5.6 : Membro de Três Forças
A rigid body subjected to three forces acting at three points is known as a three-force member. These forces must have concurrent lines of action, except for parallel forces, where the lines of action are parallel.
For example, consider a dumpster connected to a pin support at point A and a pin attached to a hydraulic cylinder at point B.
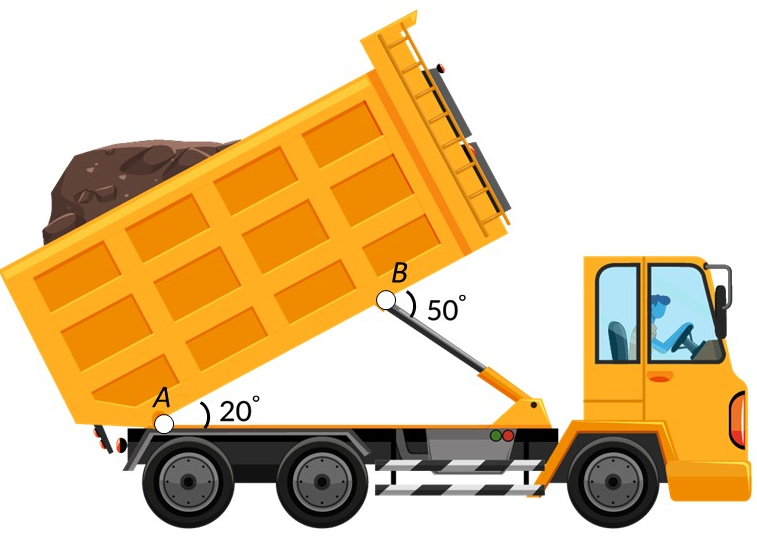
In this case, the hydraulic cylinder is a two-force member in equilibrium. The force due to the weight acts through the center of gravity and the reaction forces due to the support act at point A.
To solve for unknown forces FA and FCB, the first step involves creating a free-body diagram of the entire system, including all the forces acting on the dumpster.
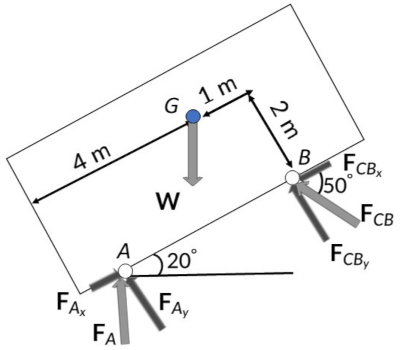
Next, the force and moment equilibrium equations can be used to determine the values of the unknown forces.
The moment equilibrium condition at point A gives the value of the force FCB as 24.08 kN. Meanwhile, the force equilibrium condition along the vertical direction determines the vertical reaction force FAy as 9.74 kN. Similarly, applying the force equilibrium condition along the horizontal direction yields the horizontal reaction force FAx as 25.74 kN.
Do Capítulo 5:

Now Playing
5.6 : Membro de Três Forças
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
931 Visualizações

5.1 : Condições de Equilíbrio
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
650 Visualizações

5.2 : Reações de Suporte
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
371 Visualizações

5.3 : Forças Internas e Centro de Gravidade
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
290 Visualizações

5.4 : Conjuntos Alternativos de Equações de Equilíbrio
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
365 Visualizações

5.5 : Membro de Duas Forças
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
846 Visualizações

5.7 : Equações de Equilíbrio em Três Dimensões
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
1.0K Visualizações

5.8 : Reações de Apoio em Três Dimensões
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
875 Visualizações

5.9 : Restrições e Determinação Estática
Equilíbrio de um Corpo Rígido
570 Visualizações
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos os direitos reservados