A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy for Diagnosing Interstitial Lung Diseases and Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions - A Stepwise Approach
In This Article
Summary
Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) for diagnosing interstitial lung disease and peripheral pulmonary lesions is a high-yield diagnostic and safe procedure. We describe a stepwise approach to conduct TBLC for the different indications mentioned with a flexible bronchoscope, which might be helpful for novice bronchoscopists performing TBLC.
Abstract
Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) is an invasive procedure increasingly implemented during the last decade as an alternative to video-assisted thoracic surgery lung biopsy (SLB) for diagnosing interstitial lung diseases (ILDs). The indication for TBLC has primarily been to sub-classify a specific ILD subtype when this cannot be achieved on the basis of a preceding multidisciplinary team discussion. Although SLB is considered the gold standard for establishing a histological diagnosis, TBLC has been gradually suggested as the first-choice histological diagnostic modality in patients with unclassified ILDs due to a comparable diagnostic yield with SLB, but superior to SLB in terms of complications, including mortality. During recent years, radial endobronchial ultrasound (R-EBUS) and electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB)-guided TBLC for peripheral pulmonary lesions have also been described as safe procedures, which may improve the diagnostic yield compared to forceps biopsies. Still, the diagnostic properties of TBLC rely on the quality of the procedure's performance. This article aims to describe the stepwise approach to conducting TBLC with a flexible bronchoscope for the different indications mentioned, which might be helpful for novice bronchoscopists performing TBLC.
Introduction
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) constitute a group of both acute and chronic lung diseases that affect one or more of all the lung parenchymal components forming the interstitium such as bronchi, alveoli, connective tissue, and blood- and lymphatic vessels. Despite being rare diseases, the more than 200 different subtypes of ILDs represent a heterogeneous disease category with different clinical, radiological, and cyto-histological characteristics. ILDs typically manifest as inflammation, fibrosis, or a combination of both, which are the underlying causes for the patients' usual perceived symptoms as dry cough, dyspnea on exertion, and fatigue1,2.
ILDs are categorized as idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), interstitial pneumonia of known etiology (e.g., connective tissue disease interstitial lung disease, drug-induced ILD, and work-related pneumoconiosis), granulomatous interstitial affection (e.g., sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonia), and orphan ILDs (e.g., multiple cystic lung diseases and eosinophilic pneumonia)1. This categorization and further diagnostic subtyping are fundamental to determining optimal treatment and follow-up, and allow prognostication. However, as the diagnostic puzzle may be challenging, interpretation of available clinical (including anamnesis, disposition, and potential exposures) and paraclinical information as chest high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), lung physiology, and autoimmunology obtained on the basis of a multidisciplinary team discussion (MDD) is recommended3,4,5. If a confident MDD diagnosis is not obtainable6,7, histological sampling to increase the likelihood of a definite ILD subtype diagnosis is indicated by the use of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC)8,9. In well-selected patients, TBLC is considered a safe invasive procedure with a diagnostic accuracy close to that of video-assisted thoracic surgery lung biopsy (SLB), which is still regarded as the histological gold standard for histological ILD diagnostics10,11,12,13,14. The TBLC procedure is performed as a systematic bronchoscopy, applying special cryoprobes for histological sampling and with recommended fluoroscopic guidance. It is recommended that TBLC is performed in tertiary ILD centers using an MDD setting and by interventional pulmonologists familiar with the management of TBLC complications, who have undergone training in a dedicated center with TBLC expertise9,10,11,15,16,17.
TBLC has also recently gained attention as a procedure to be combined with radial endobronchial ultrasound (R-EBUS) for ILD diagnostics18,19. Furthermore, TBLC has been combined with both R-EBUS and electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB) for diagnosing peripheral pulmonary lesions (PPL) to improve the diagnostic yield when compared to conventional transbronchial forceps biopsies20,21. However, this relatively novel approach for PPL diagnostics has not yet been implemented as a standard procedure and thus, warrants further evidence in this specific area. The aim of the present report is to describe a stepwise approach to conducting TBLC with a flexible bronchoscope in a clinical setting for the indications mentioned.
Protocol
The authors come from two Danish TBLC centers (Odense University Hospital and Aarhus University Hospital) that both conduct research in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics approval was not necessary as the study was observational in nature. All patients included for research purposes gave written informed consent. It is important to emphasize that the described stepwise approach for TBLC conductance relates to the use of a flexible bronchoscope and is based on a combination of recommendations from international guidelines, expert statements, state-of-art reviews, and experiences from the two TBLC centers9,10,11,15,16,17,22,23,24,25.
1. PreTBLC considerations
- Ensure that TBLC is indicated, which is justified in patients in whom integration of information from HRCT, biochemistry, and autoimmunology in a preceding MDD involving pulmonologists and radiologists has not been able to establish a confident ILD diagnosis.
- Select appropriate patients by avoiding the contraindications described in Table 1.
| Relative contraindications | Absolute contraindications |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) < 50% of predicted value | Thrombocytopenia < 50 x 109/L or INR > 1.5 |
| Diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide for the lung (DLCO) < 35% of predicted value | Uncorrected bleeding diathesis |
| Systolic pulmonary arterial pressure > 50 mmHg (e.g., estimation based on an echocardiography) | Progressive and clinical decline due to an increased risk of complications in patients with compromised pulmonary function |
| Body mass index > 35 kg/m2 |
Table 1: Contraindications for TBLC. Relative and absolute contraindications for TBLC conductance. Abbreviation: TBLC = transbronchial lung cryobiopsy.
2. PreTBLC preparation
- Review the HRCT and suggestions from the thoracic radiologist to plan from which bronchial segments (BS) histological sampling is best accessible according to radiological disease manifestation.
- Test that the system works prior to TBLC performance.
- Press the gas (carbon dioxide (CO2) or the nitrous oxide (NO)) tank capacity button on the settings panel to check the volume of the gas in the cylinder.
- Place the cryoprobe on a tray and observe the probe while pressing the pedal footswitch for 5-10 s. Look for an ice ball at the tip of the probe that will indicate it is functioning properly (Figure 1).
- Use general anesthesia (GA) or deep sedation under TBLC and consider premedication with tranexamic acid of 0.5-1 g to reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Place a special double luminal endotracheal tube (ETT) of 7.5-8.5 mm size in the trachea.
NOTE: The ETT has a main channel that allows access for the bronchoscope while the patient is ventilated and has a minor side channel that serves as a working channel for the bronchial blocker catheter.- Spray continuously with local anesthesia (e.g., lidocaine spray 10%) to reduce cough. See also step 3.5.
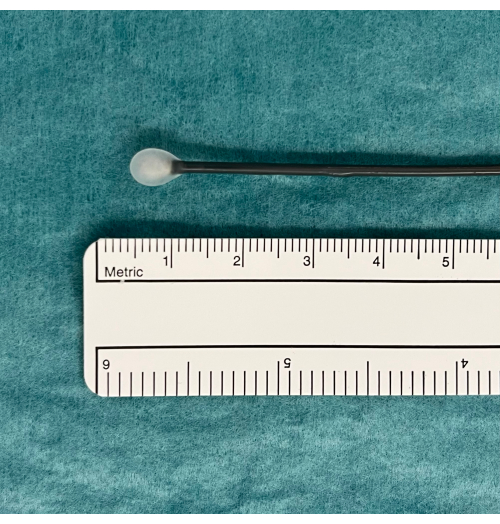
Figure 1: An ice ball as an indication of usable TBLC equipment. A pedal activates CO2 gas diffusion from the tank and induced freezing. This is tested in water where an ice ball will appear at the tip of the cryoprobe if functioning properly. Abbreviation: TBLC = transbronchial lung cryobiopsy. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. TBLC conductance
- Introduce a flexible bronchoscope through the ETT and perform the bronchoscopy procedure.
NOTE: A rigid bronchoscope is used in some TBLC centers to intubate the trachea. If the trachea is intubated by a rigid bronchoscope, a flexible bronchoscope can be passed through the rigid one.- Introduce the flexible cryoprobe through the working channel of the bronchoscope and into the selected BS.
NOTE: The cryoprobes occur as both single-use probes (1.1, 1.7, and 2.4 mm) and reusable probes (1.9 and 2.4 mm). - Use fluoroscopy to ensure that the placement of the tip of the cryoprobe is approximately 10 mm from the thorax wall corresponding to the selected BS (Figure 2).
- Introduce a bronchial blocker catheter (e.g., a Fogarty balloon) in the side channel of the double luminal ETT and place it at the selected BS ostium (Figure 3).
- Inflate the bronchial blocker catheter to evaluate the appropriateness of placement and blockage for potential bleeding occurring distally with respect to the balloon (Figure 4).
- Deflate the bronchial blocker catheter if the balloon is well placed.
- Secure the placement of the balloon by fixing the bronchial blocker catheter with a pean.
- Use small amounts of lidocaine spray or saline in the respective ETT and its side channel to reduce any friction experienced due to the introduction of the cryoprobe in the ETT and the balloon catheter in the ETT's side channel.
- When steps 3.1.1-3.1.3 are satisfactorily performed, step on the freezing pedal for 3-6 s, depending on the cryoprobe size, to exploit the Joule-Thompsons law to freeze the lung parenchymal tissue to approximately -45-79 °C for CO2 and -89 °C for NO.
- Retract the flexible bronchoscope containing the cryoprobe in one quick movement while holding the freezing pedal down to continue freezing and prevent the biopsy from falling off during the retraction.
- During the maneuver described in step 3.1.5, have a person other than the bronchoscopist keep the balloon inflated to block the biopsy site distal of the selected BS ostium to control for potential bleeding.
- Introduce the flexible cryoprobe through the working channel of the bronchoscope and into the selected BS.
- Continue step 3.1.6 until at least two biopsies from two BS from the same lobe are obtained.
- Place the biopsies in saline, and when all biopsies are obtained, fix them in formaldehyde (4%) (Figure 5).
- Send the biopsies for pathological examination prior to MDD.
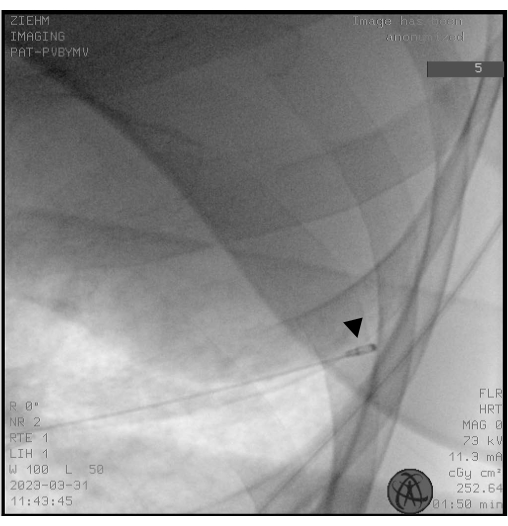
Figure 2: Fluoroscopy. Fluoroscopy is used to ensure correct placement of the cryoprobe before freezing. The tip of the cryoprobe appears as the head of a drumstick (black arrowhead). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
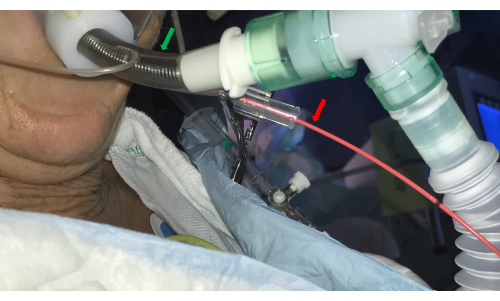
Figure 3: Endotracheal tube. A double-luminal endotracheal tube (green arrow) allows access to the airways by the bronchoscope and concurrently controls bleeding by introducing a balloon catheter in the side channel (red arrow). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Figure 4: Inflation of the balloon catheter. Inflation of the balloon catheter to ensure blockage and prevent potential bleeding distal of the balloon distributing to other parts of the lobe after having performed a transbronchial lung cryobiopsy. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
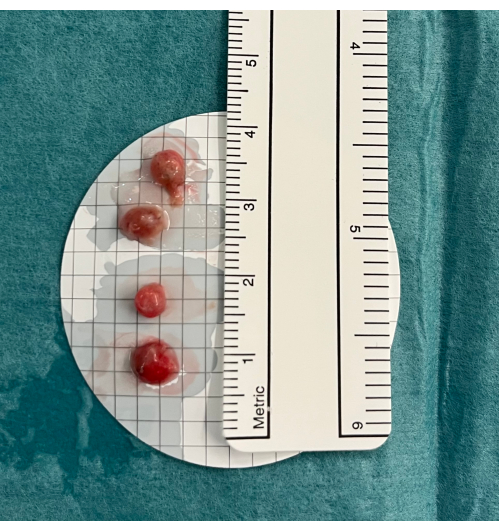
Figure 5: Biopsies. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsies are placed in cold saline before fixation in formaldehyde. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. PostTBLC procedures
- After each biopsy, reintroduce the bronchoscope into the BS and deflate the balloon to observe whether bleeding occurs.
- Reinflate the balloon if bleeding is observed (Figure 6). If the balloon is in the proper position and blocks the BS, wait for a few minutes for the bleeding to stop, and then, continue the TBLC procedure.
- If bleeding is still observed after step 4.1.1., install ice-cold saline distally to the balloon.
- In case of ongoing bleeding after step 4.1.2. or balloon failure where blood spills into other BSs, use a combination of suction, endobronchially administered ice-cold saline with or without adrenalin, and tranexamic acid.
- If the coagulated blood blocks the airways, use the cryoprobe to open up the airway again by freezing the tip of the cryoprobe into the blood clot and retracting it up through the ETT.
- If the bleeding remains uncontrolled, change the ETT to one that allows both ventilation of the non-biopsied lung and blockage of the main bronchus on the bleeding lung, and transfer the patient to an intensive care unit.
- Perform a focused lung ultrasound (FLUS) after TBLC, while the patient is still sedated to identify the indicatives of an iatrogenic pneumothorax (PTX).
- Consider insertion of a FLUS-guided pleural drain with a pigtail catheter (Fr 7-16) if FLUS observations indicate a high probability of PTX. Pleural drainage is indicated if FLUS indicates a rapidly increasing size of PTX, and especially if the clinical state of the patient is deteriorating.
- Postpone extubation by 5-10 min if FLUS reveals a small PTX and the patient is clinically stable. If the PTX size progresses hereafter or the patient becomes clinically unstable, insert a pleural drain prior to extubation.
- Extubate the patient after step 4.2 or step 4.2.2 if there is no indication of PTX or progress of the PTX size and the patient remains clinically stable.
- Observe the patient in a recovery room after TBLC. Just before the clinically stable patient goes home, ensure that late-onset PTX is not present by either repeated FLUS or a chest X-ray.
- Discuss the presentation of the histological characteristics of the biopsies at a following MDD with pulmonologists, radiologists, and pathologists in conjunction with other details to conclude an ILD subtype with high diagnostic probability.
- Inform the patient of the MDD conclusion from step 4.5 in the outpatient clinic, and plan potential treatment and follow-up.
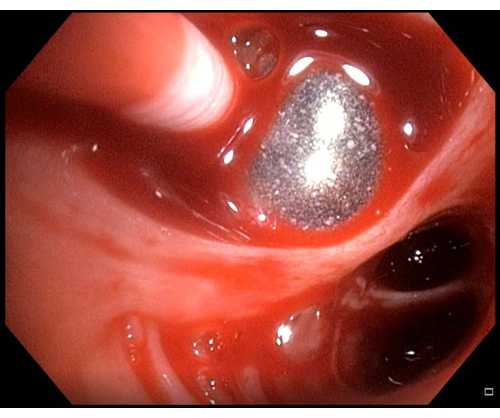
Figure 6: Minor bleeding. If bleeding is observed after having performed a transbronchial lung cryobiopsy, in this case, minor bleeding, the balloon catheter should be kept inflated a few minutes before deflating is retried. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. TBLC in conjunction with R-EBUS and ENB for PPL diagnostics
- Navigate and confirm the location of the peripheral pulmonary lesion.
- Insert the 1.1 mm cryoprobe in the extended working channel under the guidance of fluoroscopy.
- Match the tip of the freezing probe with the position of the radial EBUS probe.
- Step on the freezing pedal for 4-8 s.
- Retract the cryoprobe through the extended working channel in one quick movement while holding the freezing pedal down to continue freezing and prevent the biopsy from falling off during the retraction.
- Keep the bronchoscope and the extended working channel in position while the cryoprobe is retracted.
- Repeat steps 5.2-5.4 until a sufficient number of biopsies are obtained.
- Handle the biopsies as described in steps 3.3 and 3.4.
Results
Based on the observations from the authors from two TBLC centers, the described stepwise procedure for TBLC with a flexible bronchoscope allowed histological sampling in well-selected Danish patients with yet undiagnosed ILD subtypes despite preceding MDD. Detailed observations from these cohorts are reported in two recently published studies23,25 and for the center of the first author summarized in Table 2.
Discussion
Regardless of the indication for TBLC, its diagnostic properties rely on the quality of the procedure's performance and the selected criteria for undergoing the procedure. This emphasizes the recommendation of implementing a formal and certified training program to acquire the competences required to perform a standardized TBLC procedure. Despite the fact that no official TBLC education is currently obtainable, the recent European Respiratory Society guideline on TBLC for ILD suggests that interventional pulmonologis...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the personnel from the Departments of Thoracic Surgery and Anesthesiology at the Bronchoscopy Ward at Odense University Hospital, Denmark, for their help with the preparation of the figures for this article.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| "Chimney" for tube | |||
| CO2 gas bottle adapter | |||
| CO2 gas tank | Erbe | ||
| Endoscopy column | |||
| Endotracheal tube, size 7.5-8.5 mm | Erbe | ||
| Erbecryo pedal footswitch | Erbe | ||
| Erbecryo2 workstation | Erbe | ||
| Flexible bronchoscope | |||
| Flexible gas hose | Mediland | ||
| Flexible single use cryoprobe, OD 1.1 mm | Erbe | ||
| Flexible single use cryoprobe, OD 1.7 mm | Erbe | ||
| Flexible single use cryoprobe, OD 2.4 mm | |||
| Fluoroscope | |||
| Fogarty balloon catheter | |||
| Formalin glasses in closed system | |||
| NaCl incl. cold NaCl | |||
| Pean for fixating Fogarty balloon | |||
| Sterile disposable cup | |||
| Sterile suction tube | |||
| Sterile tweesers | |||
| Syringe for Fogarty balloon inflation/deflation | |||
| Table bag for flouroscope | |||
| Three way tap for Fogarty balloon syringe | |||
| Tracheal suction | |||
| Ultrasound machine | Erbe | ||
| Valve for biopsy chanel | |||
| Valve to suction duct |
References
- Travis, W. D., et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 188 (6), 733-748 (2013).
- Ruaro, B., et al. Editorial: Pulmonary fibrosis: One manifestation, various diseases. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 13, 1027332 (2022).
- Lamas, D. J., et al. Delayed access and survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a cohort study. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 184 (7), 842-847 (2011).
- Tomassetti, S., Piciucchi, S., Tantalocco, P., Dubini, A., Poletti, V. The multidisciplinary approach in the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a patient case-based review. European Respiratory Review. 24 (135), 69-77 (2015).
- Walsh, S. L. F., et al. Multicentre evaluation of multidisciplinary team meeting agreement on diagnosis in diffuse parenchymal lung disease: a case-cohort study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 4 (7), 557-565 (2016).
- Ryerson, C. J., et al. A standardized diagnostic ontology for fibrotic interstitial lung disease. An International Working Group perspective. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 196 (10), 1249-1254 (2017).
- Cottin, V., et al. Integrating clinical probability into the diagnostic approach to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An International Working Group perspective. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 206 (3), 247-259 (2022).
- Rodrigues, I., et al. Diagnostic yield and safety of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy and surgical lung biopsy in interstitial lung diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Respiratory Review. 31 (166), 210280 (2022).
- Korevaar, D. A., et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines on transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. European Respiratory Journal. 60 (5), 2200425 (2022).
- Colella, S., Haentschel, M., Shah, P., Poletti, V., Hetzel, J. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in interstitial lung diseases: best practice. Respiration. 95 (6), 383-391 (2018).
- Hetzel, J., et al. Transbronchial cryobiopsies for the diagnosis of diffuse parenchymal lung diseases: expert statement from the Cryobiopsy Working Group on safety and utility and a call for standardization of the procedure. Respiration. 95 (3), 188-200 (2018).
- Ravaglia, C., Poletti, V. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy for the diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine. 28 (1), 9-16 (2022).
- Troy, L. K., et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy for interstitial lung disease diagnosis (COLDICE): a prospective, comparative study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 8 (2), 171-181 (2020).
- Ruaro, B., et al. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy and pulmonary fibrosis: A never-ending story. Heliyon. 9 (4), e14768 (2023).
- Lentz, R. J., Argento, A. C., Colby, T. V., Rickman, O. B., Maldonado, F. Transbronchial cryobiopsy for diffuse parenchymal lung disease: a state-of-the-art review of procedural techniques, current evidence, and future challenges. Journal of Thoracis Disease. 9 (7), 2186-2203 (2017).
- Maldonado, F., et al. Transbronchial cryobiopsy for the diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 157 (4), 1030-1042 (2020).
- Avasarala, S. K., Wells, A. U., Colby, T. V., Maldonado, F. Transbronchial cryobiopsy in interstitial lung diseases: State-of-the-art review for the interventional pulmonologist. Journal of Bronchology Interventional Pulmonology. 28 (1), 81-92 (2021).
- Abdelghani, R., Thakore, S., Kaphle, U., Lasky, J. A., Kheir, F. Radial Endobronchial Ultrasound-guided Transbronchial Cryobiopsy. Journal of Bronchology Interventional Pulmonology. 26 (4), 245-249 (2019).
- Inomata, M., et al. Utility of radial endobronchial ultrasonography combined with transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in patients with diffuse parenchymal lung diseases: a multicentre prospective study. BMJ Open Respiratory Research. 8 (1), e000826 (2021).
- Benn, B. S., Gmehlin, C. G., Kurman, J. S., Doan, J. Does transbronchial lung cryobiopsy improve diagnostic yield of digital tomosynthesis-assisted electromagnetic navigation guided bronchoscopic biopsy of pulmonary nodules? A pilot study. Respiratory Medicine. 202, 106966 (2022).
- Ankudavicius, V., Miliauskas, S., Poskiene, L., Vajauskas, D., Zemaitis, M. Diagnostic yield of transbronchial cryobiopsy guided by radial endobronchial ultrasound and fluoroscopy in the radiologically suspected lung cancer: A single institution prospective study. Cancers. 14 (6), 1563 (2022).
- Ravaglia, C., et al. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in diffuse parenchymal lung disease: Comparison between biopsy from 1 segment and biopsy from 2 segments - diagnostic yield and complications. Respiration. 93 (4), 285-292 (2017).
- Davidsen, J. R., Skov, I. R., Louw, I. G., Laursen, C. B. Implementation of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in a tertiary referral center for interstitial lung diseases: a cohort study on diagnostic yield, complications, and learning curves. BMC Pulmonary Medicine. 21 (1), 67 (2021).
- Laursen, C. B., et al. Lung ultrasound assessment for pneumothorax following transbronchial lung cryobiopsy. ERJ Open Research. 7 (3), 00045-2021 (2021).
- Kronborg-White, S., et al. Integration of cryobiopsies for interstitial lung disease diagnosis is a valid and safe diagnostic strategy-experiences based on 250 biopsy procedures. Journal of Thoracic Disease. 13 (3), 1455-1465 (2021).
- Barisione, E., et al. Competence in transbronchial cryobiopsy. Panminerva Medica. 61 (3), 290-297 (2019).
- Raghu, G., et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (an update) and progressive pulmonary fibrosis in adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 205 (9), e18-e47 (2022).
- Ravaglia, C., et al. Diagnostic yield and risk/benefit analysis of trans-bronchial lung cryobiopsy in diffuse parenchymal lung diseases: a large cohort of 699 patients. BMC Pulmonary Medicine. 19 (1), 16 (2019).
- Hernandez-Gonzalez, F., et al. Cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of diffuse interstitial lung disease: yield and cost-effectiveness analysis. Archivos de Bronconeumología. 51 (6), 261-267 (2015).
- Cooley, J., et al. Safety of performing transbronchial lung cryobiopsy on hospitalized patients with interstitial lung disease. Respiratory Medicine. 140, 71-76 (2018).
- Hetzel, J., et al. Transbronchial cryobiopsy increases diagnostic confidence in interstitial lung disease: a prospective multicenter trial. European Respiratory Journal. 56 (6), 1901520 (2020).
- Kheir, F., et al. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in patients with interstitial lung disease: a systematic review. Annals of the American Thoracic Society. 19 (7), 1193-1202 (2022).
- Walscher, J., et al. Transbronchial cryobiopsies for diagnosing interstitial lung disease: real-life experience from a tertiary referral center for interstitial lung disease. Respiration. 97 (4), 348-354 (2019).
- Gnass, M., et al. Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy guided by radial mini-probe endobronchial ultrasound in interstitial lung diseases - a multicenter prospective study. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 88 (2), 123-128 (2020).
- Ma, X., et al. Global and regional burden of interstitial lung disease and pulmonary sarcoidosis from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. Thorax. 77 (6), 596-605 (2022).
- Kronborg-White, S., et al. A pilot study on the use of the super dimension navigation system for optimal cryobiopsy location in interstitial lung disease diagnostics. Pulmonology. 29 (2), 119-123 (2021).
- Wijmans, L., et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy as a guidance tool for transbronchial lung cryobiopsies in interstitial lung disorder. Respiration. 97 (3), 259-263 (2019).
- Kheir, F., et al. Using bronchoscopic lung cryobiopsy and a genomic classifier in the multidisciplinary diagnosis of diffuse interstitial lung diseases. Chest. 158 (5), 2015-2025 (2020).
- Renzoni, E. A., Poletti, V., Mackintosh, J. A. Disease pathology in fibrotic interstitial lung disease: is it all about usual interstitial pneumonia. Lancet. 398 (10309), 1437-1449 (2021).
- Chaudhary, S., et al. Interstitial lung disease progression after genomic usual interstitial pneumonia testing. European Respiratory Journal. 61 (4), 2201245 (2023).
- Raghu, G., et al. Use of a molecular classifier to identify usual interstitial pneumonia in conventional transbronchial lung biopsy samples: a prospective validation study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 7 (6), 487-496 (2019).
- Kheir, F., et al. Use of a genomic classifier in patients with interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of American Thoracic Society. 19 (5), 827-832 (2022).
- Glenn, L. M., Troy, L. K., Corte, T. J. Novel diagnostic techniques in interstitial lung disease. Frontiers in Medicine. 10, 1174443 (2023).
- Kim, S. H., et al. The additive impact of transbronchial cryobiopsy using a 1.1-mm diameter cryoprobe on conventional biopsy for peripheral lung nodules. Cancer Research and Treatment. 55 (2), 506-512 (2023).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved