23.3 : Gauss's Law
If a closed surface does not have any charge inside where an electric field line can terminate, then the electric field line entering the surface at one point must necessarily exit at some other point of the surface. Therefore, if a closed surface does not have any charges inside the enclosed volume, then the electric flux through the surface is zero. What happens to the electric flux if there are some charges inside the enclosed volume? Gauss's law gives a quantitative answer to this question.
To get an understanding of what to expect, let's calculate the electric flux through a spherical surface around a positive point charge, q, since we already know the electric field in such a situation. Recall that when we place the point charge at the origin of a coordinate system, the electric field at a point that is at a distance r from the charge at the origin is given by
Using this electric field, the flux through the spherical surface of radius r can be found.
Then, substituting the known values into the electric flux expression for the closed system and integrating the expression, the flux through the closed spherical surface at radius r is obtained as
A remarkable fact about this equation is that the flux is independent of the size of the spherical surface. This can be directly attributed to the fact that the electric field of a point charge decreases at 1/r2 with distance, which just cancels out the r2 rate of increase of the surface area.
Gauss's law generalizes this result to cases with any number of charges and any location of the charges in the space inside the closed surface. According to Gauss's law, the flux of the electric field, 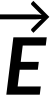 , through any closed surface, also called a Gaussian surface, is equal to the net charge enclosed, qenc, divided by the permittivity of free space, ε0:
, through any closed surface, also called a Gaussian surface, is equal to the net charge enclosed, qenc, divided by the permittivity of free space, ε0:
To use Gauss's law effectively, you must have a clear understanding of what each term in the equation represents. The field, 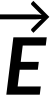 is the total electric field at every point on the Gaussian surface. This total field includes contributions from charges inside and outside the Gaussian surface. However, qenc is just the charge inside the Gaussian surface. Finally, the Gaussian surface is any closed surface in space. That surface can coincide with the actual surface of a conductor, or it can be an imaginary geometric surface. The only requirement imposed on a Gaussian surface is that it be closed.
is the total electric field at every point on the Gaussian surface. This total field includes contributions from charges inside and outside the Gaussian surface. However, qenc is just the charge inside the Gaussian surface. Finally, the Gaussian surface is any closed surface in space. That surface can coincide with the actual surface of a conductor, or it can be an imaginary geometric surface. The only requirement imposed on a Gaussian surface is that it be closed.
From Chapter 23:

Now Playing
23.3 : Gauss's Law
Gauss's Law
6.0K Views

23.1 : Electric Flux
Gauss's Law
6.5K Views

23.2 : Calculation of Electric Flux
Gauss's Law
1.3K Views

23.4 : Gauss's Law: Problem-Solving
Gauss's Law
1.2K Views

23.5 : Gauss's Law: Spherical Symmetry
Gauss's Law
6.4K Views

23.6 : Gauss's Law: Cylindrical Symmetry
Gauss's Law
6.6K Views

23.7 : Gauss's Law: Planar Symmetry
Gauss's Law
7.0K Views

23.8 : Electric Field Inside a Conductor
Gauss's Law
5.2K Views

23.9 : Charge on a Conductor
Gauss's Law
4.1K Views

23.10 : Electric Field at the Surface of a Conductor
Gauss's Law
4.1K Views

23.11 : Electric Field of a Non Uniformly Charged Sphere
Gauss's Law
1.2K Views

23.12 : Electric Field of Parallel Conducting Plates
Gauss's Law
598 Views

23.13 : Divergence and Curl of Electric Field
Gauss's Law
4.4K Views
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved