Method Article
Profiling Changes in Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Phosphorylation using Antibody Arrays - ADVERTISEMENT
Podsumowanie
Proteome Profiler antibody arrays are a convenient and cost efficient way to screen for changes in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) phosphorylation without performing numerous immunoprecipitation (IP) Westerns. The ARY001 Human RTK array allows for the qualitative measurement of multiple RTKs in a single sample using chemiluminescence detection.
Streszczenie
The dysregulation of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) expression and phosphorylation is frequently associated with the development and metastatic spread of cancerous cells.1-3 Significant effort has been focused on developing inhibitors to target specific RTKs and interrupt the aberrant signaling pathways associated with disease states.4-7 The purpose of this study was to measure the effects of a select number of inhibitors on RTK phosphorylation. This study used the Human Phospho-RTK array, which is a membrane based sandwich immunoassay to monitor increases or decreases in phosphorylation for numerous RTKs simultaneously in a single sample. In this assay, both phosphorylated and unphosphorylated RTKs present in a lysate sample are captured by discrete antibodies printed in duplicate across a nitrocellulose membrane the size of a microscope slide. After washing, the arrays are incubated with anti-phospho-tyrosine-horseradish peroxidase (HRP), which sandwiches with phosphorylated RTKs captured on the array. Following a second wash step, the arrays are incubated with chemiluminescent reagents. Signal generated at each array spot is proportional to the amount of phospho-protein bound by each capture antibody. In these experiments, arrays were used to measure increases in phosphorylation following ligand stimulation of either MDA-MB-453 breast cancer or KATO III gastric carcinoma cells, as well as to characterize decreases in phosphorylation associated with the treatment of cells with inhibitors selective towards ErbB or FGF R family members.
Protokół
1. Sample Preparation
- Collect lysates from untreated, ligand treated, or inhibitor and ligand treated cells following the guidelines in the Human Phospho-RTK array datasheet. The lysis buffer has been optimized for this kit. The substitution of other lysis buffers may affect the final performance of the array. To prevent proteolytic sample degradation, add 10 μg/ml Aprotinin, 10 μg/ml Leupeptin, and 10 μg/ml Pepstatin A to the volume of lysis buffer required for each cell lysate preparation fresh for each use.
- Lysate concentration should be measured using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. Sample concentration may be empirically adjusted for optimal sensitivity and low background. A range of 100-300 μg of lysate is recommended as an initial starting point.
- Freeze/thaw cycles of samples should be avoided and proper storage of lysates is required for optimal performance. Thaw frozen lysate samples on ice.
2. Array Assay
- Bring all kit components to room temperature before use. To avoid contamination, wear gloves while performing the procedures.
- Pipette 2.0 ml of Array Buffer 1 into each well of the 4-Well Multi-dish to be used. Array Buffer 1 serves as a block buffer.
- Using flat-tip tweezers, remove each membrane to be used from between the protective sheets and place in a well of the 4-Well Multi-dish. The array number should be facing upward.
- Upon contact with Array Buffer 1, the blue dye from the spots will disappear, but the capture antibodies are retained in their specific locations.
- Incubate for 1 hr on a rocking platform. Orient the tray so that each array rocks end to end in its well. The surface of the array should be completely wetted and covered by block buffer.
- While the membranes are blocking, dilute the desired quantity of cellular lysate to a final volume of 1.5 ml with Array Buffer 1.
- Aspirate Array Buffer 1 from the wells of the 4-Well Multi-dish and add diluted lysate solutions. Place the lid on the 4-Well Multi-dish.
- Incubate overnight at 2-8 °C on a rocking platform. A shorter incubation time may be used if optimal sensitivity is not required.
- Carefully remove each membrane from the 4-Well Multi-dish and place into individual plastic containers with 20 ml of 1X Wash Buffer. The 4-Well Multi-dish may not be used to complete wash steps. Rinse the 4-Well Multi-dish with deionized or distilled water and dry thoroughly.
- Wash each membrane with 1X Wash Buffer for 10 min on a rocking platform shaker. Repeat two times for a total of 3 washes.
- Dilute the anti-phospho-tyrosine-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) detection buffer in 1X Array Buffer 2 using the dilution factor on the vial label. Pipette 2.0 ml of diluted solution into each well of the 4-Well Multi-dish.
- Carefully remove each membrane from its wash container. Allow excess buffer to drain from the membrane and return the membrane to the 4-Well Multi-dish containing the diluted anti-phospho-tyrosine-HRP. Cover the wells with the lid.
- Incubate for 2 hr at room temperature on a rocking platform.
- Wash each array as described previously.
- Complete the remaining steps without interruption. Carefully remove each membrane from its wash container. Allow excess buffer to drain from the membrane by blotting the lower edge onto absorbent paper. Place each membrane on a plastic sheet protector with the identification number facing up.
- Pipette 1 ml of the prepared Chemi Reagent Mix evenly onto each membrane. Using less than 1 ml of Chemi Reagent Mix per membrane may result in incomplete membrane coverage. Substitution of some high intensity chemiluminescent reagents for Chemi Reagents 1 and 2 may cause either increased background or diminished signal depending on the reagent.
- Carefully cover with a plastic sheet protector. Gently smooth out any air bubbles and ensure Chemi Reagent Mix is spread evenly to all corners of each membrane. Incubate for 1 min.
- Position paper towels on top and sides of plastic sheet protector containing the membranes and carefully squeeze out excess Chemi Reagent Mix.
- Remove the top plastic sheet protector and carefully lay an absorbent lab wipe on top of the membranes to blot off any remaining Chemi Reagent Mix.
- Leaving membranes on the bottom plastic sheet protector, cover the membranes with plastic wrap taking care to gently smooth out any air bubbles. Wrap the excess plastic wrap around the back of the sheet protector so that the membranes and sheet protector are completely wrapped.
- Place the membranes with the identification numbers facing up, in an autoradiography film cassette that is not used with radioactive isotope detection.
- Expose to Kodak BioMax Light film for 1-10 min. Multiple exposures are recommended. Alternatively, images may be collected using a chemiluminescence compatible imager such as the Carestream Health Image Station 4000MM PRO.
3. Data Analysis
- Positive signals seen on developed film can be quickly identified by placing the transparency overlay on the array image and aligning it with the pairs of reference spots printed in the corners for this purpose. The stamped identification number on the array should be placed on the left had side. The location of controls and capture antibodies is listed in the Appendix of the Human Phospho-RTK array datasheet.
- Pixel densities on developed film can be collected using a transmission-mode scanner such as the Epson Perfection V750 PRO.
- Create a template to analyze pixel density in each spot of the array using an appropriate imaging analysis software program. Compatible programs include ImageQuant or ArrayVision software from GE, Western Vision software with templates specific to Proteome Profiler Arrays, BioRad Quantity One, Adobe Photoshop, NIH ImageJ, and Protein Simple AlphaView.
- Export signal values to a spreadsheet file for manipulation in a program such as Microsoft Excel.
- Determine the average signal (pixel density) of the pair of duplicate spots representing each RTK.
- Subtract an averaged background signal from each spot. Use a signal from a clear area of the array or negative control spots as a background value.
- Compare corresponding signals on different arrays to determine the relative change in RTK phosphorylation levels between samples.
4. Representative Results
This protocol demonstrates how the Human Phospho-RTK array may be used to screen the effects of ligand stimulation and inhibitors on RTK phosphorylation. In Figure 1, data is shown for MDA-MB-453 cells that were untreated, treated with 100 ng/ml rhNRG-β1/HRG-β1 (HRG-β1) for 5 min, or pre-treated with known ErbB family inhibitors8-11 prior to HRGβ1 treatment. For inhibitor experiments, the cells were incubated with 1 μM HDS 029, 200 nM PD 153035, or 200 nM PD 158780 in SFM for three hours. Each array was incubated with 100 μg of lysate. An increase in phosphorylation is observed for ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4 capture spots when comparing untreated cells with HRG-β1 treated MDA-MB-453 cells. The treatment of cells with all three ErbB family selective inhibitors prior to HRG-β1 incubation caused reductions in ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4 phosphorylation.
In Figure 2, data is shown for Kato III cells known to overexpress the RTK FGF R2. In this set of experiments, Kato III cells were untreated, treated with 100 ng/ml rhFGF acidic (FGF) and 1 μg/ml heparin, or pretreated with FGF R selective inhibitors12-15 prior to treatment with FGF and heparin. The inhibitors PD173074, PD 161570, and PD 166285 were used at a concentration of 1 μM and incubated with the Kato III cells for 3 hr in serum free media. While there is constitutive phosphorylation of both EGF R and FGF R2 in untreated KATO III cells, an increase in FGF R2 phosphorylation was observed upon FGF treatment. Incubating the cells with PD 173074, PD 161570, or PD 166285 resulted in decreased FGF R2 and EGF R phosphorylation. Although these inhibitors are known affect the phosphorylation of FGF R family members, these results demonstrate the utility of the Human Phospho-RTK array for monitoring the effect a specific concentration of inhibitor may have on other RTKs, such as EGF R in this case.
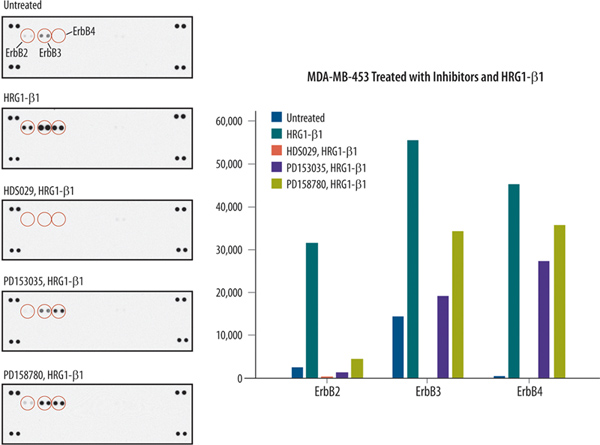
Figure 1. Induction and inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. Array images from Proteome Profiler Human Phospho-RTK arrays and the corresponding histogram profiles are shown. MDA-MB-453 cells were untreated or treated with RTK inhibitors followed by treatment with NRG-β1/HRG-β1. The array was used to monitor the effects of inhibitors on kinase phosphorylation in MDA-MB-453 cells. Click here to view larger figure.

Figure 2. Induction and inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in gastric cancer cells. Array images from a Proteome Profiler Human Phospho-RTK array and the corresponding histogram profiles are shown. Kato III cells were untreated or treated with RTK inhibitors followed by treatment with FGF acidic and heparin. Click here to view larger figure.
References
- Henriksson, M.L., Edin, S., Dahlin, A.M., Oldenborg, P.A., Oberg, A., Van Guelpen, B., Rutegard, J., Stenling, R., & Palmqvist, R. Colorectal cancer cells activate adjacent fibroblasts resulting in FGF1/FGFR3 signaling and increased invasion. Am. J. Pathol. 178, 1387-1394 (2011).
- Morishita, A., Gong, J., Nomura, T., Yoshida, H., Izuishi, K., Suzuki, Y., Kushida, Y., Haba, R., D'Armiento, J., & Masaki, T. The use of protein array to identify targetable receptor tyrosine kinases for treatment of human colon cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 37, 829-835 (2010).
- Agaram, N.P., Laquaglia, M.P., Ustun, B., Guo, T., Wong, G.C., Socci, N.D., Maki, R.G., DeMatteo, R.P., Besmer, P., & Antonescu, C. R. Molecular characterization of pediatric gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 3204-3215 (2008).
- Stommel, J.M., Kimmelman, A.C., Ying, H., Nabioullin, R., Ponugoti, A.H., Wiedemeyer, R., Stegh, A.H., Bradner, J.E., Ligon, K.L., Brennan, C., Chin, L., & DePinho, R.A. Coactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies. Science. 318, 287-290 (2007).
- Agarwal, S., Zerillo, C., Kolmakova, J., Christensen, J.G., Harris, L.N., Rimm, D.L., DiGiovanna, M.P., & Stern, D.F. Association of constitutively activated hepatocyte growth factor receptor (Met) with resistance to a dual EGFR/Her2 inhibitor in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer. 100, 941-949 (2009).
- Dewaele, B.M., Floris, G., Finalet-Ferreiro, J., Fletcher, C.D., Coindre, J.M., Guillou, L., Hogendoorn, P.C., Wozniak, A., Vanspauwen, V., Schoffski, P., Marynen, P., Vandenbergh, P., Sciot, R., & Debiec-Rychter, M. Co-activated PDGFRA and EGFR are potential therapeutic targets in intimal sarcoma. Cancer Res. 70, 7304-7314 (2010).
- Yoon, Y.K., Kim, H.P., Han, S.W., Hur, H.S., Oh, D.Y., Im, S.A., Bang, Y.J., & Kim, T.Y. Combination of EGFR and MEK1/2 inhibitor shows synergistic effects by suppressing EGFR/HER3-dependent AKT activation in human gastric cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, 2526-2536 (2009).
- Fry, D.W., Nelson, J.M., Slintak, V., Keller, P.R., Rewcastle, G.W., Denny, W.A., Zhou, H., & Bridges, A.J. Biochemical and antiproliferative properties of 4-[Ar(alk)ylamino]pyridopyrimidines, a new chemical class of potent and specific epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 54, 877-887 (1997).
- Bos, M., Mendelsohn, J., Kim, Y.M., Albanell, J., Fry, D.W., & Baselga, J. PD153035, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, prevents epidermal growth factor receptor activation and inhibits growth of cancer cells in a receptor number-dependent manner. Clin. Cancer Res. 3, 2099-2106 (1997).
- Stoll, S.W., Kansra, S., Peshick, S., Fry, D.W., Leopold, W.R., Wiesen, J.F., Sibilia, M., Zhang, T., Werb, Z., Derynck, R., Wagner, E.F., & Elder, J.T. Differential utilization and localization of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases in skin compared to normal and malignant keratinocytes. Neoplasia. 3, 339-350 (2001).
- Klutchko, S.R., Zhou, H., Winters, R.T., Tran, T.P., Bridges, A.J., Althau, I.W., Amato, D.M., Elliott, W.L., Meade, M.A., Roberts, B.J., Fry, D.W., Gonzales, A.J., Harvey, P.J., Nelson, J.M, Sherwood, V., Han, H.K., Pace, G., Smaill, J.B., Denny, W.A., & Showalter, H.D. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 19. 6-alknyamides of 4-anilinoquinazolines and 4-anilinopyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidines as irreversible inhibitors of the ErbB family of tyrosine kinase receptors. J. Med. Chem. 49, 1475-1485 (2006).
- Kunii, K., Davis, L., Gorenstein, J., Hatch, H., Yashiro, M., Di Bacco, A., Elbi, C., & Lutterbach, B. FGFR2-amplified gastric cancer cell lines require FGFR2 and Erbb3 signaling for growth and survival. Cancer Res.68, 2340-2348 (2008).
- Zhou, W., Hur, W. McDermott, U., Dutt, A., Xian, W., Ficarro, S.B., Zhang, J., Sharma, S.V., Brugge, J., Meyerson, M., Settleman, J. & Gray, N.S. A structure-guided approach to creating covalent FGFR inhibitors. Chem. Biol. 17, 285-295 (2010).
- Batley, B.L., Doherty, A.M., Hamby, J.M., Lu, G.H., Keller, P., Dahring, T.K., Hwang, O., Crickard, K., & Panek R.L. Inhibition of FGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase activity by PD 161570, a new protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Life Sci. 62 143-150 (1998).
- Panek, R.L, Lu G.H., Klutchko, S.R., Batley, B.L., Darhing, T.K., Hamby, J.M., Hallak, H., Doherty, A.M., & Keiser, J.A. In vitro pharmacological characterization of PD 166285, a new nanomolar potent and broadly active protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283, 1433-1444 (1997).
Dyskusje
The Human Phospho-RTK is an economical and fast alternative to traditional methods such as immunoprecipitation (IP) Western for screening changes in RTK phosphorylation. Using this method, the relative levels of 42 phospho-RTKs were screened simultaneously using a single sample of MDA-MB-453 or Kato III cell lysate. In addition, this array assay required 2.5 hr of hands-on time, making this method far more time-effective than performing multiple IP-Westerns. By employing a chemiluminescence detection method, no specialized equipment beyond what is typically used to collect Western data was required. Arrays are sensitive and may be used to compare changes in phosphorylation caused by both ligand and inhibitor treatment. This method also allows the evaluation of inhibitor selectivity to off-target RTKs. Positive hits may be further evaluated using a quantitative assay such as an ELISA.
To effectively employ arrays to screen for changes in phosphorylation, some key experimental guidelines should be followed. First, experiments should include appropriate control samples. For example, in these experiments the effect of inhibitors on MDA-MB-453 or Kato III lysates were measured on lysate samples prepared on the same day. Only array data that is collected within the same experiment should be analyzed to minimize variations in signal due to differences in sample handling, incubation time, pipet technique, or wash technique. Comparing signal intensities between two analytes on the same membrane is not recommended, since capture antibodies were not selected to have parallel affinities.
Podziękowania
This work was funded by R&D Systems, Inc.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Name of the reagent | Company | Catalogue number | Comments (optional) |
| Human Phospho-RTK Array Kit | R&D Sytems | ARY001 | |
| Aprotinin | Sigma | A6279 | |
| Leupeptin | Tocris | 1167 | |
| Pepstatin A | Tocris | 1190 | |
| MDA-MB-453 cells | |||
| Kato III cells | |||
| Recombinant Human NRG1-beta 1/HRG1-beta 1 EGF Domain | R&D Systems | 396-HB-050 | |
| Recombinant Human FGF acidic (aa 16-155) | R&D Systems | 232-FA-025 | |
| Heparin | Sigma | H4784 | |
| HDS 029 | Tocris | 2646 | |
| PD 153035 | Tocris | 1037 | |
| PD 158780 | Tocris | 2615 | |
| PD 173074 | Tocris | 3044 | |
| PD 161570 | Tocris | 3724 | |
| PD 166285 | Tocris | 3785 | |
| BCA assay | Pierce | 23225 | |
| Phosphate-Buffer Saline (PBS) | |||
| Pipettes and pipette tips | |||
| Gloves | |||
| Deionized or distilled water | |||
| Flat-tipped tweezers | |||
| Rocking platform shaker | |||
| Microcentrifuge | |||
| Plastic containers with the capacity to hold 50 ml | For washing arrays | ||
| Plastic transparent sheet protector | |||
| Plastic wrap | |||
| Absorbent lab wipes | |||
| Paper towels | |||
| Autoradiography cassette | |||
| Film developer | |||
| Kodak BioMax Light Film | Carestream Health | 178 8207 | |
| Film developer | |||
| Image Station 4000MM PRO | Carestream Health | Chemiluminescence imager compatible with collection of western data may be used instead of film and a film developer. | |
| Epson Perfection Scanner | Epson | V750 PRO | Flatbed scanner with transparency adaptor capable of transmission mode |
| Image Analysis Software | GE,WesternVision, BioRad, Adobe, NIH, Protein Simple, etc | ImageQuant, ArrayVision, Western Vision, Quantity One, Photoshop, ImageJ, AlphaView, or other compatible program | |
| Microsoft Excel | Microsoft | ||
| Computer capable of running image analysis software and Microsoft Excel. |
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone