Enzyme kinetics studies the rates of biochemical reactions. Scientists monitor the reaction rates for a particular enzymatic reaction at various substrate concentrations. Additional trials with inhibitors or other molecules that affect the reaction rate may also be performed.
The experimenter can then plot the initial reaction rate or velocity (Vo) of a given trial against the substrate concentration ([S]) to obtain a graph of the reaction properties. For many enzymatic reactions involving a single substrate, this data fits the Michaelis-Menten equation, an equation derived by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten.
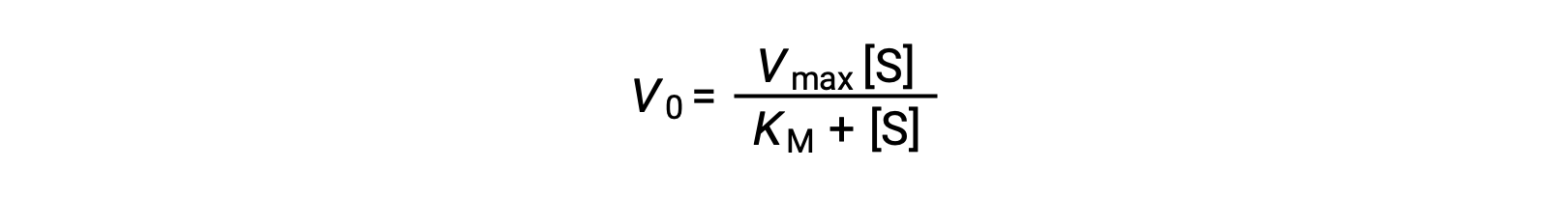
The equation estimates the maximum velocity (Vmax) and the Michaelis constant (KM) for the enzyme being studied and is based on the following assumptions:
- No product is present at the start of the reaction.
- The rate of enzyme-substrate complex formation equals the rate of dissociation and breakdown into products.
- The enzyme concentration is minimal compared to the substrate concentration.
- Only the initial reaction rates are measured.
- The enzyme is present either in the free form or in the enzyme-substrate complex.
Different rearrangements of the Michaelis-Menten equation, such as the Lineweaver-Burke, Eadie-Hofsteot, and Hanes-Woolf plots, are alternate ways to graph kinetic parameters. The Lineweaver-Burke or double reciprocal plot is often used to estimate the KM and the Vmax. The plot uses the reciprocals values of the x and y-axis from the Michaelis-Menten plot. Mathematically, the y-intercept equals 1/Vmax, and the x-intercept equals −1/KM.
The Lineweaver-Burke plot can be used to visually differentiate between inhibitor types – competitive, non-competitive, and uncompetitive. Different rearrangements of the Michaelis-Menten equation, such as the Eadie-Hofstee and Hanes-Woolf plots, are also used to determine kinetic parameters.
Z rozdziału 3:

Now Playing
3.13 : Introduction to Enzyme Kinetics
Energy and Catalysis
19.5K Wyświetleń

3.1 : Pierwsza zasada termodynamiki
Energy and Catalysis
5.3K Wyświetleń

3.2 : Druga zasada termodynamiki
Energy and Catalysis
5.0K Wyświetleń

3.3 : Entalpia w komórce
Energy and Catalysis
5.7K Wyświetleń

3.4 : Entropia w komórce
Energy and Catalysis
10.2K Wyświetleń

3.5 : Wprowadzenie do darmowej energii
Energy and Catalysis
8.0K Wyświetleń

3.6 : Reakcje endergoniczne i egzergoniczne w komórce
Energy and Catalysis
14.4K Wyświetleń

3.7 : Stała wiązania równowagi i siła wiązania
Energy and Catalysis
9.0K Wyświetleń

3.8 : Darmowa energia i równowaga
Energy and Catalysis
6.0K Wyświetleń

3.9 : Nierównowaga w komórce
Energy and Catalysis
4.1K Wyświetleń

3.10 : Utlenianie i redukcja cząsteczek organicznych
Energy and Catalysis
5.9K Wyświetleń

3.11 : Wprowadzenie do enzymów
Energy and Catalysis
16.8K Wyświetleń

3.12 : Enzymy i energia aktywacji
Energy and Catalysis
11.4K Wyświetleń

3.14 : Liczba obrotów i wydajność katalityczna
Energy and Catalysis
9.7K Wyświetleń

3.15 : Katalitycznie doskonałe enzymy
Energy and Catalysis
3.8K Wyświetleń
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone