17.5 : Standard Entropy Change for a Reaction
Entropy is a state function, so the standard entropy change for a chemical reaction (ΔS°rxn) can be calculated from the difference in standard entropy between the products and the reactants.
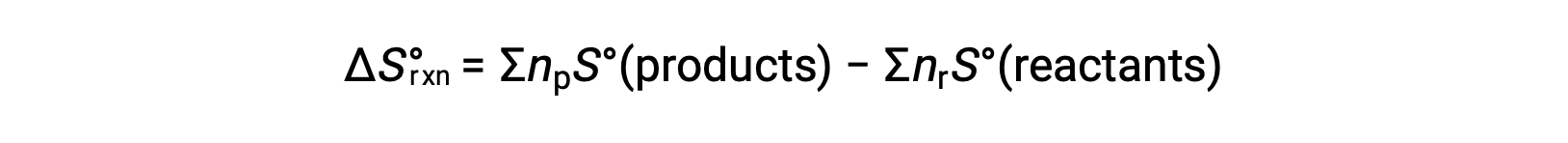
where np and nr represent the stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced equation of the products and reactants, respectively.
For example, ΔS°rxn for the following reaction at room temperature
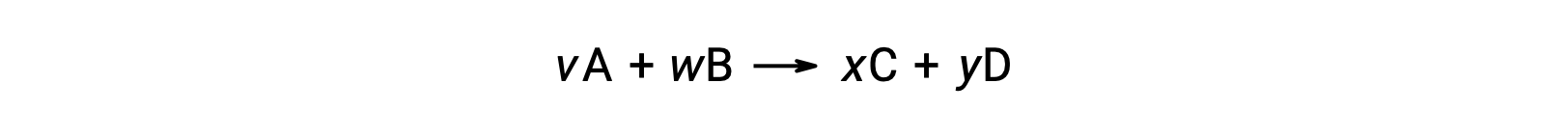
is computed as follows:
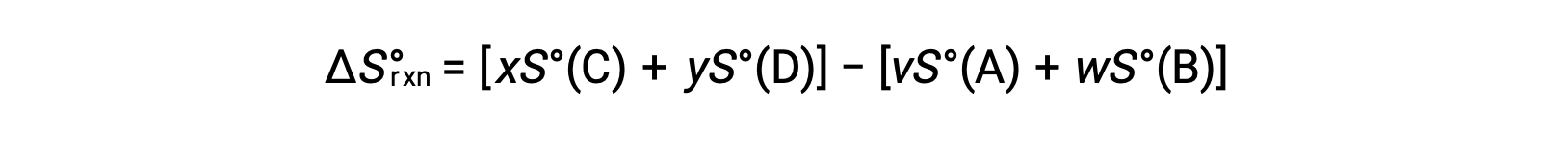
A partial listing of standard entropies is provided in the table.
| Substance | S° (J/mol·K) |
| C (s, graphite) | 5.740 |
| C (s, diamond) | 2.38 |
| CO (g) | 197.7 |
| CO2 (g) | 213.8 |
| CH4 (g) | 186.3 |
| C2H4 (g) | 219.5 |
| C2H6 (g) | 229.5 |
| CH3OH (l) | 126.8 |
| C2H5OH (l) | 160.7 |
| H2 (g) | 130.57 |
| H (g) | 114.6 |
| H2O (g) | 188.71 |
| H2O (l) | 69.91 |
| HCI (g) | 186.8 |
| H2S (g) | 205.7 |
| O2 (g) | 205.03 |
Determination of ΔS°
Consider the condensation of water, in which 1 mole of gaseous H2O changes into 1 mole of liquid H2O.
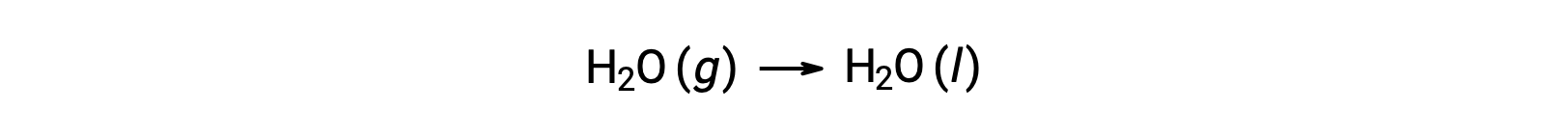
The standard entropy changes for the reaction, ΔS°rxn is calculated using the standard molar entropies and stoichiometric coefficients.
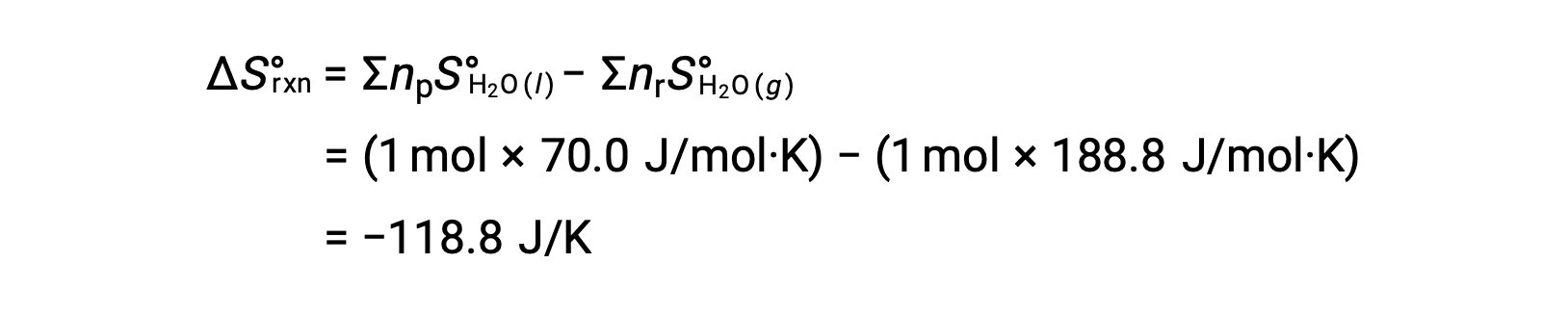
The value for ΔS°rxn is negative, as expected for this phase transition (condensation).
As a second example, consider the combustion of methanol, CH3OH:
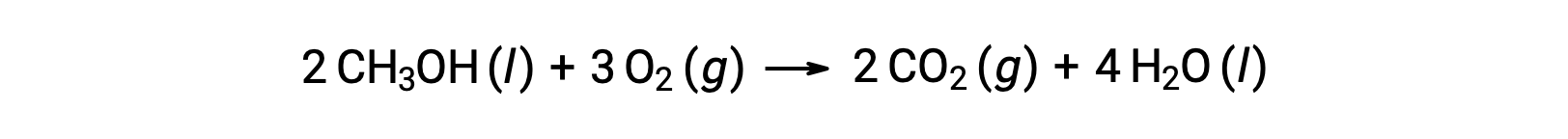
The same procedure is followed to calculate the standard entropy change of the reaction:
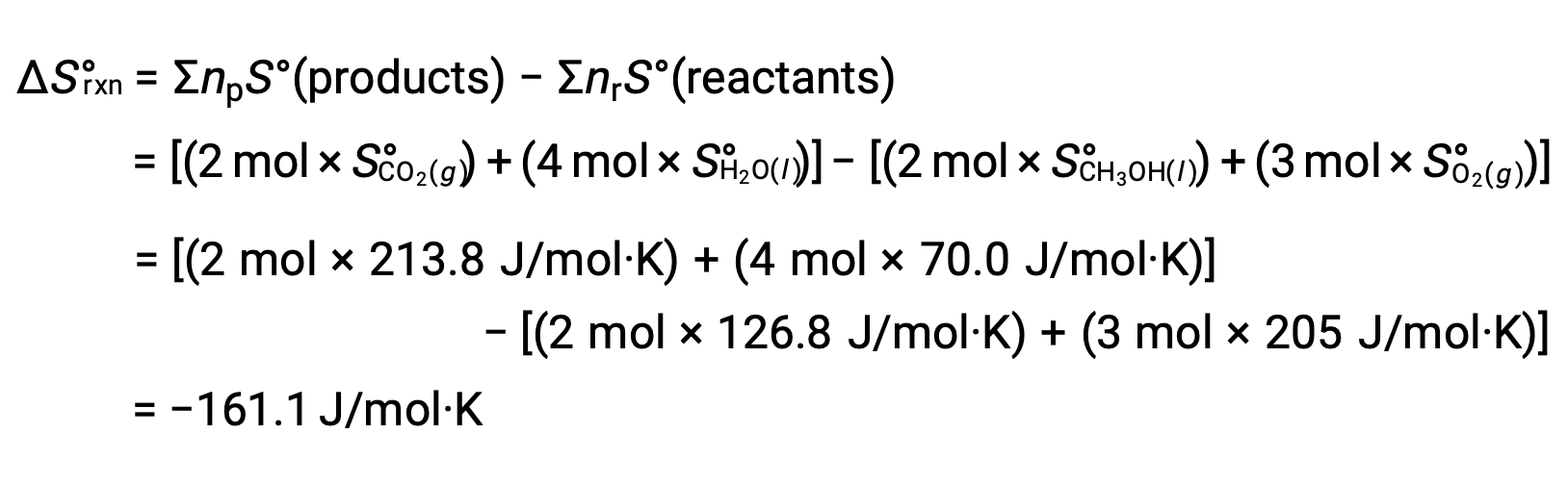
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 16.2: The Second and Third Law of Thermodynamics.
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten