods and laminar flow cabinets are useful tools in the laboratory to prevent harm from hazardous materials and to keep a clean working space when using sensitive materials. However, fume hoods and laminar flow cabinets are only effective when used properly. Following simple operating guidelines and performing regular maintenance, fume hoods and laminar flow cabinets can be effective tools in the laboratory.
- American National Standard for Laboratory Ventilation," American National Standards Institute, Inc./ American Industrial Hygiene Association, ANSI/AIHA Z9.5, 2012.
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
Fume Hoods and Laminar Flow Cabinets
Lab Safety
68.1K Views

Proper Personal Protective Equipment
Lab Safety
231.6K Views

Emergency Eyewash and Shower Stations
Lab Safety
82.1K Views

Electrical Safety
Lab Safety
41.8K Views

Working with Centrifuges
Lab Safety
95.3K Views

Working with Hot and Cold Sources
Lab Safety
41.4K Views

Guidelines in Case of a Laboratory Emergency
Lab Safety
180.1K Views

Chemical Storage: Categories, Hazards And Compatibilities
Lab Safety
108.1K Views

Safe Handling of Mineral Acids
Lab Safety
44.6K Views

Handling Chemical Spills
Lab Safety
87.1K Views

Proper Use of Autoclaves
Lab Safety
87.1K Views

Handling Air- and Water-Sensitive Chemicals Using a Schlenk Line
Lab Safety
21.8K Views

Proper Operation of Vacuum Based Equipment
Lab Safety
15.8K Views

Operating the Glovebox
Lab Safety
28.4K Views

Operation of High-pressure Reactor Vessels
Lab Safety
16.0K Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved