28.6 : Magnetic Force
In addition to the electric forces between electric charges, moving electric charges exert magnetic forces on each other. A magnetic field is created by a moving charge or a group of moving charges known as the electric current. A magnetic force is experienced by a second current or moving charge in response to this magnetic field. Fundamentally, interactions between moving electrons in the atoms of two bodies produce magnetic forces between them.
The magnetic force acting on a moving charge has four main properties. First, its magnitude is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. Secondly, the magnitude of the force is proportional to the magnitude of the field. For two identical bar magnets instead of one, the force on a moving charge particle doubles without changing its velocity and charge.
The third characteristic is that the magnetic force depends on the test charge's velocity, unlike the electric force, which remains constant whether the charge is moving or not. No magnetic force is exerted on a charged particle at rest. Fourth, the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the velocity and the magnetic field.
The magnetic force, F, on a charge, Q, moving with velocity, v, in a magnetic field, B, is
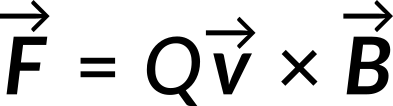
This is known as the Lorentz force law.
If the charge, Q, moves by an amount
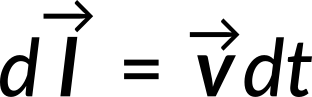
then the work done is
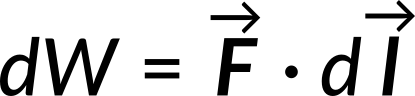
Combining the three equations leads to
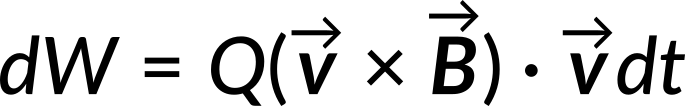
Hence the magnetic force does zero work. It can only change a test charge's direction of motion. The speed of the particle remains unaffected by the magnetic force.
Du chapitre 28:

Now Playing
28.6 : Magnetic Force
Magnetic Forces and Fields
891 Vues

28.1 : Magnétisme
Magnetic Forces and Fields
6.2K Vues

28.2 : Champs magnétiques
Magnetic Forces and Fields
5.9K Vues

28.3 : Lignes de champ magnétique
Magnetic Forces and Fields
4.0K Vues

28.4 : Flux magnétique
Magnetic Forces and Fields
3.5K Vues

28.5 : Mouvement d’une particule chargée dans un champ magnétique
Magnetic Forces and Fields
4.5K Vues

28.7 : Force magnétique sur un conducteur porteur de courant
Magnetic Forces and Fields
4.0K Vues

28.8 : Force magnétique sur les fils porteurs de courant : exemple
Magnetic Forces and Fields
1.4K Vues

28.9 : Force sur une boucle de courant dans un champ magnétique
Magnetic Forces and Fields
3.2K Vues

28.10 : Couple sur une boucle de courant dans un champ magnétique
Magnetic Forces and Fields
3.8K Vues

28.11 : L’effet Hall
Magnetic Forces and Fields
2.2K Vues

28.12 : L’expérience e/m de Thomson
Magnetic Forces and Fields
3.2K Vues