Synthesis of an Oxygen-Carrying Cobalt(II) Complex
Source: Deepika Das, Tamara M. Powers, Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University
Bioinorganic chemistry is the field of study that investigates the role that metals play in biology. Approximately half of all proteins contain metals and it is estimated that up to one third of all proteins rely on metal-containing active sites to function. Proteins that feature metals, called metalloproteins, play a vital role in a variety of cell functions that are necessary for life. Metalloproteins have intrigued and inspired synthetic inorganic chemists for decades, and many research groups have dedicated their programs to modeling the chemistry of metal-containing active sites in proteins through the study of coordination compounds.
The transport of O2 is a vital process for living organisms. O2-transport metalloproteins are responsible for binding, transporting, and releasing oxygen, which can then be used for life processes such as respiration. The oxygen-carrying cobalt coordination complex, [N,N'-bis(salicylaldehyde)ethylenediimino]cobalt(II) [Co(salen)]2 has been studied extensively to gain understanding about how metal complexes reversibly bind O2.1
In this experiment, we will synthesize [Co(salen)]2 and study its reversible reaction with O2 in the presence of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). First, we will quantify the amount of O2 consumed upon exposure of [Co(salen)]2 to DMSO. We will then visually observe the release of O2 from the [Co(salen)]2-O2 adduct by exposing the solid to CHCl3.
1. Synthesis of Inactive [Co(salen)]2
- Charge a 250 mL 3-neck round-bottom flask with 120 mL of 95% EtOH and 2.20 g (0.192 mL, 0.018 mol) of salicylaldehyde.
- Fit the center neck with a condenser connected to N2. Fit the other two necks with a rubber septum and an addition funnel fitted with a rubber septum.
- Stir the reaction in a water bath and heat the solution to reflux (80 °C).
- Add ethylene diamine (0.52 g, 0.58 mL, 0.0087 mol) via syringe through the
Characterization of Inactive [Co(salen)]2:
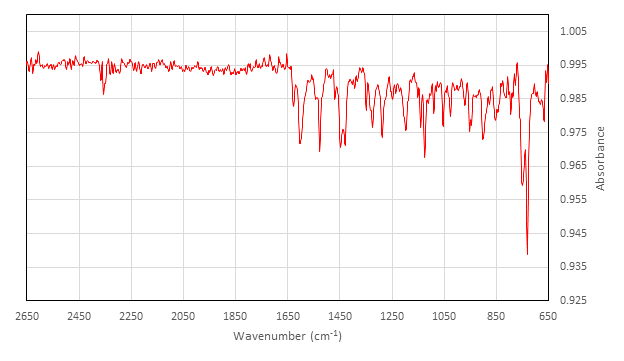
IR (cm-1) collected on ATR attachment: 2357 (w), 1626 (w), 1602 (m), 1542 (w), 1528 (m), 1454 (w), 1448 (m), 1429 (m), 1348 (w), 1327 (w), 1323 (m), 1288 (m), 1248 (w), 1236 (w), 1197 (m), 1140 (m), 1124 (m), 1089 (w), 1053 (m), 1026 (w), 970 (w), 952 (w), 947 (w), 902 (m), 878 (w), 845 (w), 813 (w), 794 (w), 750 (s), 730 (
In this video, we explained the different ways that diatomic oxygen can coordinate to metal center(s). We synthesized the oxygen-carrying cobalt complex [Co(salen)]2 and studied its reversible binding with O2. Experimentally we demonstrated that inactive [Co(salen)]2 reversibly binds O2 and forms a 2:1 Co:O2 adduct in the presence of DMSO.
All vertebrates depend on hemoglobin, a metalloprotein found in red blood cells, to transport oxygen
- Niederhoffer, E. C., Timmons, J. H., Martell, A. E. Thermodynamics of Oxygen Binding in Natural and Synthetic Dioxygen Complexes. Chem Rev. 84, 137-203 (1984).
- Appleton, T. G. Oxygen uptake by cobalt(II) complex. An undergraduate experiment. J Chem Educ. 54 (7), 443 (1977).
- Ueno, K., Martell, A. E. Infrared Studies on Synthetic Oxygen Carriers. J Phys Chem.60, 1270–1275 (1956).
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
Synthesis of an Oxygen-Carrying Cobalt(II) Complex
Inorganic Chemistry
51.2K Views

Synthesis Of A Ti(III) Metallocene Using Schlenk Line Technique
Inorganic Chemistry
31.4K Views

Glovebox and Impurity Sensors
Inorganic Chemistry
18.5K Views

Purification of Ferrocene by Sublimation
Inorganic Chemistry
54.1K Views

The Evans Method
Inorganic Chemistry
67.4K Views

Single Crystal and Powder X-ray Diffraction
Inorganic Chemistry
103.3K Views

Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Spectroscopy
Inorganic Chemistry
25.3K Views

Mössbauer Spectroscopy
Inorganic Chemistry
21.9K Views

Lewis Acid-Base Interaction in Ph3P-BH3
Inorganic Chemistry
38.7K Views

Structure Of Ferrocene
Inorganic Chemistry
78.5K Views

Application of Group Theory to IR Spectroscopy
Inorganic Chemistry
44.8K Views

Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
Inorganic Chemistry
35.0K Views

Quadruply Metal-Metal Bonded Paddlewheels
Inorganic Chemistry
15.2K Views

Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
Inorganic Chemistry
15.5K Views

Photochemical Initiation Of Radical Polymerization Reactions
Inorganic Chemistry
16.6K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved
