11.17 : מוצקים מתכתיים
Metallic solids such as crystals of copper, aluminum, and iron are formed by metal atoms. The structure of metallic crystals is often described as a uniform distribution of atomic nuclei within a “sea” of delocalized electrons. The atoms within such a metallic solid are held together by a unique force known as metallic bonding that gives rise to many useful and varied bulk properties.
All metallic solids exhibit high thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic luster, and malleability. Many are very hard and quite strong. Because of their malleability (the ability to deform under pressure or hammering), they do not shatter and, therefore, make useful construction materials. The melting points of the metals vary widely. Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C. Several post-transition metals also have low melting points, whereas the transition metals melt at temperatures above 1000 °C. These differences reflect differences in the strengths of metallic bonding among metals.
Properties of Metallic Solids
Owing to their crystalline structure, metallic solids exhibit few unique properties associated with the structure and have been tabulated in the following table.
| Type of Solid | Type of Particles | Type of Attractions | Properties | Examples |
| Metallic | Atoms of electropositive elements | Metallic bonds | shiny, malleable, ductile, conducts heat and electricity well, variable hardness and melting temperature | Cu, Fe, Ti, Pb, U |
Crystal Structure of Metallic Solids: Close-packing
Solids that are made of identical atoms can have two types of arrangements: square or close-packed (Figure 1). Since close-packing maximizes the overall attractions between atoms and minimizes the total intermolecular energy, the atoms in most metals pack in this manner.

Figure 1. Square vs close-packed arrangement.
We find two types of closest packing in simple metallic crystalline structures: hexagonal closest packing (HCP), and cubic closest packing (CCP). Both consist of repeating layers of hexagonally arranged atoms. In both types, a second layer (B) is placed on the first layer (A) so that each atom in the second layer is in contact with three atoms in the first layer. The third layer is positioned in one of two ways.
In HCP, atoms in the third layer are directly above atoms in the first layer (i.e., the third layer is also a type A), and the stacking consists of alternating type A and type B close-packed layers (i.e., ABABAB⋯) (Figure 2a).
In CCP, atoms in the third layer are not above atoms in either of the first two layers (i.e., the third layer is type C), and the stacking consists of alternating type A, type B, and type C close-packed layers (i.e., ABCABCABC⋯) (Figure 2b). Cubic face-centered (FCC) and CCP arrangements are actually the same structures with compact packing of atoms, occupying 74% of the volume.
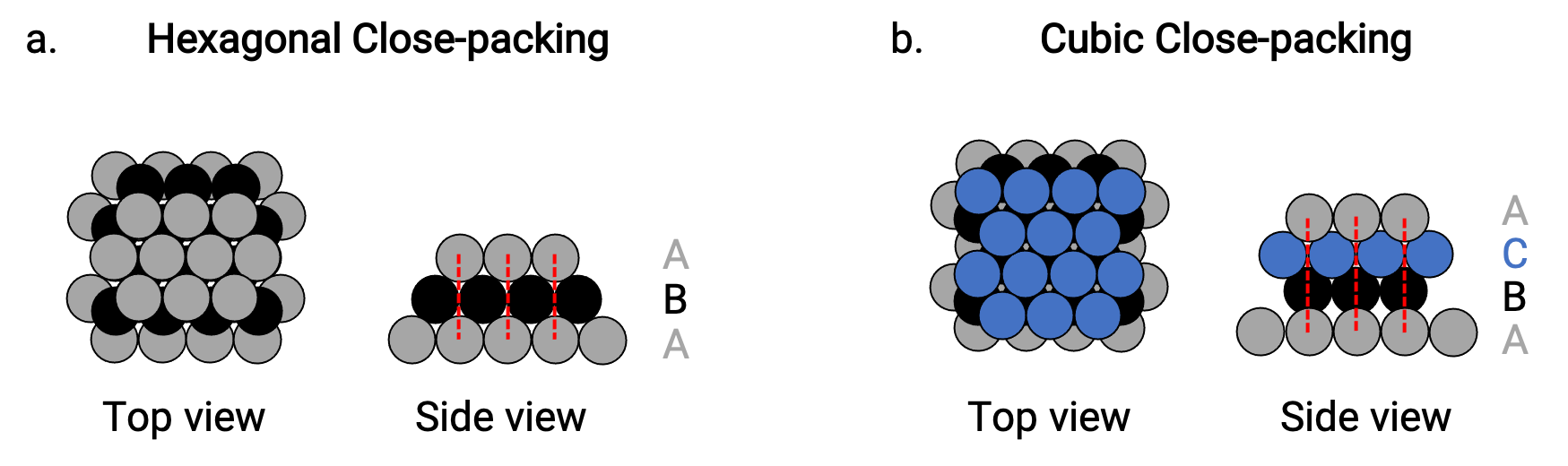
Figure 2. (a) Hexagonal close-packing consists of two alternating layers (ABABAB…). (b) Cubic close-packing consists of three alternating layers (ABCABCABC…).
In bothtypes of packing, each atom contacts six atoms in its own layer, three in the layer above, and three in the layer below. Thus each atom touches 12 near neighbors and therefore has a coordination number of 12.
About two–thirds of all metals crystallize in closest-packed arrays with coordination numbers of 12. Metals that crystallize in an HCP structure include Cd, Co, Li, Mg, Na, and Zn, and metals that crystallize in a CCP structure include Ag, Al, Ca, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Pt.
This text has been adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Sections 10.5 The Solid State of Matter, and 10.6 Lattice Structures in Crystalline Solids.
Tags
From Chapter 11:

Now Playing
11.17 : מוצקים מתכתיים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
18.2K Views

11.1 : השוואה מולקולרית של גזים, נוזלים ומוצקים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
40.5K Views

11.2 : כוחות בין מולקולריים לעומת תוך מולקולריים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
86.5K Views

11.3 : כוחות בין מולקולריים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
57.7K Views

11.4 : השוואת כוחות בין מולקולריים: נקודת התכה, נקודת רתיחה ומסיסות
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
43.8K Views

11.5 : מתח פנים, פעילות קפילרית וצמיגות
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
27.5K Views

11.6 : מעברי פאזה
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
18.8K Views

11.7 : מעברי פאזה: אידוי ועיביוי
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
17.2K Views

11.8 : לחץ אדים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
34.3K Views

11.9 : משוואת קלאוזיוס- קלפרון
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
55.9K Views

11.10 : מעברי פאזה: התכה וקיפאון
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
12.3K Views

11.11 : מעברי פאזה: המראה וריבוץ
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.7K Views

11.12 : עקומות חימום וקירור
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
22.5K Views

11.13 : דיאגרמת פאזות
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
39.7K Views

11.14 : מבנים של מוצקים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
14.0K Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved