10.6 : Relating Angular And Linear Quantities - II
In the case of circular motion, the linear tangential speed of a particle at a radius from the axis of rotation is related to the angular velocity by the relation:
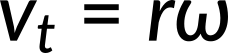
This could also apply to points on a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. In a circular motion, both uniform and nonuniform, there exists a centripetal acceleration. The centripetal acceleration vector points inward from the particle executing circular motion toward the axis of rotation. In uniform circular motion, when the angular velocity is constant and the angular acceleration is zero, we observe a linear acceleration—that is, centripetal acceleration—since the tangential speed is constant. If the circular motion is nonuniform, then the rotating system has an angular acceleration, and we have both a linear centripetal acceleration and linear tangential acceleration.
The centripetal acceleration is due to a change in the direction of tangential velocity, whereas the tangential acceleration is due to any change in the magnitude of the tangential velocity. The tangential and centripetal acceleration vectors are always perpendicular to each other. To complete this description, a total linear acceleration vector is assigned to a point on a rotating rigid body or a particle executing circular motion at a radius r from a fixed axis. The total linear acceleration vector is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations. The total linear acceleration vector in the case of nonuniform circular motion points at an angle between the centripetal and tangential acceleration vectors.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 10.3: Relating Angular and Translational Quantities.
来自章节 10:

Now Playing
10.6 : Relating Angular And Linear Quantities - II
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
5.4K Views

10.1 : 角速度和位移
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
15.1K Views

10.2 : 角速度和加速度
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
9.1K Views

10.3 : 具有恒定角加速度的旋转 - I
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
6.7K Views

10.4 : 具有恒定角加速度的旋转 - II
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
5.9K Views

10.5 : 关联角度量和线性量 - I
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
6.5K Views

10.7 : 转动惯量
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
12.0K Views

10.8 : 转动惯量和旋转动能
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
7.3K Views

10.9 : 转动惯量:计算
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
6.7K Views

10.10 : 复合对象的惯性矩
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
6.1K Views

10.11 : 平行轴定理
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
6.5K Views

10.12 : 垂直轴定理
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
2.7K Views

10.13 : 旋转坐标系中的矢量变换
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
1.5K Views

10.14 : 科里奥利力
Rotation and Rigid Bodies
3.2K Views
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。