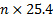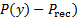射流撞击斜面板
Overview
资料来源: 里卡多梅希亚-阿尔瓦雷斯和 Hussam Hikmat, 密歇根州立大学机械工程系, 东兰辛, MI
本实验的目的是通过将动压转化为静压来证明流体流动对结构的作用力。为此, 我们将使一个平面射流撞击平板, 并将测量由此产生的压力分布沿板块。由此产生的力将通过在压力分布和适当定义的板块表面的面积差之间进行积分来估计。这一实验将重复的两个角度的板块倾斜的方向的喷气和两个流速。每个配置都产生不同的压力分布沿板块, 这是不同水平的结果, 动态压力转换为静态压力在板的表面。
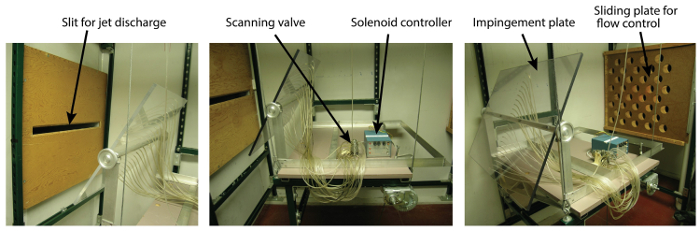
对于这个实验, 压力将测量与一个膜片压力传感器连接到一个扫描阀。该板本身有一个小穿孔称为压力水龙头, 通过软管连接到扫描阀。扫描阀将压力从这些水龙头传送到压力传感器一次。压力感应器转换成电压, 在膜片上产生机械偏转。这个电压与隔膜两侧的压差成正比。
Procedure
1. 设置设施
- 确保设施中没有流动。
- 根据图2中的示意图设置仪器。
- 将板调整为所需角度.
 在表1中记录此值。
在表1中记录此值。 - 测量喷嘴宽度W.在表1中记录此值。
- 测量板跨度L.在表1中记录此值。
- 零压力传感器。
- 注意压力传感器的校准常数, mp (Pa/V)。在表1中记录此值。
- 将传感器的高压端口 (标记为 +) 连接到压舱的压力分路器 (标记为).
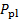
- 由于所有的操作都发生在接收器内, 所以将传感器的低压端口 (标记为-) 打开, 以感知接收器中的压力 ().
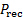
- 启动流量设备 (
Results
Application and Summary
References
- Arnau, A. (ed.). Piezoelectric transducers and applications. Vol. 2004. Heidelberg: Springer, 2004.
- Tropea, C., A.L. Yarin, and J.F. Foss. Springer handbook of experimental fluid mechanics. Vol. 1. Springer Science & Business Media, 2007.
- White, F. M. Fluid Mechanics, 7th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2009.
- Chapra, S.C. and R.P. Canale. Numerical methods for engineers. Vol. 2. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1998.
- Buckingham, E. Note on contraction coefficients of jets of gas. Journal of Research,6:765-775, 1931.
- Munson, B.R., D.F. Young, T.H. Okiishi. Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 5th ed., Wiley, 2006.
- Lienhard V, J.H. and J.H. Lienhard IV. Velocity coefficients for free jets from sharp-edged orifices. ASME Journal of Fluids Engineering, 106:13-17, 1984.
Tags
跳至...
此集合中的视频:

Now Playing
射流撞击斜面板
Mechanical Engineering
10.8K Views

浮力和拖曳在浸没的身体
Mechanical Engineering
30.1K Views

浮动容器的稳定性
Mechanical Engineering
22.6K Views

推进力和推力
Mechanical Engineering
21.8K Views

管道网络和压力损失
Mechanical Engineering
58.4K Views

淬火和沸腾
Mechanical Engineering
7.7K Views

液压跳跃
Mechanical Engineering
41.1K Views

换热器分析
Mechanical Engineering
28.0K Views

制冷概论
Mechanical Engineering
24.7K Views

热丝测速
Mechanical Engineering
15.6K Views

测量紊流
Mechanical Engineering
13.5K Views

通过钝体流的可视化
Mechanical Engineering
12.0K Views

系统分析中的能量守恒方法
Mechanical Engineering
7.4K Views

质量守恒和流速测量
Mechanical Engineering
22.7K Views

用控制容积法测定扁板的撞击力
Mechanical Engineering
26.0K Views
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。
 图 4中所示的点。
图 4中所示的点。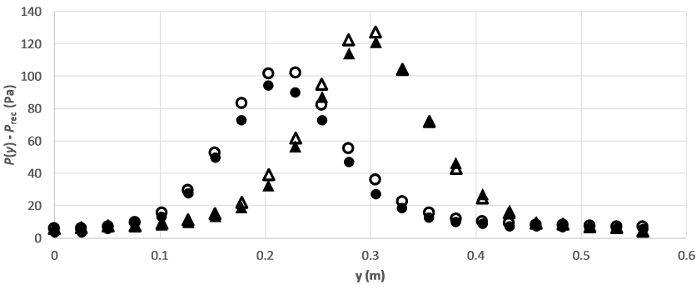
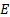 在表2中记录此值。
在表2中记录此值。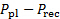 在表2中记录此值。
在表2中记录此值。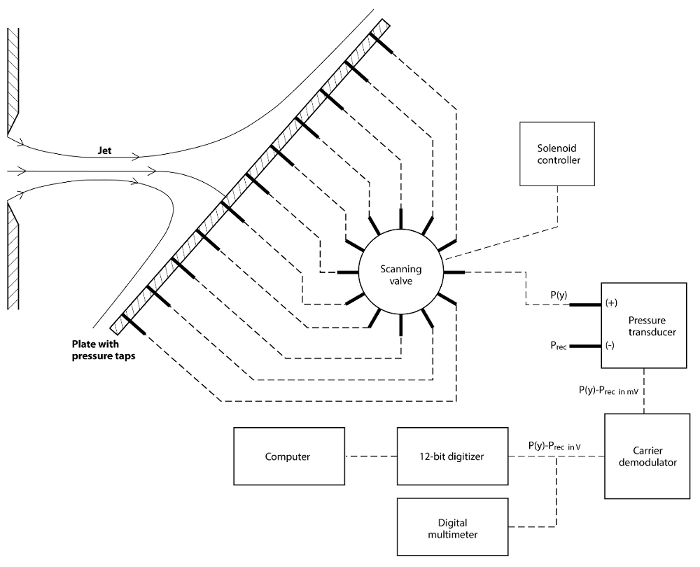
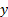 考虑到压力水龙头的间距是25.4mm。因此, 该位置将为 mm, 其中是从0开始的分路器的索引.
考虑到压力水龙头的间距是25.4mm。因此, 该位置将为 mm, 其中是从0开始的分路器的索引.