16.7 : Titration Calculations: Weak Acid - Strong Base
Calculating pH for Titration Solutions: Weak Acid/Strong Base
For the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M CH3CO2H with 0.100 M NaOH, the reaction can be represented as:
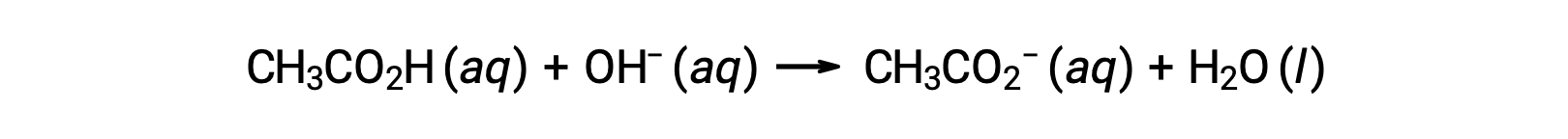
The pH of the titration solution after the addition of the different volumes of NaOH titrant can be calculated as follows:
(a) The initial pH is computed for the acetic acid solution in the usual ICE approach:
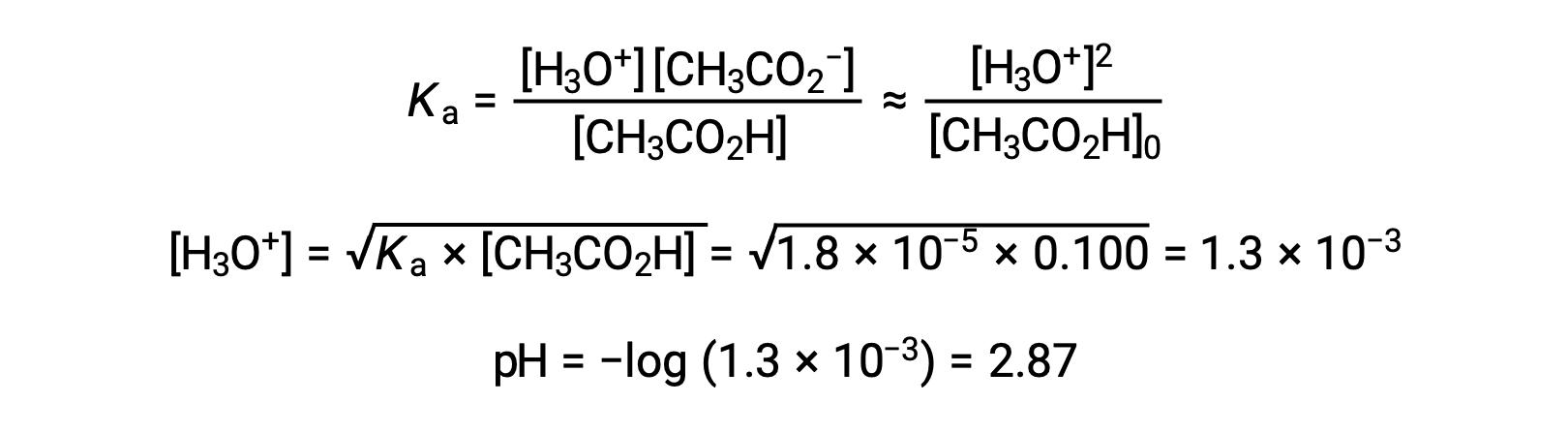
(b) The acid and titrant are both monoprotic and the sample and titrant solutions are equally concentrated; thus, this volume of titrant represents the equivalence point. Unlike the strong-acid example, the reaction mixture in this case contains a weak conjugate base (acetate ion). The solution pH is computed considering the base ionization of acetate, which is present at a concentration of
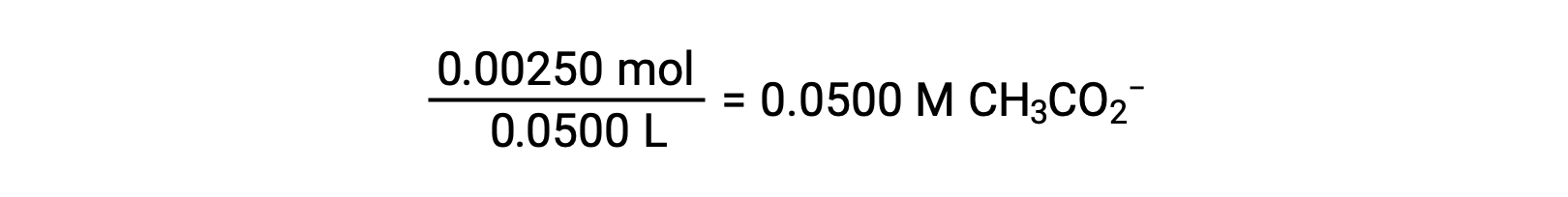
Base ionization of acetate is represented by the equation
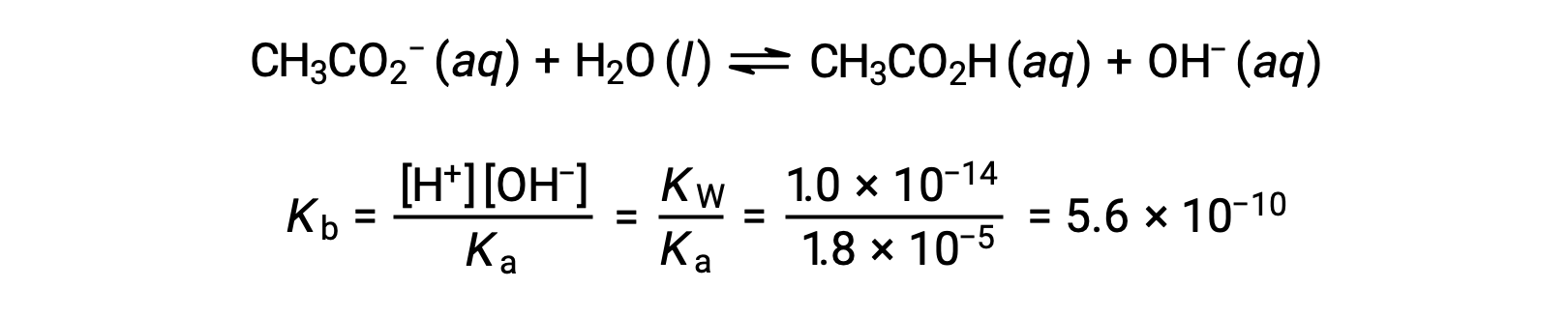
Assuming x << 0.0500, the pH may be calculated via the usual ICE approach:
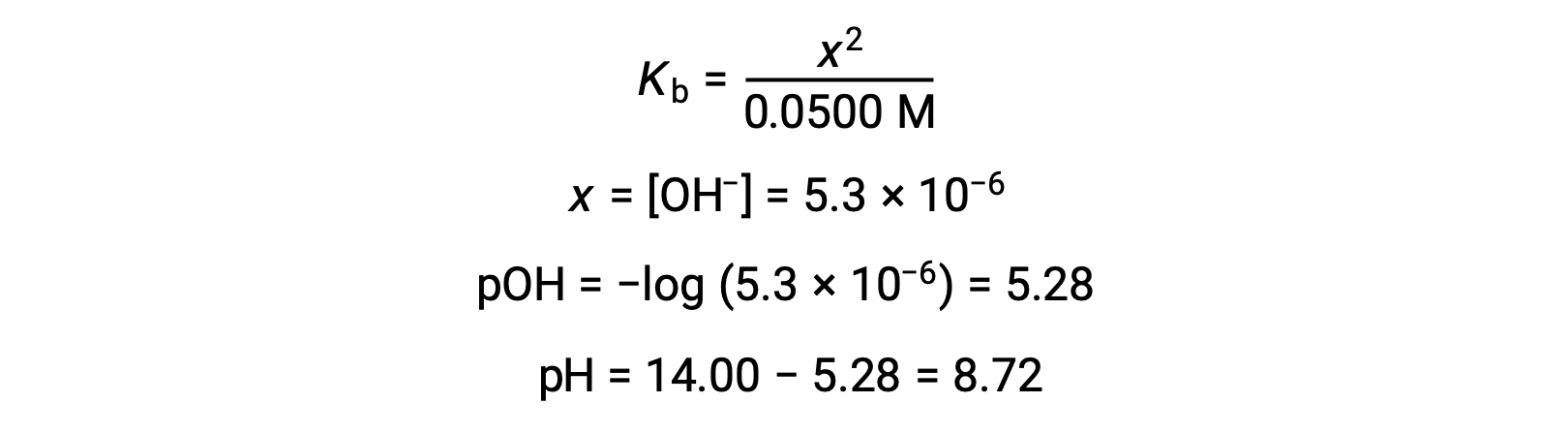
Note that the pH at the equivalence point of this titration is significantly greater than 7, as expected when titrating a weak acid with a strong base.
(c) Titrant volume = 12.50 mL. This volume represents one-half of the stoichiometric amount of titrant, and so one-half of the acetic acid has been neutralized to yield an equivalent amount of acetate ion. The concentrations of these conjugate acid-base partners, therefore, are equal. A convenient approach to computing the pH is use of the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
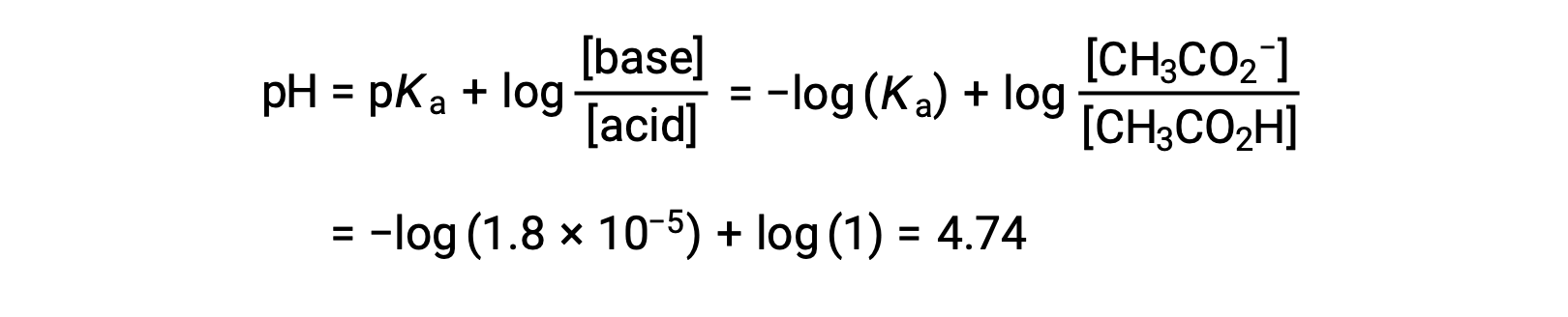
(pH = pKa at the half-equivalence point in a titration of a weak acid)
(d) Titrant volume = 37.50 mL. This volume represents a stoichiometric excess of titrant, and a reaction solution containing both the titration product, acetate ion, and the excess strong titrant. In such solutions, the solution pH is determined primarily by the amount of excess strong base:

This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.7: Acid-base Titrations.
Aus Kapitel 16:

Now Playing
16.7 : Titration Calculations: Weak Acid - Strong Base
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
43.8K Ansichten

16.1 : Gemeinsamer Ioneneffekt
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
41.0K Ansichten

16.2 : Puffer
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
163.5K Ansichten

16.3 : Henderson-Hasselbalch-Gleichung
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
68.2K Ansichten

16.4 : Berechnung von pH-Änderungen in einer Pufferlösung
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
52.7K Ansichten

16.5 : Wirksamkeit des Puffers
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
48.5K Ansichten

16.6 : Titrationsberechnungen: Starke Säure - Starke Base
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
29.0K Ansichten

16.8 : Indikatoren
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
47.8K Ansichten

16.9 : Titration einer polyprotischen Säure
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
95.7K Ansichten

16.10 : Löslichkeits-Gleichgewichte
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
52.0K Ansichten

16.11 : Faktoren, die die Löslichkeit beeinflussen
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
33.0K Ansichten

16.12 : Bildung komplexer Ionen
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
23.2K Ansichten

16.13 : Ausfällung von Ionen
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
27.6K Ansichten

16.14 : Qualitative Analyse
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
21.5K Ansichten

16.15 : Säure-Base-Titrationskurven
Säure-Base- und Löslichkeitsgleichgewicht
126.5K Ansichten
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten