33.14 : Standing Waves in a Cavity
A household microwave and lasers are examples of standing electromagnetic waves in a cavity. When two conducting metal plates are placed parallel at the nodal planes, it creates a cavity where standing waves are formed. The cavity between the two planes is analogous to a stretched string held at the points x = 0 and x = L. Here, the distance 'L' between the two planes must be an integer multiple of half of the wavelength. The wavelengths that satisfy this condition are given by:
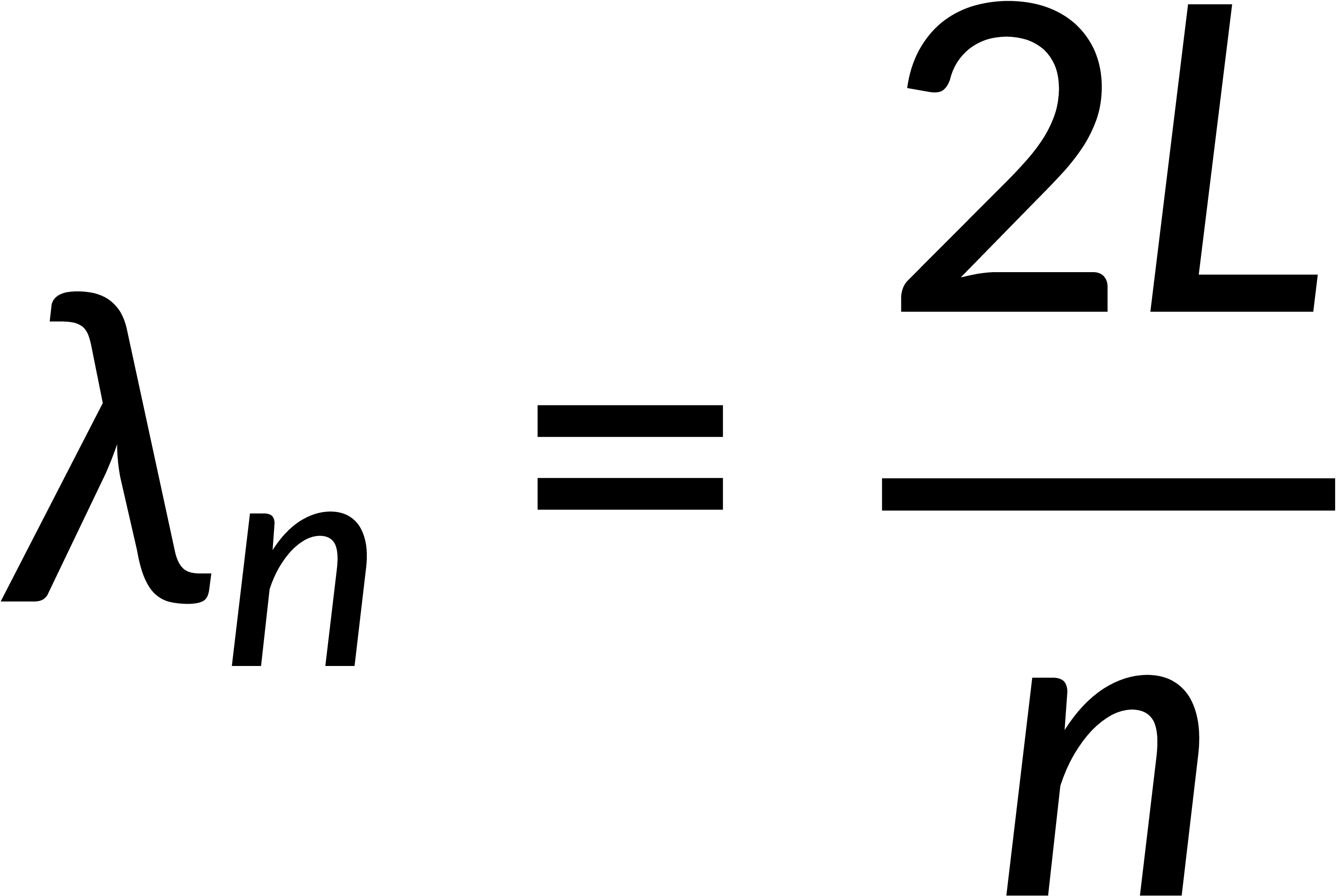
The corresponding frequencies are:

Each characteristic frequency, wave shape, and node pattern constitutes a set of normal modes. The wavelength can be estimated by measuring the node positions, and if the frequency is known, the wave speed can also be determined.
Apart from conducting surfaces, the reflection of electromagnetic waves can also occur at an interface between two insulating materials with different dielectric or magnetic properties. The mechanical analog is a junction of two strings with equal tension but different linear mass density. Typically, a wave incident on such a boundary surface is partly transmitted into the second material and partly reflected back into the first. For instance, light is transmitted through a glass window, but its surfaces also reflect the light.
Du chapitre 33:

Now Playing
33.14 : Standing Waves in a Cavity
Electromagnetic Waves
857 Vues

33.1 : Ondes électromagnétiques
Electromagnetic Waves
8.5K Vues

33.2 : Génération de rayonnements électromagnétiques
Electromagnetic Waves
2.6K Vues

33.3 : Le spectre électromagnétique
Electromagnetic Waves
15.6K Vues

33.4 : Équation des ondes électromagnétiques
Electromagnetic Waves
984 Vues

33.5 : Ondes électromagnétiques planes I
Electromagnetic Waves
3.6K Vues

33.6 : Ondes électromagnétiques planes II
Electromagnetic Waves
3.0K Vues

33.7 : Vitesse de propagation des ondes électromagnétiques
Electromagnetic Waves
3.3K Vues

33.8 : Ondes électromagnétiques dans la matière
Electromagnetic Waves
2.9K Vues

33.9 : Énergie transportée par les ondes électromagnétiques
Electromagnetic Waves
2.9K Vues

33.10 : Intensité des ondes électromagnétiques
Electromagnetic Waves
4.4K Vues

33.11 : Quantité de mouvement et pression de rayonnement
Electromagnetic Waves
1.9K Vues

33.12 : Pression de rayonnement : résolution de problèmes
Electromagnetic Waves
309 Vues

33.13 : Ondes électromagnétiques stationnaires
Electromagnetic Waves
1.4K Vues