The phase of a given substance depends on the pressure and temperature. Thus, plots of pressure versus temperature showing the phase in each region provide considerable insights into the thermal properties of substances. Such plots are known as phase diagrams. For instance, in the phase diagram for water (Figure 1), the solid curve boundaries between the phases indicate phase transitions (i.e., temperatures and pressures at which the phases coexist).
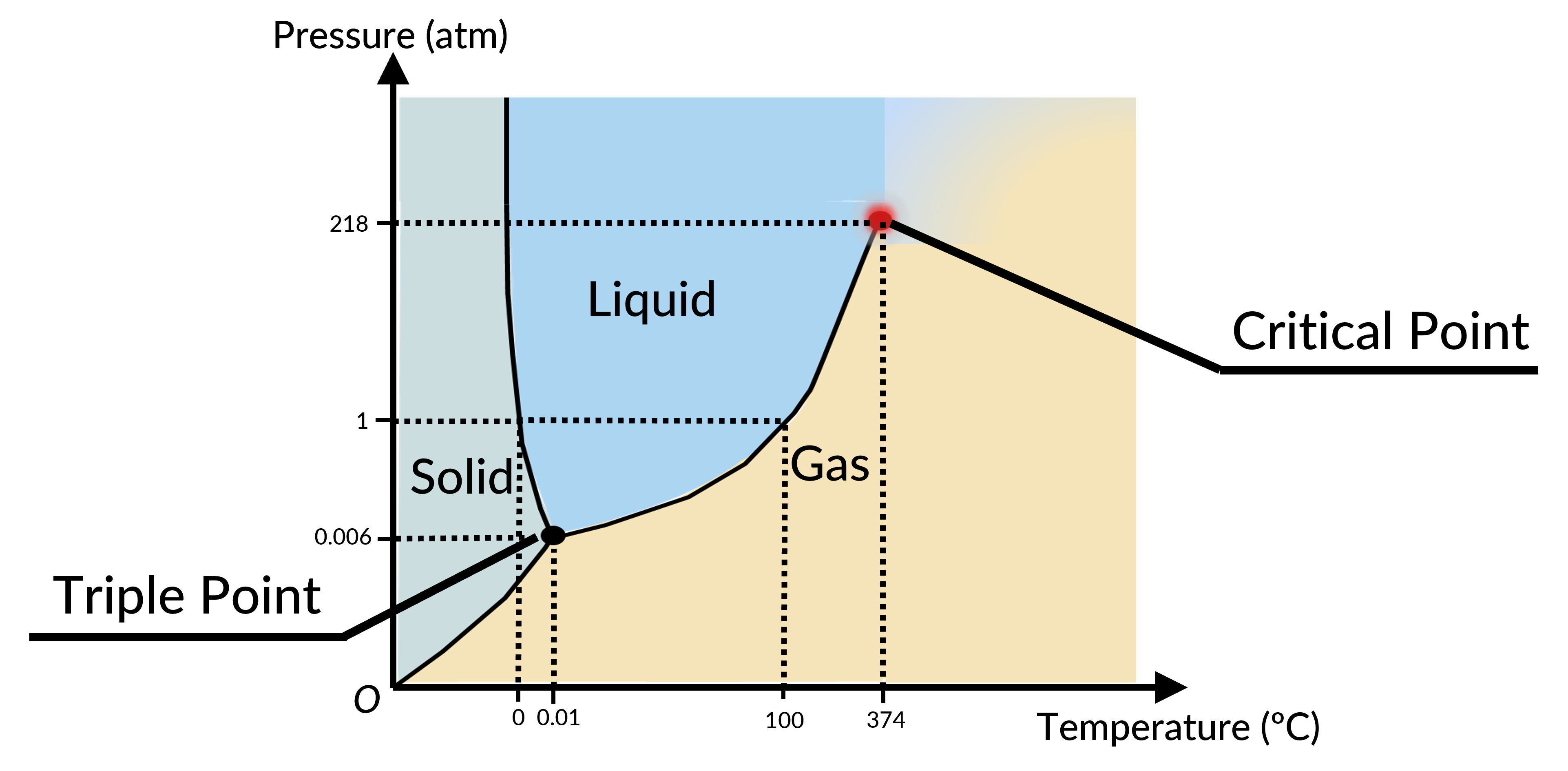
As the pressure increases, the boiling temperature of water rises gradually to 374 °C at a pressure of 218 atm. This can be demonstrated in a pressure cooker, which cooks food faster than an open pot, because the water can exist as a liquid at temperatures greater than 100 °C without all boiling away. The boiling point curve ends at a certain point called the critical point, the temperature above which the liquid and gas phases cannot be distinguished; the substance is called a supercritical fluid. At a sufficiently high pressure above the critical point, a gas has the density of a liquid but does not condense. The pressure at this critical point is known as the critical pressure. Carbon dioxide, for example, is supercritical at all temperatures above 31.0 °C, the point at which all three phases exist in equilibrium. For water, the triple point occurs at 273.16 K (0.01 °C) and 611.2 Pa; this is a more accurate calibration temperature than the melting point of water at 1.00 atm, or 273.15 K (0.0 °C).
From Chapter 19:

Now Playing
19.9 : Phase Diagram
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
5.4K Views

19.1 : Equation of State
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
1.4K Views

19.2 : Ideal Gas Equation
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
5.5K Views

19.3 : Van der Waals Equation
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
3.2K Views

19.4 : pV-Diagrams
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
3.6K Views

19.5 : Kinetic Theory of an Ideal Gas
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
2.8K Views

19.6 : Molecular Kinetic Energy
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
3.9K Views

19.7 : Distribution of Molecular Speeds
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
3.1K Views

19.8 : Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution: Problem Solving
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
1.1K Views

19.10 : Mean free path and Mean free time
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
2.4K Views

19.11 : Heat Capacity: Problem-Solving
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
372 Views

19.12 : Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
1.1K Views

19.13 : Escape Velocities of Gases
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
781 Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved