Method Article
一个协议,用于远程监督经颅直流电刺激(TDCS)在多发性硬化症的使用(MS)
摘要
The goal of this pilot study is to describe a protocol for the remotely-supervised delivery of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) so that the procedure maintains standards of in-clinic practice, including safety, reproducibility, and tolerability. The feasibility of this protocol was tested in participants with multiple sclerosis (MS).
摘要
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a noninvasive brain stimulation technique that uses low amplitude direct currents to alter cortical excitability. With well-established safety and tolerability, tDCS has been found to have the potential to ameliorate symptoms such as depression and pain in a range of conditions as well as to enhance outcomes of cognitive and physical training. However, effects are cumulative, requiring treatments that can span weeks or months and frequent, repeated visits to the clinic. The cost in terms of time and travel is often prohibitive for many participants, and ultimately limits real-world access.
Following guidelines for remote tDCS application, we propose a protocol that would allow remote (in-home) participation that uses specially-designed devices for supervised use with materials modified for patient use, and real-time monitoring through a telemedicine video conferencing platform. We have developed structured training procedures and clear, detailed instructional materials to allow for self- or proxy-administration while supervised remotely in real-time. The protocol is designed to have a series of checkpoints, addressing attendance and tolerability of the session, to be met in order to continue to the next step. The feasibility of this protocol was then piloted for clinical use in an open label study of remotely-supervised tDCS in multiple sclerosis (MS). This protocol can be widely used for clinical study of tDCS.
引言
tDCS is a relatively recent therapy that operates through the use of low amplitude (2.0 mA or less) direct current to modulate cortical excitability 1. Hundreds of clinical trials have demonstrated tDCS to be safe and well-tolerated2-4. tDCS is easier to use, lower in cost, and better tolerated when compared to other methods such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (e.g., tDCS has not been associated with the development of seizures 5,6). Multiple tDCS sessions are required for benefit, especially when administered with the goal of enhancing rehabilitation outcomes.7-10
It is not yet known how many tDCS sessions are necessary or optimal, but the effects are cumulative with little evidence that tDCS over a single session produces behaviorally meaningful changes.2,11 For example, studies of depression have found 30 or more sessions needed for full benefit in some participants. 12,13 Multiple sessions are especially important when pairing tDCS with a behavioral therapy, which only occurs with rigorous repetition across many sessions. 14
For many patients and caregivers, traveling to the outpatient facility to receive repeated tDCS treatment sessions is a major obstacle in terms of time, cost and travel arrangements. This real-world limitation has resulted in studies with small sample sizes and without adequate power or design to draw conclusions that can lead to clinical use.15 Remote tDCS delivery would allow for participation in study protocols from home or other locations, and reach those patients who otherwise would not have access to these trials. Further, it allows the possibility for testing "on-demand" application for indications such as epilepsy and migraines.
We have worked with a diverse group of clinical investigators interested in remotely-supervised tDCS to develop guidelines and standards for remotely-supervised tDCS delivery including specialized equipment and specific training requirements both for staff and study participants16. Here, we developed a protocol to follow these guidelines and test for feasibility in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), a disorder where tDCS may be a useful tool for the management of its symptoms. 11,17-23
研究方案
伦理声明:纽约州立石溪大学的机构审查委员会(IRB)批准了该协议于2015年2月10日。
1.参加者招募的远程监督TDCS的
- 提供招募研究参与者与设备上的信息十天研究协议。
2.包含/排除标准
- 健康
- 确保临床医生已经在基线访问所有登记的与会者提供体检合格证明。
- TDCS耐受性和笔记本电脑资质
- 确保参与者所熟悉的一台笔记本电脑的基本功能,以及如何将计算机连接到Wi-Fi网络。对于这两种使用笔记本电脑,而TDCS设备的设置,确保参与者(或代理),有灵巧来完成的过程。
- 除了设置,在基线参观,让参与者1.5 1分钟试验剂量TDCS毫安确定的耐受性。如果参与者不能忍受这种会议,为1.0 mA的低剂量可以应用。如果没有容忍,排除参与者。
- 环境的
- 确认参与者有机会获得分心自由,光线充足,整洁的环境与安全区来存储设备和设备套件。
- 合规
- 如果参与者不符合预定的视频会议会话及时,排除参与者。
- 停止标准
- 在每个参与者的互动,审查了一系列的规定"停止标准",以确保参与者容忍的会议,坚持学习进度和安全操作设备无不良影响。应任何这些得到满足,排除在研究参与者(图1)。
3.材料
注意:至于建议中的远程监督使用16的出版方针,精确的电极的制备和位置必须反映该诊所的协议相对于剂量的控制和持续监控。
- 设备工具包
- 准备每个远程TDCS参与者相同的材料。这包括提供研究膝上型计算机与安全的视频会议软件,装置,和一个装置套件。
- 设计该装置套件的易用性和白天组织它(图2)。
- 制备具有大小5x5cm的带穿孔20裹海绵的口袋的试剂盒的顶部(每所需的10天的研究天),20注射器预填充用6mL的每个海绵的口袋的盐溶液,用洗瓶填充有额外的盐,备用电池的设备,以及手持镜子耳机应用。
- 此外,需要研究用户拥有便携式家用电话或移动电话的工作区为每会话。
- 设备
- 选择,只有通过一个一次性使用的解锁码释放会话的TDCS设备。确保研究设备具有这样一种功能后研究的技术人员所提供的代码,参与者只能管理一个会话。此外,确保在研究设备的选择,接触质量不断监测,以确保安全和正常使用。
- 视频监控
- 选择一个安全的视频会议软件,以便设备,最佳的接触质量的正确安装的远程监控,并且所需的用户正在应用的会话。
- 使用视频会议软件作为培训的另一种方法。指导用户如何打开设备,阅读他们的接触质量,排除接触质量差,输入一个一次性使用的解锁码,并且关机后安全地删除该设备。
- 帽子
- 设计头饰的SIM卡PLE和强大的电极定位。使用单位头饰消除房间的用户错误,并帮助节省了放置蒙太奇。配置一个帽状设计,具有明确标明海绵标记以加强与所述阳极电极放置在左侧的单位置头套放置的可靠性。
4.培训
注:远程研究的第一基准会议期间完成大部分参与者的培训。大约1-2小时的基线访问应该花在培训。让参与者观看一个教学TDCS视频作为自己的第一个指令。
- 教学视频
- 建立教学视频下面的基线访发挥的参与者。在观看,允许参与者能够访问该设备和装置套件,并跟随在每一个步骤。
- 准备先介绍particip视频蚂蚁的材料,然后过渡到一个一步一步的指导,模仿实际的学习会的流程。
- 目前TDCS耳机缓慢而清晰的设置(并使其可用于重播),如果用户需要澄清。还提供了一个参与视图,使这项研究的参与者能够获得什么样的设备屏幕期望,以及如何提供一定的读数时,该设备显示将出现感。
- 视频部分
注:远程技术人员不会为设备提供解锁代码,除非适当的接触质量的实现。- 设计教学视频细节故障排除联系信息质量差,包括施加压力和润湿海绵口袋的手段。确保视频还提供了学习材料的安全使用信息,以及该协议,以结束会话跟踪。
- 指导有关程序与会者终止会话,并要求看齐ticipants保持在整个会话期间电话接入,保证在诊所安全保持在紧急情况下的电平,
- 之后的视频,允许参与者以尝试自己的一套与一个研究的技术人员的帮助。
- 使用手册
- 准备在视频呈现的信息,以及照片和材料的图,装置的屏幕截图,和笔记本电脑的信息的转录,在手动的形式。
- 现场培训
- 监视参与者,因为他们开始菜单。
- 完成每个步骤(滋润海绵口袋,将电极浸入海绵,海绵固定到耳机,耳机的地方头部,中心头戴式耳机,确认研究的技术人员,并打开设备)教练参加。
- 澄清过程或设备在必要。
- 与会者那段经历一系列故障排除向上难度
- 如果参与者奋斗与设置,重复该方法的示范。
- 如果参与者未能完成组建经过反复尝试,终止会话。这被定义为一个研究"停"的标准。
5.参与者准备学习会议
- 指导参与者建立自己的研究笔记本电脑,移动电话,设备工具包,设备和耳机在干净,照明良好的区域。与会者通报拉头发向后,尽量减少干扰。
- 让参与者指的是教学视频或手动一步协议的步骤指南。
- 首先启动网络会议开头的设置,以便有持续监测遵守16前的研究参与者。
在学习会话6.设备安装
- 启动视频会议结束后,指示参与者开始集U页。
- 打开海绵口袋和滋润使用6毫升注射器(每个海绵口袋一个针筒)。约3毫升可用于润湿海绵的口袋的每一侧。
- 应用碳橡胶电极进行电流从TDCS刺激。包住海绵口袋里的电极。将每个碳橡胶电极插入海绵的口袋里完全。注:由于橡胶电极直接接触皮肤是痛苦的,电极,装在口袋里的海绵。
- 确保红色电缆连接到设备上标有"阳极"红色接收器插件。确保黑色电缆连接到设备上标有"阴极"黑接收器插件。这些电缆是永远不会从设备中删除。
- 连接海绵的口袋和电极的耳机使用公共双边背外侧前额叶皮质(DLPC),与设置在左侧的阳极电极(一个连接到红色线)。注:标注耳机与红色和黑色,以确保适当的电极放置。
- 使用固定在海绵上的口袋适合插入耳机槽按钮耳机。海绵口袋光滑的一面总是朝向朝前额。
注意:此提供方便可靠的电极放置和广泛的治疗应用。 - 后海绵的口袋被紧固,定位在头上的耳机。掖在头部背面的槽下方的背带,并与鼻根对准中央按钮。这可以通过在设备工具包,并通过视频会议软件的研究技术人员提供的手持镜子确认。
- 在这一点上,指示参与者朗读设备屏幕上的接触质量。注:中度或最佳读取所需的会话代码管理。
- 如果接触质量有待提高,指导学员按照预先设定的故障排除步骤。首先,建议将压力施加到海绵的口袋。如果该DOES并不成功,让参与者施加少量的盐溶液使用洗瓶(提供任何溢出纸巾)海绵口袋里的选项。
- 一旦接触良好品质实现,管理的会话一个一次性使用的解锁码。注:对于时间和幅度设定的数额这些代码进行了预编程的研究人员。
7.会议结束
注:在与会者进入解锁代码,该设备的屏幕上会显示倒计时的分钟,直到会议结束的计时器。该设备也将指示电极在整个会议的接触质量。当1分钟保留在计时器下,会发生在秒的倒数。
- 如果接触质量低于"温和"提供了关于如何使用6.9的故障排除步骤来改善它的说明。
- 提醒参与者不要取下耳机,直到秒都充分递减计数到零,并且装置关闭(以哔噪声确认)。
- 指导参与者取下耳机时,该设备会发出蜂鸣声。
- 直接参与者从设备中取出海绵袋和丢弃。注射器是一次性使用,以及也应丢弃。
- 确保参与者存储设备和耳机在试剂盒中。
- 提醒参与者安全地存储在笔记本电脑,设备,并为下一届会议的所有材料。
8.结束研究分析的
- 评估使用一个参与者跟踪每个研究参与者。这可作为记录学习达标,不良事件,并会完成的方法。在研究结束时,检查每个参与者的数据,以确定研究的成功。对于这个协议的目的,研究成功将80%的参与者被定义已经完成了80%,学习班24。
- 验证SES锡永成功通过日常会议签到每日疼痛评分的,审查的记录和之前和之后的刺激问卷不良事件请参阅补充代码文件抽样问卷。
注:验证的刺激的20分钟是完全可以交付试验结束时进行审查。该研究的技术人员可以访问该设备用于完成代码的确认。
结果
我们已经适应了这个协议中的MS使用。我们有针对性的十TDCS刺激会交付提供了两个多星期,十9,10的前两个会议是面对面的培训课程,并在以下八个被远程监督(图3),第二届由一个环境适宜的评估那里的研究技术人员参观了参与者的家,确认相应的设定。
要完成以下远程监督会议,与会者提供了TDCS设备专门设计的用于远程使用和修改的易用性,引导正确电极放置了一个耳机。的装置试剂盒提供并包括在设备和耳机,一次性使用海绵的口袋的电极和注射器填充有生理盐水的需要为每个海绵所测量的量,与由天和器官单独标记的所有项目美化版的易用性。电极10 9,10放置成与阳极电极放置在左侧的双边背外侧前额叶皮质(DLPC)位置。这提供易于可靠电极放置,宽治疗应用。根据我们的目标1.5 mA的20分钟之前的研究会话。该协议9,10允许电流降低至1.0 mA的基线,如果这改善了整体的主题耐受性。
参加者给予配置为研究对象,包括方便的教学视频和链接,随着研究的技术人员安全的视频会议连接的一项研究提供的笔记本电脑。这款笔记本电脑还包括一个用于远程监控所有计算机活动和程序来远程访问计算机的技术支持。对于操作的详细说明书,使用由参与者和研究的技术人员都和粘合剂为自-R提供了EPORT措施。
共有n个= 20 MS参与者完成了这项研究。纳入标准指定一个扩展残疾状态量表* 25 6.0或以下或6.5以上或具有代理(EDSS),以确保最小的马达要求进行操作的设备。注册已经代表,在MS的范围减值(运动障碍,认知障碍,或两者)的。所有的20名学员中,n = 4的代理,成功地训练自我应用TDCS会话和192会话总数已经完成。 如图4,40 the192会话包括培训;其余152人专门进行远程监督会议。在远程监督会议,100%是有成功放置电极,设备操作和刺激耐受性良好的传递正确执行。
负载/ 53542 / 53542fig1.jpg"/>
图1.停止标准流程 。下图详细介绍了各种标准,表明参与者无法再进行或参与远程监督TDCS的研究。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
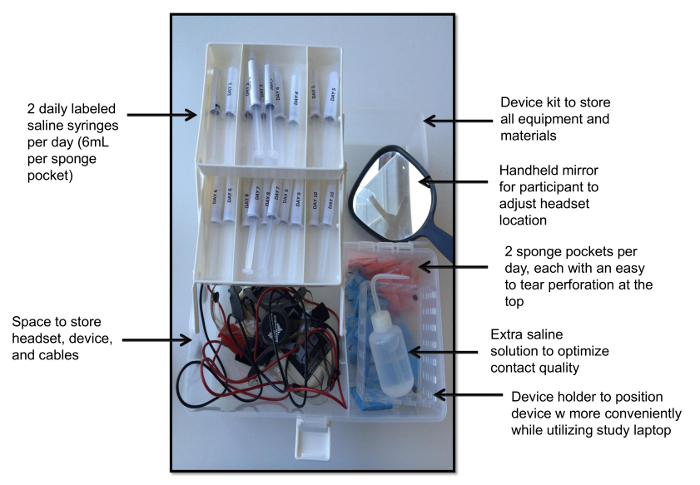
图2.设备工具包。这种观点说明与独立包装海绵口袋里的设备工具包,每人每天海绵1生理盐水充式注射器,手持镜设备支架,备用生理盐水,设备与头盔。 请点击这里查看一个更大的版本这个数字。

图3.参与者学习时间表 。这个时间表展示了一种方法,通过研究各10天参加招生周期研究试剂盒和设备。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
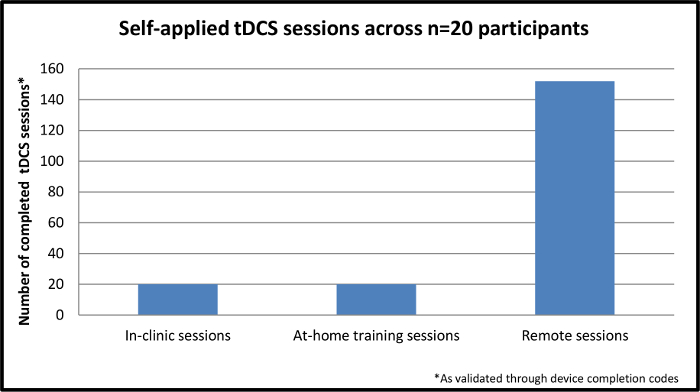
图跨越N = 20名学员4.自申请TDCS会议。这个数字说明了完成的,自申请会跨越N = 20名学员参加了学习。初始会话完成的诊所,而其余九个交易日都通过远程监控,在参与者的家中完成。 请点击此处查看大v版为这一数字的。
讨论
在协议中的关键步骤
由于远程监督TDCS是从一个临床医生,入选和排除标准的设计直接监督管理的路程,以保证参与者有没有禁忌的健康状况或环境的干扰,并且完全有能力使用一台笔记本电脑(包括自适应技术),用于研究小组沟通。此外,参加者必须能够忍受TDCS会议,并提交到预定的会议时间学习的时间。
而远程TDCS提供方便的治疗的研究和管理,自导参与者使用是不可取的,由于双方的安全问题以及无法监视和标准化所递送的刺激。相反,我们的协议遵循的标准和准则进行远程监督TDCS 16延长CL通过交付在偏远地区INIC标准。该准则确保科研人员经过适当培训的学员的互动,使用户有机会参加远程TDCS适当的能力,并有持续的培训材料,以及在研究的每个步骤中的参与者的评估。刺激是一致的和可重复使用的1.5毫安整整20分钟,在每一个会议上发表,而不需要通过会话或个人的任何中断或变化。
修改协议和故障排除提示
该协议包括一些小的修改。首先,我们扩大了使用这种协议来MS参与者有一个EDSS评分超过6.5在有访问管理每个剂量的代理实例。此外,我们还实施了一项程序,使我们远程访问参加者提供学习的笔记本电脑发起网络confe伦斯为那些谁需要耐受性的额外支持和审查措施,并通过一个共享的文件学习经验。未来的修改目前的协议包括允许不同程度的远程监控,使参与者证明谁最有能力的技术将只需要初期督导,以确认设备的设置和接收解锁代码。
该技术的局限性
虽然我们的初步研究结果支持该协议的可行性,样本大小是有限的。作为注册的扩展,分析将被用于在训练间隙制成,如何简化会话,增强教学视频,和使该技术更容易获得那些具有运动功能障碍(即,自适应老鼠计算机使用中,海绵的口袋/耳机修改以进一步缓解应用程序)。在EDSS一些与会者的范围低于6.5(不需要代理),可能还是会遇到一些DIFficulty在耳机的准备和故障排除的计算机相关的问题。此外,虽然这项研究建议在所有会话完整的远程监控的参与者,未来的研究可能会认为一些与会者充分的训练来操作设备,而无需监管对话的全部内容。
该方法相对于现有方法的意义
这些初步结果表明我们的协议进行远程监督TDCS交付的临床试验,下面的一组指导原则和标准,必须采用安全的可行性,并有效地管理远程监督下TDCS。该协议被设计为具有决策树一系列关卡以"停止"的准则(上文2.5.1节),必须以继续在每一步被清除(见图1)。这些检查点解决痛苦或不良反应的耐受性(经验s到治疗)及合规(及时的会议出席率和适当的技术)。对于每个会话1到10,参与者完成简短的不良事件报告前,他们的课程后(与在以前的试验中最常见的TDCS的副作用列表导出项目)。此外,与会者完成了自我报告的措施来解决耐受性(之前和之后的会议),并可以完成症状库存为好。这项研究是在它建立了一个技术审查MS疗法提供足够的功率,同时也提供了一个TDCS处理更广泛的访问显著。
该技术的未来应用
一旦方法进行远程监督TDCS已在MS人群得到了充分的驾驶,更大规模,随机对照试验,可以发起针对症状的管理。通过使用教学培训材料和结构周围的日常参与者INTERActions,远程监督TDCS可以通过更广泛的患者人群进行访问,并扩大该技术的临床研究。
披露声明
CUNY has patents with Marom Bikson as inventor. Marom Bikson has equity in Soterix Medical Inc. CUNY has patents with Abhishek Datta as inventor. Abhishek Datta has equity in Soterix Medical Inc.
致谢
Supported by The Lourie Foundation, Inc.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Mini-CT transcranial direct current stimulation device | Soterix | Device to deliver direct current stimultion in a remote manner | |
| Study Kit | Provided to participant with all required setup items - device, headset, sponge pockets, pre-filled syringes, Kleenex, handheld mirro, spare batteries | ||
| Laptop | Provided to allow secure video conferecing during device setup and headset placement | ||
| Instruction Manual | Transcription of instructional video and detailed instructions for protocol |
参考文献
- Filmer, H. L., Dux, P. E., Mattingley, J. B. Applications of transcranial direct current stimulation for understanding brain function. Trends in neurosciences. 37, 742-753 (2014).
- Brunoni, A. R., et al. Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): challenges and future directions. Brain stimulation. 5, 175-195 (2012).
- Nitsche, M. A., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation: State of the art 2008. Brain stimulation. 1, 206-223 (2008).
- Iyer, M. B., et al. Safety and cognitive effect of frontal DC brain polarization in healthy individuals. Neurology. 64, 872-875 (2005).
- Vanneste, S., et al. Bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulation for tinnitus by transcranial direct current stimulation: a preliminary clinical study. Experimental brain research. 202, 779-785 (2010).
- Priori, A., Hallett, M., Rothwell, J. C. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation or transcranial direct current stimulation?. Brain stimulation. 2, 241-245 (2009).
- Demirtas-Tatlidede, A., Vahabzadeh-Hagh, A. M., Pascual-Leone, A. Can noninvasive brain stimulation enhance cognition in neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuropharmacology. 64, 566-578 (2013).
- Martin, D. M., et al. Can transcranial direct current stimulation enhance outcomes from cognitive training? A randomized controlled trial in healthy participants. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology / official scientific journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum. 16, 1927-1936 (2013).
- Elmasry, J., Loo, C., Martin, D. A systematic review of transcranial electrical stimulation combined with cognitive training. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 18 (6), 065018 (2015).
- Brunoni, A. R., Vanderhasselt, M. A. Working memory improvement with non-invasive brain stimulation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain and cognition. 86, 1-9 (2014).
- Meesen, R. L., Thijs, H., Leenus, D. J., Cuypers, K. A single session of 1 mA anodal tDCS-supported motor training does not improve motor performance in patients with multiple sclerosis. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 32, 293-300 (2014).
- Shiozawa, P., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for major depression: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology / official scientific journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum. 17, 1443-1452 (2014).
- Loo, C. K., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for depression: 3-week, randomised, sham-controlled trial. The British journal of psychiatry : the journal of mental science. 200, 52-59 (2012).
- Lampit, A., Hallock, H., Valenzuela, M. Computerized cognitive training in cognitively healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of effect modifiers. PLoS medicine. 11, e1001756 (2014).
- Magalhaes, R., et al. Are cognitive interventions for multiple sclerosis effective and feasible. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 32, 623-638 (2014).
- Charvet, L. E., et al. Remotely-supervised transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for clinical trials: guidelines for technology and protocols. Frontiers in systems neuroscience. 9, 26 (2015).
- Palm, U., Ayache, S. S., Padberg, F., Lefaucheur, J. P. Non-invasive Brain Stimulation Therapy in Multiple Sclerosis: A Review of tDCS, rTMS and ECT Results. Brain stimulation. 7, 849-854 (2014).
- Mori, F., et al. Effects of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on chronic neuropathic pain in patients with multiple sclerosis. The journal of pain : official journal of the American Pain Society. 11, 436-442 (2010).
- Mori, F., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation ameliorates tactile sensory deficit in multiple sclerosis. Brain stimulation. 6, 654-659 (2013).
- Tecchio, F., et al. Multiple sclerosis fatigue relief by bilateral somatosensory cortex neuromodulation. Journal of neurology. 261, 1552-1558 (2014).
- Saiote, C., et al. Impact of transcranial direct current stimulation on fatigue in multiple sclerosis. Restorative neurology and neuroscience. 32, 423-436 (2014).
- Ferrucci, R., et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for fatigue in multiple sclerosis. NeuroRehabilitation. 34, 121-127 (2014).
- Cuypers, K., et al. Anodal tDCS increases corticospinal output and projection strength in multiple sclerosis. Neuroscience letters. 554, 151-155 (2013).
- Zanao, T. A., et al. Impact of two or less missing treatment sessions on tDCS clinical efficacy: results from a factorial, randomized, controlled trial in major depression. Neuromodulation : journal of the International Neuromodulation Society. 17, 737-742 (2014).
- Kurtzke, J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 33, 1444-1452 (1983).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。