Descodificación de imágenes auditivas con análisis Multivoxel
Visión general
Fuente: Laboratorios de Jonas T. Kaplan y Sarah I. Gimbel, University of Southern California
Imagine el sonido de un timbre de campana. ¿Lo que está sucediendo en el cerebro cuando nos evocan un sonido como este en el "oído de la mente"? Hay creciente evidencia de que el cerebro utiliza los mismos mecanismos de imaginación que utiliza para la percepción. 1 por ejemplo, al imaginar imágenes visuales, se activa la corteza visual, y cuando imaginar sonidos, la corteza auditiva se dedica. Sin embargo, ¿hasta qué punto son estas activaciones de cortezas sensoriales específicas al contenido de nuestra imaginación?
Una técnica que puede ayudar a responder a esta pregunta es multivoxel análisis (MPVA), en cuyas imágenes funcionales del cerebro se analizan utilizando técnicas de aprendizaje máquina. 2-3 experimento en un MPVA, formamos un algoritmo de aprendizaje automático para distinguir entre los diferentes patrones de actividad evocada por estímulos diferentes. Por ejemplo, nos podríamos preguntar si imaginar el sonido de una campana produce diferentes patrones de actividad en la corteza auditiva en comparación con imaginando el sonido de una motosierra, o el sonido de un violín. Si nuestro clasificador aprende a diferenciar los patrones de actividad cerebral producidos por estos tres estímulos, entonces podemos concluir que la corteza auditiva se activa de forma distinta por cada estímulo. Una forma de pensar de este tipo de experimento es que en lugar de preguntar simplemente sobre la actividad de una región del cerebro, nos pregunta sobre el contenido de información de la región.
En este experimento, basado en Meyer et al., 2010,4 nos se cue los participantes a imaginar varios sonidos presentándoles videos silencio suelen evocar imágenes auditivas. Ya que estamos interesados en la medición de los patrones sutiles evocados por la imaginación en la corteza auditiva, es preferible si los estímulos se presentan en completo silencio, sin la interferencia de los ruidos hechos por el escáner de fMRI. Para lograr esto, usaremos un tipo especial de secuencia de MRI funcional conocida como escaso muestreo temporal. En este enfoque, un volumen único fMRI es adquirido 4-5 s después de cada estímulo, para capturar el pico de la respuesta hemodinámica.
Procedimiento
1. participante reclutamiento
- Reclutar a 20 participantes.
- Los participantes deben ser diestros y no tienen antecedentes de trastornos neurológicos o psicológicos.
- Los participantes deben tener visión normal o corregida a normal para que sean capaces de ver los indicios visuales correctamente.
- Los participantes no deben tener metal en su cuerpo. Se trata de un requisito de seguridad debido al alto campo magnético en fMRI.
- Participantes no debe sufrir de claustrofobia, ya que el fMRI requiere tumbado en el pequeño espacio del escáner del alesaje.
2. analizar los procedimientos
- Llenar papeleo de exploración previa.
- Cuando los participantes su análisis de fMRI, indíqueles que primero llene una forma metálica para asegurarse de que no tienen ninguna contra indicación para MRI, forma hallazgos INCIDENTALES, dar su consentimiento para su exploración a ser analizado por un radiólogo y un formulario de consentimiento que detalla los riesgos y beneficios del estudio.
- Preparar a los participantes a ir en el explorador al quitar todo el metal de su cuerpo, incluyendo cinturones, carteras, teléfonos, hebillas, monedas y todas las joyas.
3. proporcionar instrucciones para el participante.
- Dígale a los participantes a que vean una serie de varios videos cortos dentro del esc‡ner. Estos videos serán silencios, pero pueden evocar un sonido en su "oído de la mente". Pregunte al participante centrarse en y fomentar estas imágenes auditivas, para tratar de "escuchar" el sonido de lo mejor que pueden.
- Estrés al participante la importancia de mantener su cabeza todavía a lo largo de la exploración.
4. poner al participante en el escáner.
- Dar al participante tapones para proteger sus oídos del ruido de los teléfonos escáner y oído usar para que puedan escuchar al experimentador durante la exploración y tenerlas tumbadas en la cama con su cabeza en la bobina.
- Dar al participante la bola del apretón emergencia e instruirlos para apretar en caso de emergencia durante la exploración.
- Use almohadillas de espuma para garantizar a los participantes la cabeza en la bobina para evitar exceso de movimiento durante la exploración y recordar al participante que es muy importante que permanezca todavía como posible durante la exploración, como incluso el más pequeño desenfoque de movimientos las imágenes.
5. recolección de datos
- Recoger la exploración anatómica de alta resolución.
- Comenzar la exploración funcional.
- Sincronizar el inicio de la presentación del estímulo con el inicio del escáner.
- Para lograr el escaso muestreo temporal, establecer el tiempo de la adquisición de un volumen de MRI a 2 s, con un retraso de 9 s entre adquisiciones de volumen.
- Presente los videos silenciosa a través de un ordenador portátil conectados a un proyector. El participante tiene un espejo por encima de sus ojos, lo que refleja que una pantalla en la parte posterior del escáner del alesaje.
- Sincronizar el inicio de cada clip de vídeo de 5-s para iniciar 4 s después de la adquisición anterior de MRI se inicia. Esto asegurará que el siguiente volumen de MRI es adquirido 7 s después del comienzo del videoclip, para capturar la actividad hemodinámica que corresponde a la mitad de la película.
- Presentar tres diferentes videos silenciosos que evocan imágenes auditivas vivas: una campana que hace pivotar hacia adelante y hacia atrás, un corte de la motosierra a través de un árbol y una persona tocando un violín.
- En cada exploración funcional, presentar cada video 10 veces, en orden aleatorio. Cada ensayo dura 11 s, esto resultará en una exploración 330 s (5,5 min) largo.
- Realizar el análisis funcionales 4.
6. Análisis de datos
- Definir una región de interés (ROI).
- Utilice la exploración anatómica de alta resolución de cada participante para rastrear los vóxeles que corresponden a la corteza auditiva temprana (figura 1). Esto corresponde a la superficie del lóbulo temporal, llamado el planum temporale. Utilice las características anatómicas del cerebro de cada persona para crear una máscara específica para su corteza auditiva.
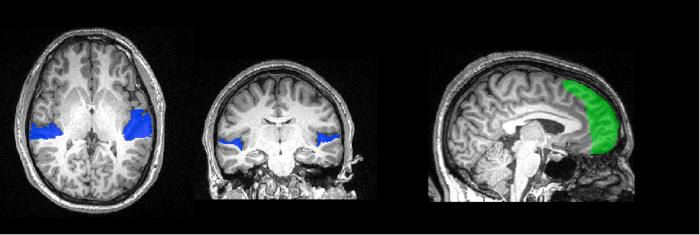
Figura 1: región de localización de interés. La superficie del planum temporale ha sido trazada en alta resolución imagen anatómica de este participante y a continuación se muestra en azul. En verde es la mascara del poste frontal. Estos vóxeles se utilizará para el análisis de la MVPA.
- Procesamiento previo de los datos.
- Realizar corrección de movimiento para reducir artefactos de movimiento.
- Realizar el filtrado temporal para quitar señal derivas.
- Entrenar y probar el algoritmo clasificador.
- Dividir los datos de entrenamiento y pruebas de sistemas. Datos de entrenamiento se utilizarán para entrenar el clasificador, y los datos de prueba de salida de la izquierda se utilizará para evaluar lo ha aprendido. Para maximizar la independencia de la formación y datos de prueba, deje los datos de una exploración funcional como el conjunto de pruebas.
- Entrenar un algoritmo de máquina de Vector de apoyo en los datos de marcada formación de la corteza auditiva en cada tema. Evaluar capacidad de clasificador de adivinar correctamente la identidad del conjunto de pruebas sin etiqueta y registrar precisión del clasificador.
- Repetir este procedimiento 4 veces, dejando de lado cada análisis como datos de prueba cada vez. Este tipo de procedimiento, en el que cada sección de los datos queda hacia fuera una vez, se denomina validación cruzada.
- Combinar exactitudes de clasificador a través de los 4 pliegues de validación cruzada por un promedio de.
- La prueba estadística
- Para determinar si el clasificador realiza mejor que oportunidad (33%), podemos comparar resultados a nivel de grupo al azar. Para ello, se reúnen las exactitudes de cada materia y prueba que la distribución es diferente de la posibilidad de usar una prueba no paramétrica de Wilcoxon Signed-Rank.
- También podemos preguntar si el clasificador realiza mejor que oportunidad para cada individuo. Para determinar la probabilidad de que un nivel dado de exactitud en datos oportunidad, crear una distribución nula capacitación y probando el algoritmo MVPA en datos cuya etiqueta ha sido barajada al azar. Permutar las etiquetas 10.000 veces para crear una distribución nula de valores de exactitud y luego comparar el valor de la precisión real a esta distribución.
- Para demostrar la especificidad de la información dentro de la corteza auditiva, podemos entrenar y prueba el clasificador en vóxeles desde una ubicación diferente en el cerebro. Aquí, utilizamos una máscara del polo frontal, tomado de un atlas probabilístico y deformado para cerebro individual del cada sujeto.
Resultados
La precisión del clasificador promedio en el planum temporale en todos los 20 participantes fue del 59%. Según el test de Wilcoxon Signed-Rank, esto es significativamente diferente del nivel de probabilidad del 33%. El rendimiento medio de la máscara frontal del poste fue 32,5%, que no es mayor que la probabilidad (Figura 2).
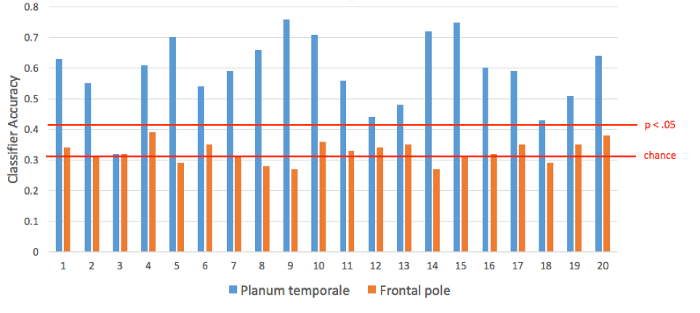
Figura 2. Rendimiento de la clasificación en cada participante. Para la clasificación de tres vías, funcionamiento de oportunidad es del 33%. Según una prueba de la permutación, el nivel alfa de p < 0.05 corresponde al 42%.
La prueba de permutación encontró que sólo el 5% de las permutaciones alcanzado exactitud superior al 42%; así, nuestro umbral estadístico para sujetos individuales es 42%. Diecinueve de los 20 sujetos tuvieron desempeño clasificador significativamente mayor de probabilidades usando voxels del planum temporale, mientras que ninguno tenía rendimiento mayor de probabilidades usando voxels del polo frontal.
Por lo tanto, somos capaces de predecir con éxito a partir de patrones de actividad en la corteza auditiva que de los tres sonidos el participante estaba imaginando. No pudimos hacer esta predicción basada en patrones de actividad desde el polo frontal, sugiriendo que la información no es global en todo el cerebro.
Aplicación y resumen
MVPA es una herramienta útil para comprender cómo representa el cerebro la información. En lugar de considerar el curso del tiempo de cada voxel por separado como en un análisis tradicional de activación, esta técnica considera patrones en vóxeles muchas a la vez, ofreciendo una mayor sensibilidad en comparación con las técnicas univariantes. A menudo un análisis multivariado revela diferencias donde no es capaz de una técnica de análisis univariados. En este caso, hemos aprendido algo acerca de los mecanismos de imágenes mentales mediante el análisis del contenido de la información en un área específica del cerebro, la corteza auditiva. La naturaleza del contenido específico de estos patrones de activación sería difícil de probar con métodos univariados.
Existen beneficios adicionales que vienen de la dirección de inferencia en este tipo de análisis. En MVPA comenzamos con patrones de actividad cerebral y tratar de inferir algo sobre el estado mental del participante. Este tipo de enfoque de la "lectura cerebral" puede conducir al desarrollo de interfaces cerebro-computadora y puede permitir nuevas oportunidades para la comunicación con aquellas personas con discurso deteriorado o movimiento.
Referencias
- Kosslyn, S.M., Ganis, G. & Thompson, W.L. Neural foundations of imagery. Nat Rev Neurosci 2, 635-642 (2001).
- Haynes, J.D. & Rees, G. Decoding mental states from brain activity in humans. Nat Rev Neurosci 7, 523-534 (2006).
- Norman, K.A., Polyn, S.M., Detre, G.J. & Haxby, J.V. Beyond mind-reading: multi-voxel pattern analysis of fMRI data. Trends Cogn Sci 10, 424-430 (2006).
- Meyer, K., et al. Predicting visual stimuli on the basis of activity in auditory cortices. Nat Neurosci 13, 667-668 (2010).
Saltar a...
Vídeos de esta colección:

Now Playing
Descodificación de imágenes auditivas con análisis Multivoxel
Neuropsychology
6.4K Vistas

El cerebro dividido
Neuropsychology
68.4K Vistas

Mapas de motor
Neuropsychology
27.5K Vistas

Perspectivas de la neuropsicología
Neuropsychology
12.0K Vistas

Toma de decisiones y la Iowa Gambling Task
Neuropsychology
32.7K Vistas

Función ejecutiva en el trastorno del espectro autista
Neuropsychology
17.8K Vistas

Amnesia Anterógrada
Neuropsychology
30.3K Vistas

Correlatos fisiológicos de reconocimiento de la emoción
Neuropsychology
16.3K Vistas

Potenciales acontecimiento-relacionados y la tarea de Oddball
Neuropsychology
27.5K Vistas

Idioma: La N400 en incongruencia semántica
Neuropsychology
19.6K Vistas

Aprendizaje y la memoria: la tarea de recordar-sabe
Neuropsychology
17.2K Vistas

Medición de las diferencias de materia gris con Morfometría basada en Voxel: el cerebro Musical
Neuropsychology
17.3K Vistas

Atención visual: fMRI Control atencional basado en la investigación del objeto
Neuropsychology
41.9K Vistas

Utilizando imágenes de Tensor de difusión en la lesión cerebral traumática
Neuropsychology
16.8K Vistas

Uso de TMS para medir la excitabilidad motora durante la observación de la acción
Neuropsychology
10.2K Vistas
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados