このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Harvesting Articular Cartilage From Joints of an Equine Donor: A Surgical Procedure to Isolate Vascular Connective Tissue From Cadaveric Joints of an Equine Donor
Overview
In this video, we demonstrate the extraction of articular cartilage from an equine cadaveric joint. The isolated articular cartilage can be used for further downstream analysis.
プロトコル
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board
1. Harvesting of Articular Cartilage from Donor (Cadaveric) Joints
- Ahead of the harvesting step, prepare 1 L of cartilage washing solution, consisting of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), supplemented with 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 1% (v/v) Amphotericin B.
- Wear gloves and a lab coat during the entire harvesting procedure, since the donor can carry pathogens.
- Obtain an intact (cadaveric) joint for cartilage isolation.
NOTE: At this point, the skin around the joint is still intact. Equine stifle cartilage obtained from horse was used in this protocol, but other joints from other species can also be used. - Remove the skin that is located around the joint area of interest by using a scalpel and a surgical tweezer. In addition, remove excessive fat and muscle tissue, if necessary, without damaging the underlying joint. Optionally, transfer the prepared cadaver to a biological safety cabinet.
- To perform an arthrotomy, i.e., a separation of the joint, first define the location where the joint articulates by performing extension and flexion of the joint.
- Carefully remove more layers of fat, muscles, and tendons with a scalpel and surgical tweezer to open up the joint area.
- Make an incision to reach the joint cavity.
NOTE: The joint cavity is filled with synovial fluid, which can drip from the cavity when performing a correct incision. - Continue to open up the joint completely by cutting through the tendons that keep the joint together.
- Inspect the cartilage for any macroscopic damage.
NOTE: If the articular cartilage does not have a glossy and smooth appearance or if evident blistering, clefts, or defects are present, discard the cartilage. - Use a sterile scalpel to remove the cartilage from the subchondral bone. Cut all the way down to the subchondral bone to also remove the deep zone of the cartilage (Figure 1). To prevent the cartilage from drying out, regularly drip cartilage washing solution on the cartilage.
NOTE: At this time, the size of the cartilage slices does not matter. - Collect the cartilage slices in 50 mL tubes containing previously prepared cartilage washing solution (Figure 2A).
- After collecting the cartilage from all the areas of interest, snap freeze the cartilage slices in liquid nitrogen for 5 min.
- Transfer the cartilage slices into 50 mL tubes and immediately lyophilize the cartilage slices for 24 h in a freeze dryer. Set the freeze dryer at approximately 0.090 mbar while the ice condenser is -51 °C (Figure 2B).
- Store the cartilage slices in a dry place at room temperature until further use.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
結果
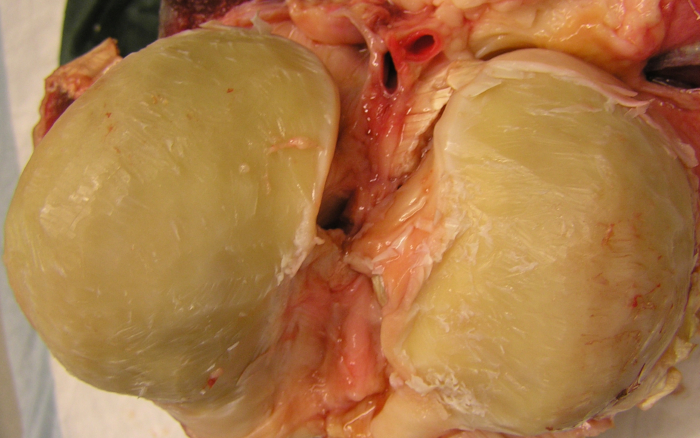
Figure 1: Equine knee after removing full-thickness cartilage. The cartilage is removed from the condyles using a scalpel until the calcified cartilage layer that cannot be cut using a scalpel is reached.
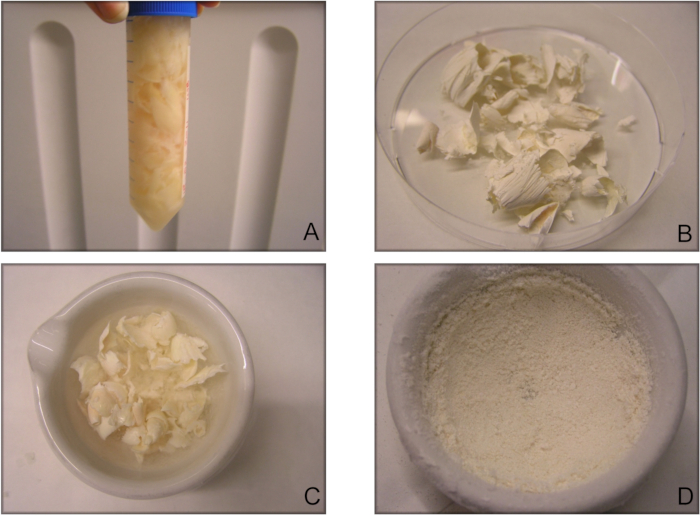

Figure 2: Sequential steps in creating decellularized cartilage-derived matrix particles. (A) Cartilage slices that have been removed from the condyles are washed in an antibiotic-infused solution. (B) Cartilage slices are lyophilized, and now have a white and paper-like appearance. (C) Snap-freezing of the lyophilized cartilage is performed right before (D) pulverizing cartilage particles by hand-milling using a mortar and pestle. Step D can also be done with automatic milling.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
開示事項
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Cadaveric joint | This can be obtained as rest material from the local butcher or veterinary center. | ||
| Sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | |||
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140 | |
| Amphotericin B | Thermo Fischer Scientific | 15290026 | |
| Liquid nitrogen | |||
| Freeze-dryer | SALMENKIPP | ALPHA 1-2 LD plus | |
| Centrifuge (for 50 mL tubes) | Eppendorf | 5810R | |
| Scalpel | |||
| Scalpel holder | |||
| Small laddle |
参考文献
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Benders, K. E. M. et al. Fabrication of Decellularized Cartilage-derived Matrix Scaffolds. J. Vis. Exp. (2019)
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved