Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Method Article
Visualización de zonas de productividad basadas en el modelo de balance de masa de nitrógeno en la bahía de Narragansett, Rhode Island
En este artículo
Resumen
Aquí, nuestro objetivo es visualizar la zonificación de la productividad biológica en la bahía de Narragansett, Rhode Island, con base en el modelo de balance de masa de nitrógeno. Los resultados servirán de base para la gestión de nutrientes en las regiones costeras para reducir la hipoxia y la eutrofización.
Resumen
La productividad primaria en las regiones costeras, vinculada a la eutrofización y la hipoxia, proporciona una comprensión crítica de la función de los ecosistemas. Aunque la productividad primaria depende en gran medida de los aportes de nutrientes fluviales, la estimación del alcance de las influencias de los nutrientes fluviales en las regiones costeras es difícil. Un modelo de balance de masa de nitrógeno es una herramienta práctica para evaluar la productividad de los océanos costeros con el fin de comprender los mecanismos biológicos más allá de las observaciones de datos. Este estudio visualiza las zonas de producción biológica en la bahía de Narragansett, Rhode Island, EE.UU., donde ocurre frecuentemente la hipoxia, mediante la aplicación de un modelo de balance de masa de nitrógeno. La bahía está dividida en tres zonas: marrón, verde y azul, en función de la productividad primaria, que se define por los resultados del modelo de balance de masas. Las zonas marrón, verde y azul representan un proceso físico alto, un proceso biológico alto y una zona de proceso biológico bajo, dependiendo del flujo del río, las concentraciones de nutrientes y las tasas de mezcla. Los resultados de este estudio pueden informar mejor sobre la gestión de nutrientes en el océano costero en respuesta a la hipoxia y la eutrofización.
Introducción
La productividad primaria, la producción de compuestos orgánicos por el fitoplancton, alimenta las redes tróficas de los ecosistemas y es importante para comprender la función del sistema en respuesta a los cambios ambientales 1,2. La productividad primaria de los estuarios también está estrechamente relacionada con la eutrofización, que se define como un exceso de nutrientes en el ecosistema1, lo que provoca varias consecuencias nocivas en las regiones costeras, como un crecimiento excesivo de fitoplancton que conduce a grandes floraciones de algas y la consiguiente hipoxia 3,4. Es importante destacar que la productividad primaria en los estuarios depende en gran medida de la carga de nutrientes fluviales, en particular de las concentraciones de nitrógeno, que son el nutriente limitante típico en la mayoría de los ecosistemas oceánicos templados 5,6. Sin embargo, sigue siendo difícil estimar la magnitud de los impactos del nitrógeno fluvial en las zonas costeras.
Para estimar la productividad primaria estuarina, un modelo de balance de masa de nitrógeno (N) es una herramienta útil para calcular los flujos de nitrógeno2. El modelo de balance de masa N también proporciona una comprensión de los mecanismos biológicos más allá de las observaciones de datos, revelando información en los bordes de diferentes zonas de productividad primaria7. Treszonas 8 diferentes, definidas como zonas marrón, verde y azul, son particularmente útiles para predecir el impacto de la carga de nutrientes en las regiones hipóxicas. La zona marrón, definida como la región más cercana de la desembocadura de un río, representa un proceso físico alto, la zona verde tiene una alta productividad biológica y la zona azul representa un proceso biológico bajo. El límite de cada zona depende del caudal del río, las concentraciones de nutrientes y las tasas de mezcla8.
La bahía de Narragansett (NB) es un estuario costero templado en Rhode Island, EE.UU., que soporta servicios y bienes económicos y ecológicos 9,10,11, en el que la hipoxia ha estado ocurriendo constantemente. Estos eventos hipóxicos, definidos como el período de bajo oxígeno disuelto (es decir, menos de 2-3 mg de oxígeno por litro), son particularmente prevalentes en julio y agosto y se ven fuertemente afectados por la carga de nitrógeno fluvial durante estos meses12. Con el aumento de la producción primaria y la hipoxia debido a las emisiones antropogénicas de nutrientes13, la comprensión de los aportes de nitrógeno en el NB es fundamental para gestionar y abordar problemas costeros como la eutrofización y la hipoxia. Por lo tanto, en este estudio, la tasa de producción primaria en NB se calcula a partir del modelo de balance de masa N utilizando datos de nutrientes observados históricamente, especialmente nitrógeno inorgánico disuelto (DIN). Con base en los resultados del modelo de balance de masa N mediante la conversión a unidades de carbono utilizando la relación Redfield, se identificaron tres zonas de productividad primaria diferentes para visualizar el alcance de la influencia del nitrógeno del río en NB. A continuación, el modelo se recreó en una representación 3D para visualizar mejor las diferentes zonas. Los productos producidos a partir de este estudio pueden informar mejor sobre el manejo de nutrientes en RN en respuesta a la hipoxia y la eutrofización. Además, los resultados de este estudio son aplicables a otras regiones costeras para visualizar los efectos del transporte fluvial sobre los nutrientes y la productividad primaria.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocolo
1. Aplicación del modelo de balance de masa N
- Descargue los datos de nitrógeno inorgánico disuelto (DIN) de la Agencia de Protección Ambiental de EE. UU. (USEPA) para 166 estaciones en la bahía de Narragansett desde 1990 hasta 2015.
NOTA: En este estudio, la suma de las concentraciones de amonio (NH4+), nitrito (NO2-) y nitrato (NO3-) se consideró como la concentración DIN. - Dividir la bahía de Narragansett en quince cuadros a lo largo de su eje, modificados del estudio anterior14 , utilizando Adobe Illustrator para dividir la bahía en el mapa (Figura 1).
- Aplique el modelo de balance de masa N para calcular la concentración media de DIN en cada caja.
NOTA: En este estudio, el modelo de balance de N-masa, que consiste en términos DIN de entrada y salida, se modificó a partir de estudios previos 2,15 y se aplicó a cada caja (1-15) de la bahía de Narragansett como Ecuación 1.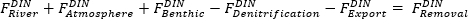 Ec. (1)
Ec. (1)
En la Tabla 1 se muestran las definiciones de cada término y unidad utilizados en este modelo de la bahía de Narragansett. El modelo calcula la concentración media de DIN determinando la diferencia en cada caja de la bahía de Narragansett, que representa la eliminación neta de DIN por producción biológica. En los estudios previos se muestra información detallada sobre el modelo de balance de masa N 2,15. Los valores detallados utilizados en el modelo de este estudio se derivaron de los estudios previos14. - Calcule la tasa de producción primaria potencial (PPA) en función de los resultados del modelo de balance de masa N convirtiendo la eliminación neta de DIN en unidades de carbono utilizando la relación Redfield (C: N = 106: 16, relación molar) en un archivo de hoja de cálculo.
2. Visualización de tres zonas en el mapa de la bahía de Narragansett
- Trazar las tres zonas identificadas en el mapa de la bahía de Narragansett como una curva de nivel utilizando el software Ocean Data View.
- Guarde los datos de la tasa PPA de cada cuadro como un archivo de texto (.txt) del archivo de hoja de cálculo.
NOTA: El archivo .txt también incluye la ubicación de cada número de caja como latitud y longitud. Ponga la longitud como un valor negativo. Los datos de la tasa de PPA se etiquetan como PPA [gC·m-2·día-1]. - Cargue los datos de la tasa de PPP en el software Ocean Data View.
- Vaya a abrir en el menú Archivo .
- Haga clic en el cuadro Asociar variables, Latitud, Longitud con P.K., latitud [degrees_north] y Longitud [degrees_east] en la ventana Asociación de variables de metadatos y, a continuación, haga clic en el botón Aceptar .
- Haga clic en el botón Aceptar en la ventana Importar .
- Dibuje la gráfica de contorno para mostrar los rangos de PPP en el mapa de la bahía de Narragansett.
- Haga clic con el botón derecho en el mapa, haga clic en Zoom, arrastre el cuadro rojo para hacer zoom en el área de datos del mapa y, a continuación, haga clic en Entrar.
- Haga clic en la ventana 1 SCATTER de las Plantillas de diseño en el menú Ver .
- Haga clic con el botón derecho en el panel Ejemplo y seleccione Variables derivadas.
- Haga clic en el botón Agregar después de seleccionar Latitud en Metadatos en la lista de opciones del panel. Haga lo mismo para Longitud y luego haga clic en el botón Aceptar .
- Seleccione drvd: Longitud [degrees_East] como X-Variable haciendo clic con el botón derecho en la ventana de dispersión.
- Seleccione drvd: Latitud [degrees_North] como Variable Y haciendo clic con el botón derecho en la ventana de dispersión.
- Seleccione PPP [gC·m-2·day -1] como Variable Z haciendo clic con el botón derecho en la ventana de dispersión.
- Seleccione Propiedades haciendo clic con el botón derecho en la ventana de dispersión y vaya a la opción Estilo de visualización .
- Seleccione el campo Cuadrícula.
- Vaya a la opción Contornos y haga clic en el botón << para que los valores 0, 0.1 y 2 solo permanezcan en los paneles ya definidos de la izquierda.
- Haga clic en el botón Aceptar .
- Guarde los datos de la tasa PPA de cada cuadro como un archivo de texto (.txt) del archivo de hoja de cálculo.
- Basándose en el gráfico de contorno del software Ocean Data View, defina el borde de las zonas marrón, verde y azul de la bahía de Narraganset y visualice las zonas con Adobe Illustrator para trazar tres zonas en el mapa.
NOTA: Siguiendo el estudio previo15, la tasa de PPA de la zona marrón fue superior a 2 gC·m-2·día-1, la zona verde estuvo entre 0,1-2 gC·m-2·día-1 y la zona azul fue inferior a 0,1 gC·m-2·día-1, respectivamente.
3. Convertir el gráfico de contorno de tres zonas en el marco tridimensional (3D) con luz LED
- Grabe tres paneles acrílicos de 5,5 '' x 8 '' con una cortadora láser para mostrar el límite de cada zona.
- Apila tres paneles acrílicos en un marco iluminado. Superponga cada panel acrílico mostrando las zonas azul, verde y marrón. Coloque un panel que muestre las zonas verdes encima del panel de zonas azules y un panel de zonas marrones encima.
- Para el segundo modelo físico, grabe cuatro láminas acrílicas de 5,5'' x 8'' con una cortadora láser, con los tres límites de zonas impresos por UV y un panel para representar toda la bahía de Narragansett (según los pasos 3.1-3.2).
- Cambia el color de cada zona a marrón, verde y azul usando los LED colocados en la parte inferior del marco.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Resultados
Tres zonas teóricas de la bahía de Narragansett basadas en el modelo de balance de masa N
Las tres zonas teóricas de la bahía de Narragansett (NB) se definieron con base en los resultados del modelo de balance de masa N, en el que los datos DIN se aplicaron a quince cajas de NB, y luego el DIN medio en cada caja se convirtió a las tasas de PPA para el período estival. Como se muestra en la Figura 2, con base en las tasas medias de PPA de verano (junio a septiembre) ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discusión
Este estudio estimó el alcance de los impactos de nutrientes de los insumos fluviales en la bahía de Narraganset (NB) con base en el modelo de balance de masa N mediante la definición de las tres zonas teóricas. Históricamente, las zonas hipóxicas aparecieron cerca del río Providence, el lado occidental de la bahía de Greenwich y la bahía de Mount Hope durante el período de verano18, que se definieron como zonas marrones en este estudio. Además, la zonificación de la RN es comparable a...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Divulgaciones
Los autores no tienen conflictos de intereses que declarar.
Agradecimientos
Este estudio contó con el apoyo de la National Science Foundation (OIA-1655221, OCE-1655686) y Rhode Island Sea Grant (NA22-OAR4170123, RISG22-R/2223-95-5-U). También nos gustaría agradecer a la Escuela de Diseño de Rhode Island por desarrollar el proyecto Vis-A-Thon y esta visualización.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Adobe Illustrator | Adobe | version 27.6.1 | https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator.html |
| Ampersand Gessobord Uncradled 1/8" Profile 8" x 8" | Risdstore | 70731053088 | https://www.risdstore.com/ampersand-gessobord-8x8-flat-1-8-profile.html |
| Ocean Data View software | https://odv.awi.de/en/software/download/ | ||
| W-Series (Wide) Flexible LED Strip Light - Ultra Bright (18 LEDs/foot) | aspectLED | SKU AL-SL-W-U | https://www.aspectled.com/products/w-wide-5050-ultra-bright?gclid=CjwKCAjwm4ukBhAuEiwA0z QxkyqisRPqBcHvXEW8KcJE-bK0d2cvGtqlOxXWJI_ E2rd6DzttPR0FLRoCgfkQAvD_BwE |
Referencias
- Nixon, S. W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia. 41, 199-219 (1995).
- Kim, J. S., Brush, M. J., Song, B., Anderson, I. C. Reconstructing primary production in a changing estuary: A mass balance modeling approach. Limnology and Oceanography. 66 (6), 2535-2546 (2021).
- Kemp, W. M., et al. Eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay: historical trends and ecological interactions. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 303, 1-29 (2005).
- Brush, M. J., et al. American Geophysical Union. Coastal Ecosystems in Transition: A Comparative Analysis of the Northern Adriatic and Chesapeake Bay. Malone, T. C., Malej, A., Faganeli, F. Chapter 5, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ. (2021).
- Howarth, R. W., Marino, R. Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Evolving views over three decades. Limnology and Oceanography. 51 (1 part 2), 364-376 (2006).
- Paerl, H. W. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater-marine continuum: Dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries and Coasts. 32, 593-601 (2009).
- Kim, J. S., Chapman, P., Rowe, G., DiMarco, S. F. Categorizing zonal productivity on the continental shelf with nutrient-salinity ratios. Journal of Marine Systems. 206, 103336(2020).
- Rowe, G. T., Chapman, P. Continental shelf hypoxia: Some nagging questions. Gulf of Mexico Science. 20 (2), 153-160 (2002).
- Nixon, S. W. Eutrophication and the macroscope. Hydrobiologia. 629, 5-19 (2009).
- Barbier, E. B., et al. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecological Monographs. 81 (2), 169-193 (2011).
- Cloern, J. E., Foster, S. Q., Kleckner, A. E. Phytoplankton primary production in the world's estuarinecoastal ecosystem. Biogeosciences. 11 (9), 2477-2501 (2014).
- Codiga, D. L., Stoffel, H. E., Oviatt, C. A., Schmidt, C. E. Managed nitrogen load decrease reduces chlorophyll and hypoxia in warming temperate urban estuary. Frontiers in Marine Science. 9, 930347(2022).
- Sigman, D. M., Hain, M. P. The biological productivity of the ocean. Nature Education Knowledge. 3 (10), 21(2012).
- Kremer, J. N., et al. Simulating property exchange in estuarine ecosystem models at ecologically appropriate scales. Ecological Modelling. 221 (7), 1080-1088 (2010).
- Kim, J. S., Chapman, P., Rowe, G., DiMarco, S. F., Thornton, D. C. O. Implications of different nitrogen input sources for potential production and carbon flux estimates in the coastal Gulf of Mexico (GOM) and Korean Peninsula coastal waters. Ocean Science. 16, 45-63 (2020).
- Lake, S. J., Brush, M. J. The contribution of microphytobenthos to total productivity in upper Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 95 (2-3), 289-297 (2011).
- Brush, M. J., Nixon, S. W. Modeling the role of macroalgae in a shallow sub-estuary of Narragansett Bay, RI (USA). Ecological Modelling. 221 (7), 1065-1079 (2010).
- Deacutis, C. F., Murray, D., Prell, W., Saarman, E., Korhun, L. Hypoxia in the upper half of Narragansett Bay, RI, during August 2001 and 2002. Northeastern Naturalist. 13 (Special Issue 4), 173-198 (2006).
- Oviatt, C., et al. Managed nutrient reduction impacts on nutrient concentrations, water clarity, primary production, and hypoxia in a north temperate estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 199, 25-34 (2017).
- Boesch, D. F. Barriers and bridges in abating coastal eutrophication. Frontiers in Marine Science. 6, 123(2019).
- Oviatt, C. A., Keller, A. A., Reed, L. Annual primary production in Narragansett Bay with no bay-wide winter-spring phytoplankton bloom. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 54, 1013-1026 (2002).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados