10.10 : Momentos de inercia de objetos compuestos
The moment of inertia is a quantitative measure of the rotational inertia of an object. It is defined as the sum of the products obtained by multiplying the mass of each particle of matter in a given body by the square of its distance from the axis. The total moment of inertia for compound objects can be found by determining and adding the moment of inertia of individual components together.
Consider a child of mass (mc) 25 kg standing at a distance (rc) of 1 m from the axis of a rotating merry-go-round. The merry-go-round is approximated as a uniform solid disk with a mass (mm) of 500 kg and a radius (rm) of 2 m. Find the moment of inertia of the compound system.
The total moment of inertia of the system can be determined by adding up the individual moments of inertia of the merry-go-round and the child rotating on the axis. Since the mass and size of the child are much smaller than the merry-go-round, the child can be considered as a point mass.
- The moment of inertia (I) for the child is calculated as
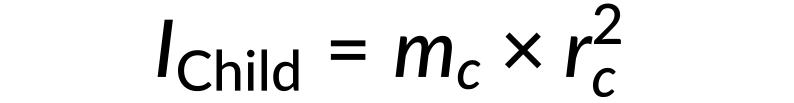
- The moment of inertia (I) for the merry-go-round is calculated as
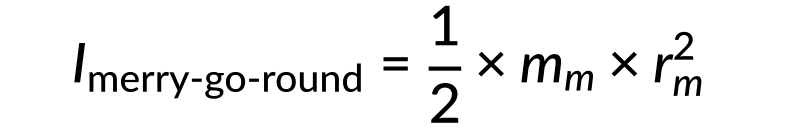
- By substituting and adding both values, the total moment of inertia of the system is determined to be 1025 kg⋅m2.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 10.5: Calculating Moments of Inertia.
Del capítulo 10:

Now Playing
10.10 : Momentos de inercia de objetos compuestos
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
6.1K Vistas

10.1 : Velocidad angular y desplazamiento
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
15.0K Vistas

10.2 : Velocidad angular y aceleración
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
9.0K Vistas

10.3 : Rotación con aceleración angular constante - I
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
6.7K Vistas

10.4 : Rotación con aceleración angular constante - II
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
5.9K Vistas

10.5 : Relacionando magnitudes angulares y lineales - I
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
6.5K Vistas

10.6 : Relacionando magnitudes angulares y lineales - II
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
5.4K Vistas

10.7 : Momento de inercia
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
11.9K Vistas

10.8 : Momento de inercia y energía cinética rotacional
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
7.3K Vistas

10.9 : Momento de inercia: cálculos
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
6.7K Vistas

10.11 : Teorema de los ejes paralelos
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
6.4K Vistas

10.12 : Teorema del eje perpendicular
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
2.7K Vistas

10.13 : Transformación vectorial en sistemas de coordenadas rotatorias
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
1.5K Vistas

10.14 : Fuerza de Coriolis
Rotación y cuerpos rígidos
3.1K Vistas
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados