14.3 : Gravitation Between Spherically Symmetric Masses
The gravitational potential energy between two spherically symmetric bodies can be calculated from the masses and the distance between the bodies, assuming that the center of mass is concentrated at the respective centers of the bodies.
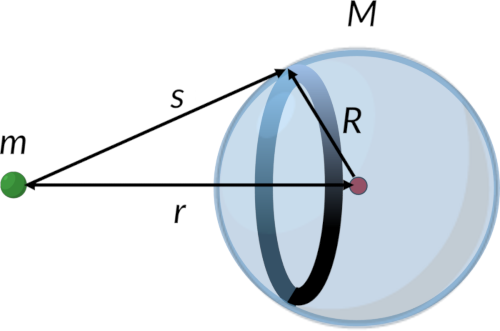
Consider that a spherically symmetric mass distribution comprises multiple concentric spherical shells. A point mass is placed at a distance 'r' from the center of mass of the spherical shell. All the particles in a given spherical ring on the surface of the shell are at equal distances from the point mass.
The potential between the point mass and the ring can be obtained from the ring's mass. Integrating the expression for the potential energy between a point mass and a ring over the limits of distance gives the gravitational potential energy, which is the same as the potential energy between two point masses.
If the point mass is inside the shell, then the limits of integration change. This shows that the potential energy does not depend on the distance and is the same everywhere for all points inside the shell. However, no work is done on the point mass if it is inside the shell.
Du chapitre 14:

Now Playing
14.3 : Gravitation Between Spherically Symmetric Masses
Gravitation
854 Vues

14.1 : Gravitation
Gravitation
6.3K Vues

14.2 : La loi universelle de la gravitation
Gravitation
12.5K Vues

14.4 : Interaction gravitationnelle entre corps sphériques
Gravitation
8.3K Vues

14.5 : Coordonnées de masse réduites : problème à deux corps isolés
Gravitation
1.2K Vues

14.6 : La pesanteur terrestre
Gravitation
10.6K Vues

14.7 : La pesanteur sur d'autres planètes
Gravitation
4.2K Vues

14.8 : Rotation de la Terre et poids apparent
Gravitation
3.5K Vues

14.9 : Variation de la pesanteur près de la surface de la terre
Gravitation
2.4K Vues

14.10 : Énergie potentielle gravitationnelle
Gravitation
5.5K Vues

14.11 : Le principe de superposition et le champ gravitationnel
Gravitation
1.3K Vues

14.12 : Vitesse de libération
Gravitation
5.6K Vues

14.13 : Orbites circulaires et vitesse critique des satellites
Gravitation
2.9K Vues

14.14 : Énergie d'un satellite en orbite circulaire
Gravitation
2.2K Vues

14.15 : La première loi de Kepler sur le mouvement des planètes
Gravitation
3.9K Vues
See More