Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
In Vitro Adhesion Assay to Detect the Adherence of Cancer Cells to Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
Dans cet article
Overview
Najmeh, S., et al. Simplified Human Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Isolation and Handling. J. Vis. Exp. (2015)
In this video, we demonstrate an assay utilizing fluorescence microscopy to detect the adhesion of cancer cells to neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). In the test wells, there is a notable increase in the number of fluorescently labeled cancer cells adhering to NETs, whereas wells treated with DNase exhibit reduced cancer cell adhesion to NETs.
Protocole
1. NET-Cancer Cell Static Adhesion Assay
- Add 100 μl of the previously obtained NET stock per well in a 96-well flat bottom plate and allow to coat wells O/N at 4 °C in the dark.
- Between 12 and 20 hr later, verify the formation of a uniform monolayer of cell-free NETs at the bottom of the wells under the microscope (Figure 1). At this point, gently aspirate all non-adherent material out of the wells, making sure not to disrupt the NET monolayer at the bottom.
- Add 100 μl of 1% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) blocking solution to each well and leave for 1 h at RT.
- Detach A549 cancer cells from a T-75 flask using 2 ml of 0.25% Trypsin solution. Once detached, add 10 ml of A549 media to trypsinized cells and centrifuge at 450 x g at 4 °C for 5 min. Discard supernatant and resuspend cells in media to obtain a concentration of 2 x104 cancer cells per 100 μl media.
NOTE: A549 cells were grown separately. Briefly, cells were cultured and maintained in DMEM F12 media containing 10% FBS and 1% Penicillin Streptomycin and incubated at 37 °C 5% CO2. Once 70 - 80% cell confluence was reached, they were detached using 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA and resuspended in the same media described above. - Stain cancer cells using CFSE by adding 1 μl of CFSE per ml of media and leaving it to stain at RT for 10 min. After staining, centrifuge down at 450 x g at 4 °C for 5 min then discard supernatant and resuspend cells in the initial volume of media to obtain a concentration of 2 x104 cancer cells per 100 μl media.
- After 1 hr of NETs blocking, gently aspirate the blocking solution and add 2 x104 cancer cells in media, which is equivalent to 100 μl, per well over the NET monolayer and allow it to adhere for 90 min at 37 °C 5% CO2. Gently aspirate the cells and add 100 μl of PBS to each well to wash any non-adherent cells.
- In some wells, add 1000U of DNAse I per well for 10 min before washing to degrade NETs. This will serve as a negative control. In other wells, add 100 μl of sterile water per well for 10 min, which will serve as the vehicle control (VC).
NOTE: 3 replicates per condition are usually performed to increase sample size. - Aspirate and discard all solutions in the wells leaving only NETs and adherent cancer cells at the bottom. Add 100 μl of 4% formaldehyde solution per well to fix adherent cancer cells to NETS and read the assay under the fluorescence microscope (Figure 1). Plot and analyze the results (Figure 2).
Résultats
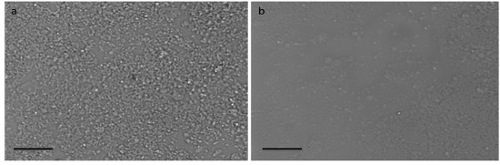
Figure 1. NET Monolayer. Light microscopy images of the 96-well plate wells coated with NETs show (A) a uniform monolayer of NETs throughout the well as opposed to (B) inadequate coating of the well with an interrupted layer of NETs. Scale bars represent 40 μm.
Déclarations de divulgation
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Dulbecco's Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS), Modified, without calcium chloride and magnesium chloride | Wisent | 311-425-CL | |
| RPMI-1640 Medium with L-glutamine | Wisent | 350-000-CL | 3% RPMI solution is made by supplementing RPMI with 3% Fetal Bovine serum |
| BD Pharm Lyse Lysing buffer | BD Biosciences | 555899 | |
| DNAse1 | Roche | 11284932001 | |
| F12 DMEM | Wisent | 319-075-CL | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Wisent | 080-150 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | |
| CFSE | Invitrogen | C1157 | |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | Gibco | 25200-056 |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon