È necessario avere un abbonamento a JoVE per visualizzare questo. Accedi o inizia la tua prova gratuita.
Multimer-PAGE for Separating Native Protein Complexes: A Hybrid Separation Technique Consisting of Blue Native-PAGE and SDS-PAGE to Separate Intact Multimeric Proteins From Tissue Lysate
In questo articolo
Overview
This video describes multimeric PAGE for separating native protein complexes from tissue homogenates. The technique is a hybrid of blue native-PAGE and SDS-PAGE techniques. The separated complexes can be characterized and studied for their role in cell functioning.
Protocollo
1. Tissue Preparation
- Prepare 10 mL of 4x BN-PAGE sample buffer (200 mM Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino-tris(hydroxymethyl)methane (Bis-Tris), 200 mM NaCl, 40% w/v glycerol, 0.004% Ponceau S, pH 7.2).
NOTE: This stock solution may be made in advance and stored at 4 °C. - Dilute 250 μL of 4x sample buffer in 750 μL dH2O containing 1x commercial protease inhibitor cocktail. Vortex and chill on ice.
- Homogenize 20 mg of target tissue in the 1 mL 1x ice-cold BN-PAGE sample buffer with 30 strokes of a clean dounce homogenizer.
NOTE: For this demonstration experiment, the target tissue is whole rat brain tissue. After homogenization, samples may be treated with a mild detergent such as 2% digitonin to solubilize and permit the electrophoresis of membrane proteins. - Transfer the homogenate to a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 14,000 x g for 30 min to pellet insoluble cellular contents. After centrifugation, decant the supernatant into a clean tube on ice.
- Follow manufacturer instructions to measure supernatant protein concentration using bicinchoninic acid (BCA) or similar protein quantitation assay.
- If the homogenate sample(s) contain detergent, add a quantity of 5% Coomassie Blue G-250 in an aqueous solution sufficient to bring the homogenate solution to 0.25% Coomassie.
2. BN-PAGE
- Dilute 25 mL 20x blue native (BN) electrophoresis buffer stock (1.0 M Bis-Tris, 1.0 M tricine, pH 6.8) into 475 mL dH2O containing 0.002% Coomassie Blue to make 500 mL of 1x running buffer.
- If samples contain detergent, instead make 250 mL of 1x running buffer containing 0.02% Coomassie and another 250 mL containing none.
- Chill buffer(s) to 4 °C.
- Clean and assemble a polyacrylamide gel pouring cassette according to manufacturer instructions.
- Pour BN polyacrylamide gel (3% T stacking layer, 6% T resolving layer) according to a standard recipe and place the well comb.
- After the gels have polymerized, rinse the cassette with dH2O and assemble the electrophoresis apparatus according to manufacturer instructions.
- Remove the well comb and fill the wells with 1x BN-PAGE running buffer. Avoid filling the entire inner chamber with buffer until samples are loaded.
- If samples contain detergent, fill the wells with the buffer containing 0.02% Coomassie Blue.
NOTE: Perform steps 2.7-2.9 at 4 °C.
- If samples contain detergent, fill the wells with the buffer containing 0.02% Coomassie Blue.
- Using gel-loading tips, pipette a volume of homogenate containing 20 μg of protein into the desired wells. Pipette an equivalent volume of 1x BN-PAGE sample buffer into any unused wells.
NOTE: Use the protein concentration determined from the BCA assay to calculate the appropriate volume of the homogenate to add to the wells. - After samples are loaded, fill the inner chamber with 1x BN-PAGE running buffer. Be sure the gel is entirely submerged in buffer. Next, fill the outer chamber with 1x running buffer to the level indicated by the manufacturer.
- If samples contain detergent, fill the inner chamber with the 1x buffer containing 0.02% Coomassie Blue, and the outer chamber with dye-free 1x running buffer.
- Connect the electrodes to the power supply and electrophorese the proteins in the gel at 150 V until the dye band progresses ~2 cm into the resolving layer. Stop and disconnect the power supply.
3. Cross-linking
NOTE: Perform Steps 3.1-3.6 at 4 °C.
- Disassemble the electrophoresis apparatus and separate the glass panes of the gel cassette. Remove and discard the stacking layer.
- Carefully cut the gel just below the bottom edge of the dye front. Take care to make this cut as smooth and straight as possible, and then discard the unused piece of gel. This will leave a ~2 cm wide, horizontal strip of polyacrylamide gel, which will contain all the protein in the homogenate sample.
- Trim away any unused portions along the edges of the gel strip.
- Carefully place the strip into 10 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS) in a small container, and gently mix by nutation for 30 min to equilibrate.
- After equilibration, discard and replace the PBS with another 10 mL. Pipette 500 μL of 25 mM DSP dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide into the PBS, and continue mixing as above (step 3.4) for 30 min.
- Pour off the DSP solution. Add 10 mL of 0.375 M tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride (Tris-HCl), pH 8.8, containing 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) to quench the unreacted DSP. Continue nutation for 15 min.
4. SDS-PAGE
- While the gel strip is quenching, prepare SDS-PAGE gel solutions according to standard methods. Do not add polymerization reagents.
- After quenching, return the ΒΝ gel strip to room temperature, and cast the strip into a new gel cassette.
- To do this, carefully pick up the gel and place it onto a clean gel cassette spacer plate.
- Orient the strip so the bottom of the dye front is nearest to the top of a new cassette (i.e., the side that travelled furthest during BN-PAGE should be closest to the top of the new cassette; the gel strip should be flipped from its prior orientation). See Figure 1.
- Place the strip such that its top edge lies even with where the top edge of the cover plate will be (i.e., it will be at the top of the new gel). Make sure the dye front is parallel to the horizontal edges of the glass plate.
- Push one side of the excised strip against one of the spacer walls, leaving room on the other side for the gel to be poured and a protein standard or ladder to be loaded.
- If the bottom edge of the gel strip contains any jagged or uneven areas, carefully cut them away. If present, they will trap bubbles during gel pouring.
- Once the gel strip is positioned correctly, lay the cover plate over the spacer plate. Apply gentle pressure to push out any trapped air bubbles.
- Continue to assemble the gel-pouring apparatus according to manufacturer instructions.
- Add polymerization reagents to the resolving gel buffer, and pour it into the prepared gel cassette, using a serological pipette. Fill the gel cassette to ~2 cm below the excised BN-PAGE gel strip, to leave room for the stacking layer.
- Add 100 μL butanol over the top of the poured gel and allow 30 min for polymerization of the resolving layer. Pour off the butanol.
- Add polymerization reagents to the stacking gel solution. Using a serological pipette, pour the stacking layer to fill all remaining empty space in the gel cassette.
- Tilt the gel cassette as the stacking layer is poured so it fills the space below the gel strip, and air bubbles are not trapped.
- As the stacking gel buffer fills the empty space below the gel strip, gradually return the gel cassette to level footing.
- Continue to fill the empty space next to the excised gel strip with the stacking gel buffer, until it nearly overflows.
- Allow the stacking layer to polymerize for 30 min.
NOTE: Make 10x SDS-PAGE running buffer (250 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (tris), 1.9 M glycine, 1% SDS) while the gel is polymerizing. This can also be made beforehand and stored at room temperature. - Dilute 50 mL 10x SDS-PAGE running buffer stock into 450 mL dH2O to make 1x working buffer.
- After the stacking layer has polymerized, remove the gel cassette from the pouring apparatus, rinse with dH2O, and assemble the electrophoresis apparatus according to manufacturer instructions.
- Fill the inner chamber completely with 1x SDS-PAGE running buffer, then fill the outer chamber to the level indicated by the manufacturer.
- Load the space next to the excised gel strip with a molecular weight ladder or appropriate protein standard.
- Attach the electrodes to the power supply, and electrophorese the samples at 120 V. When the Coomassie dye runs off the gel, stop and disconnect the power supply.
- Analyze the gel using standard methods of electroblotting and protein detection by antibody binding.
Risultati
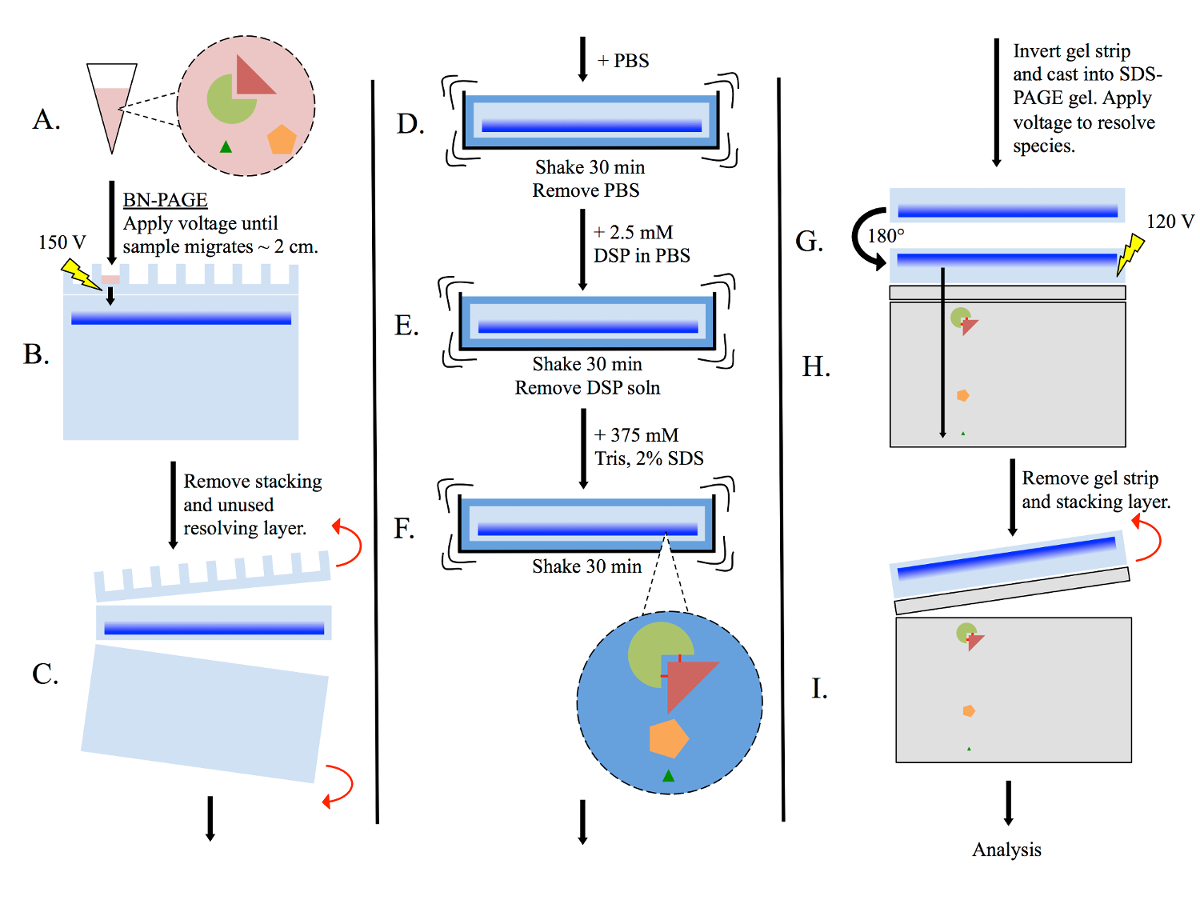
Figure 1: General multimer-PAGE flowchart.
(A) Prepare tissue lysate using non-denaturing methods, such as homogenizing in BN-PAGE sample buffer. (B) Pipette lysate into BN-PAGE gel, then perform electrophoresis (150 volts) in BN-PAGE running buffer. Allow sam...
Divulgazioni
Materiali
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Chemicals | |||
| ε-Aminocaproic acid | Sigma | A2504 | |
| Acrylamide | Acros Organics | 164855000 | Toxic. |
| Acrylamide/bisacrilamide 37.5:1 (40%T stock solution) | BioRad | 161-0148 | Toxic. |
| Ammonium persulfate | Sigma | A3678 | |
| Anti rabbit IgG-HRP from goat | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2004 | |
| Bicinchoninic acid assay kit | Thermofisher | 23225 | |
| Bis-tris | Sigma | B9754 | |
| Bovine serum albumin | Sigma | A9647 | |
| Butanol | Fisher Scientific | A399-1 | |
| Chemiluminescence substrate kit | ThermoFisher | 24078 | |
| Coomassie blue G-250 | Sigma-Aldrich | B0770 | |
| Digitonin | Sigma | D141 | Toxic. |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | Fisher Scientific | D128-1 | |
| Dithiobis(succinimidylpropionate) | Thermo Scientific | 22585 | |
| Dry nonfat milk | LabScientific | M0841 | |
| Glycerol | Sigma | G9012 | |
| Glycine | Fisher Scientific | BP381-5 | |
| Halt Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Thermofisher | 78430 | |
| Hydrochloric acid | Fisher Scientific | A144SI-212 | For titration. Caustic. |
| Methanol | Fisher Scientific | A412-4 | For PVDF membrane activation. Toxic. |
| Monoclonal anti α-synuclein IgG from rabbit | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-7011-R | |
| N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine | Sigma | T9281 | |
| N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide | Acros Organics | 16479 | Toxic. |
| NP40 | Boston Bioproducts | P-872 | |
| Polysorbate 20 (tween-20) | Fisher Scientific | BP337-500 | |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride transfer membranes | Thermo Scientific | 88518 | |
| Ponceau S | Sigma | P3504 | |
| Potassium chloride | Fisher Scientific | P217-3 | |
| Potassium phosphate monobasic | Sigma | P9791 | |
| Protease inhibitor cocktail | Thermo Scientific | 88265 | |
| SDS solution (10% w/v) | BioRad | 161-0416 | |
| Sodium chloride | Fisher Scientific | BP358-212 | |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | Sigma | L37771 | |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic | Fisher Scientific | BP329-1 | |
| Tricine | Sigma | T0377 | |
| Tris base | Fisher Scientific | BP152-500 | |
| Tris-HCl (0.5 M buffer, pH 6.8) | BioRad | 161-0799 | |
| Tris-HCl (1.5 M buffer, pH 8.8) | BioRad | 161-0798 | |
| Instruments | |||
| GE Imagequant LAS 4000 | GE Healthcare | 28-9558-10 | |
| ImageJ software NIH | |||
| Synergy H1 microplate reader | BioTek | ||
| Gel Former + Stand | Biorad | ||
| Microfuge 22R centrifuge | Beckman Coulter | ||
| 2 mL dounce homogenizer | |||
| Vortex mixer | Fisher Scientific | ||
| Ultrasonic tissue homogenizer | Fisher Scientific | FB120220 |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Rhinesmith, T. et al., Multimer-PAGE: A Method for Capturing and Resolving Protein Complexes in Biological Samples. J. Vis. Exp. (2017).