7.7 : Kinetic Energy - II
The kinetic energy of a particle is one-half of the product of the particle’s mass and the square of its speed. Note that just as Newton’s second law can be expressed as either the rate of change of momentum or mass multiplied by the rate of change of velocity, so too can the kinetic energy of a particle be expressed in terms of its mass and momentum, instead of its mass and velocity.
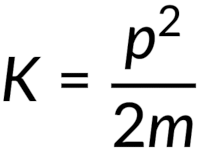
In the equation, the units of kinetic energy are mass times the speed-squared, or
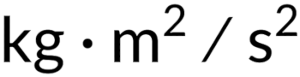
Note that the units of force are mass multiplied by acceleration. Thus, the units of kinetic energy are also the units of force multiplied by distance, which are the units of work, or joules. Hence, work and kinetic energy have the same units, since they are different forms of the same, more general, physical property.
Because velocity is a relative quantity, the value of kinetic energy depends on the frame of reference. One can generally choose a frame of reference that is suited to the purpose of analysis and that simplifies the calculations. One such frame of reference is the one in which the observations of the system are made (likely an external frame). Another choice is a frame that is attached to or moves with the system (likely an internal frame).
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 7.2: Kinetic Energy.
From Chapter 7:

Now Playing
7.7 : Kinetic Energy - II
Work and Kinetic Energy
5.9K Views

7.1 : Work
Work and Kinetic Energy
20.9K Views

7.2 : Positive, Negative, and Zero Work
Work and Kinetic Energy
18.1K Views

7.3 : Energy
Work and Kinetic Energy
12.8K Views

7.4 : Types of Potential Energy
Work and Kinetic Energy
6.4K Views

7.5 : Types of Kinetic Energy
Work and Kinetic Energy
6.6K Views

7.6 : Kinetic Energy - I
Work and Kinetic Energy
9.9K Views

7.8 : Work-energy Theorem
Work and Kinetic Energy
22.0K Views

7.9 : Work and Energy for Variable Forces
Work and Kinetic Energy
3.4K Views

7.10 : Work-Energy Theorem for Motion Along a Curve
Work and Kinetic Energy
2.5K Views

7.11 : Work Done Over an Inclined Plane
Work and Kinetic Energy
2.8K Views

7.12 : Work Done by Many Forces
Work and Kinetic Energy
3.9K Views

7.13 : Work Done by Gravity
Work and Kinetic Energy
6.5K Views

7.14 : Power
Work and Kinetic Energy
11.1K Views

7.15 : Power Expended by a Constant Force
Work and Kinetic Energy
7.2K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved