Nucleophilic Substitution
Overzicht
Source: Vy M. Dong and Daniel Kim, Department of Chemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are among the most fundamental topics covered in organic chemistry. A nucleophilic substitution reaction is one where a nucleophile (electron-rich Lewis base) replaces a leaving group from a carbon atom.
SN1 (S = Substitution, N = Nucleophilic, 1 = first-order kinetics)
SN2 (S = Substitution, N = Nucleophilic, 2 = second-order kinetics)
This video will help to visualize the subtle differences between an SN1 and SN2 reaction and what factors help to speed up each type of nucleophilic substitution reaction. The first section will focus on reactions that will help to better understand and learn about nucleophilic substitution reactions. The second section will focus on a real-world example of a substitution reaction.
Procedure
Part 1: Studying SN1 Reactions
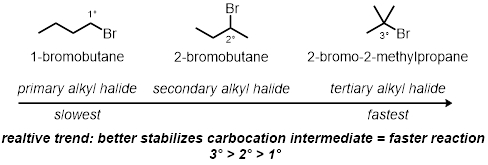
Alkyl Halide Structure:
- Measure 2 mL of a 0.1 M solution of silver nitrate in absolute ethanol into each of the three test tubes.
- Add 2 drops of 1-bromobutane into the first test tube. Add 2 drops of 2-bromobutane into the second test tube.
- Add 2 drops of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane into the final, third test tube.
- Stopper and shake each test tube.
- Note the time at which the first signs of cloudiness or pre
Resultaten
Toepassing en samenvatting
These experiments are designed to quickly show trends in nucleophilic substitution reactions. Experimentally testing these trends helps to better understand the subtle differences between an SN1 and SN2 reaction. Chemists have learned to develop and optimize reaction conditions. It all stems from first understanding the reaction: what speeds up or slows down a reaction and how can we take advantage of it? Choosing the best solvent, temperature, or concentration of reagents can greatly affect how fas
Ga naar...
Video's uit deze collectie:

Now Playing
Nucleophilic Substitution
Organic Chemistry II
99.6K weergaven

Cleaning Glassware
Organic Chemistry II
123.9K weergaven

Reducing Agents
Organic Chemistry II
43.2K weergaven

Grignard Reaction
Organic Chemistry II
149.3K weergaven

n-Butyllithium Titration
Organic Chemistry II
48.1K weergaven

Dean-Stark Trap
Organic Chemistry II
100.7K weergaven

Ozonolysis of Alkenes
Organic Chemistry II
67.2K weergaven

Organocatalysis
Organic Chemistry II
17.0K weergaven

Palladium-Catalyzed Cross Coupling
Organic Chemistry II
34.7K weergaven

Solid Phase Synthesis
Organic Chemistry II
41.3K weergaven

Hydrogenation
Organic Chemistry II
49.7K weergaven

Polymerization
Organic Chemistry II
94.9K weergaven

Melting Point
Organic Chemistry II
150.1K weergaven

Infrared Spectroscopy
Organic Chemistry II
216.2K weergaven

Polarimeter
Organic Chemistry II
100.3K weergaven