Hydronium and hydroxide ions are present both in pure water and in all aqueous solutions, and their concentrations are inversely proportional as determined by the ion product of water (Kw). The concentrations of these ions in a solution are often critical determinants of the solution’s properties and the chemical behaviors of its other solutes. Two different solutions can differ in their hydronium or hydroxide ion concentrations by a million, billion, or even trillion times. A common means of expressing quantities that may span many orders of magnitude is to use a logarithmic scale. The pH of a solution is therefore defined as shown here, where [H3O+] is the molar concentration of hydronium ion in the solution:
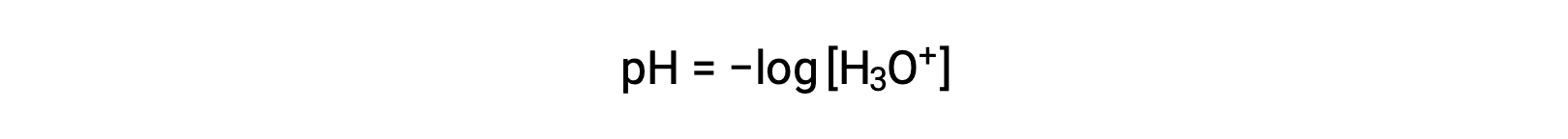
Rearranging this equation to isolate the hydronium ion molarity yields the equivalent expression:
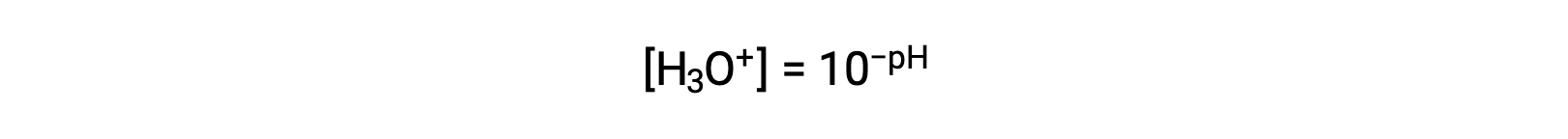
Likewise, the hydroxide ion molarity may be expressed as a p-function or pOH:
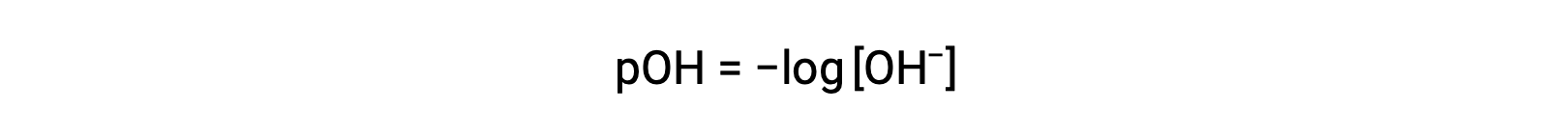
or
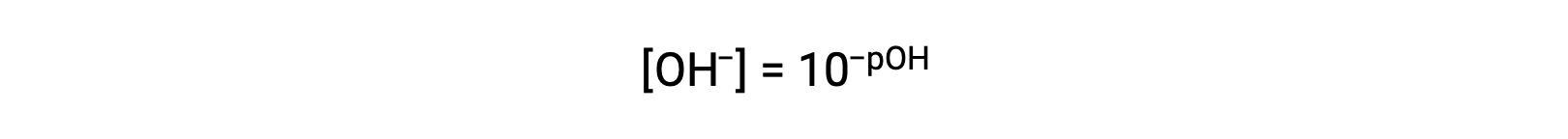
Finally, the relation between these two ion concentration expressed as p-functions is easily derived from the KW expression:
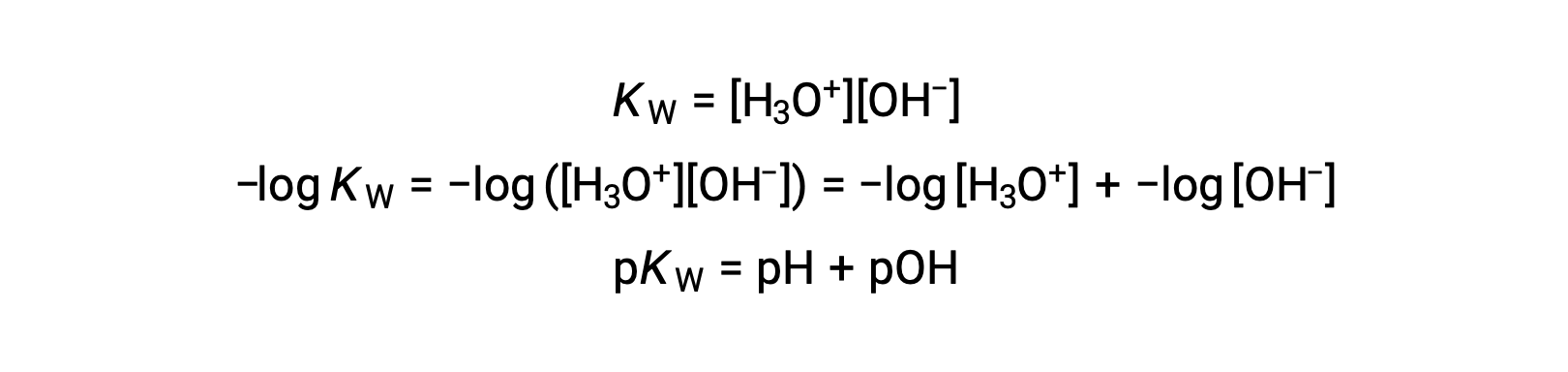
At 25 °C, the value of KW is 1.0 × 10−14, and so:
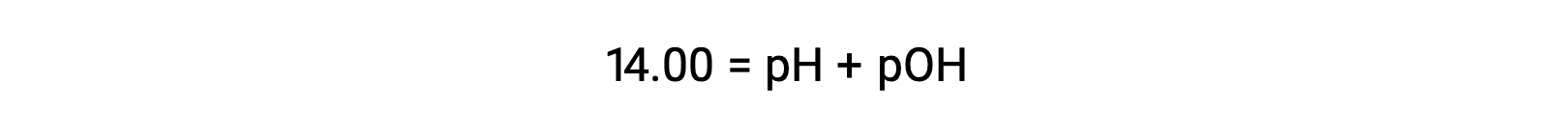
The hydronium ion molarity in pure water (or any neutral solution) is 1.0 × 10−7 M at 25 °C. The pH and pOH of a neutral solution at this temperature are therefore:
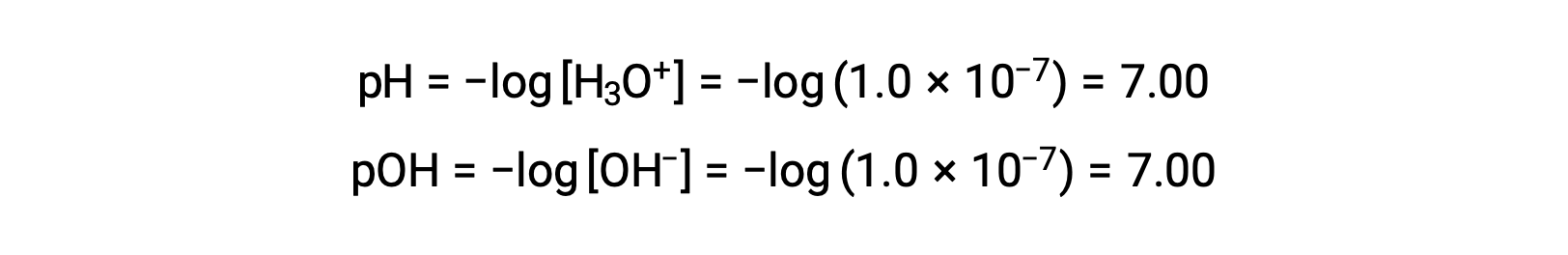
And so, at this temperature, acidic solutions are those with hydronium ion molarities greater than 1.0 × 10−7 M and hydroxide ion molarities less than 1.0 × 10−7 M (corresponding to pH values less than 7.00 and pOH values greater than 7.00). Basic solutions are those with hydronium ion molarities less than 1.0 × 10−7 M and hydroxide ion molarities greater than 1.0 × 10−7 M (corresponding to pH values greater than 7.00 and pOH values less than 7.00).
Since the autoionization constant KW is temperature dependent, these correlations between pH values and the acidic/neutral/basic adjectives will be different at temperatures other than 25 °C. For example, the hydronium molarity of pure water at 80°C is 4.9 × 10−7 M, which corresponds to pH and pOH values of:
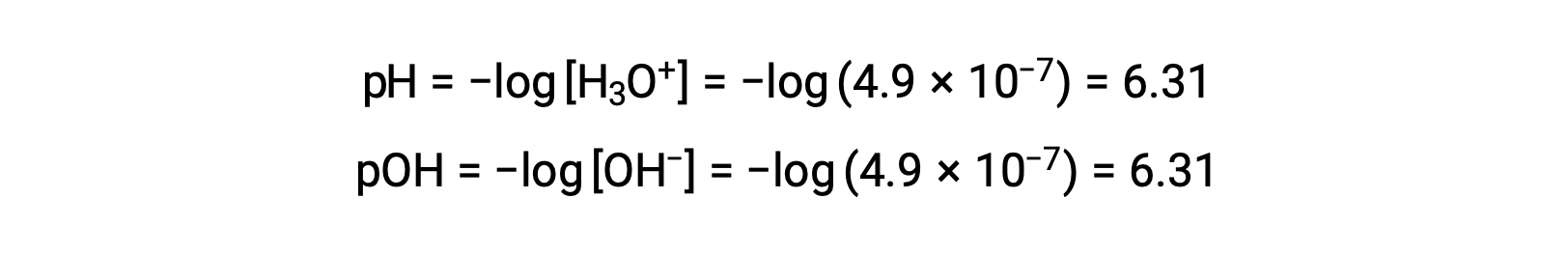
At this temperature, neutral solutions exhibit pH = pOH = 6.31, acidic solutions exhibit pH less than 6.31 and pOH greater than 6.31, whereas basic solutions exhibit pH greater than 6.31 and pOH less than 6.31. This distinction can be important when studying certain processes that occur at other temperatures, such as enzyme reactions in warm-blooded organisms at a temperature around 36 – 40 °C. Unless otherwise noted, references to pH values are presumed to be those at 25 °C.
This text is adapted fromOpenstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.2: pH and pOH.
From Chapter 15:

Now Playing
15.4 : pH Scale
Acids and Bases
66.4K Views

15.1 : Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
87.4K Views

15.2 : Acid/Base Strengths and Dissociation Constants
Acids and Bases
58.8K Views

15.3 : Water: A Bronsted-Lowry Acid and Base
Acids and Bases
48.4K Views

15.5 : Relative Strengths of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Acids and Bases
44.2K Views

15.6 : Strong Acid and Base Solutions
Acids and Bases
30.5K Views

15.7 : Weak Acid Solutions
Acids and Bases
36.6K Views

15.8 : Weak Base Solutions
Acids and Bases
21.8K Views

15.9 : Mixtures of Acids
Acids and Bases
18.8K Views

15.10 : Ions as Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
22.5K Views

15.11 : Determining the pH of Salt Solutions
Acids and Bases
41.9K Views

15.12 : Polyprotic Acids
Acids and Bases
28.2K Views

15.13 : Acid Strength and Molecular Structure
Acids and Bases
29.8K Views

15.14 : Lewis Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
41.8K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved